Ataxia in cats: what is it, treatment
Ataxia is a movement disorder characterized by disturbances in gait and coordination of movements - this symptom is included in many diseases associated with damage to the central uneven system.
The disease does not affect the cat's mental abilities, but significantly reduces life and its quality. Ataxia is a coordination disorder. As a symptom, it often accompanies diseases after damage to the central nervous system (CNS). In addition, the cat does not exhibit any chaotic movements, convulsions or paralysis. Muscle tone in the paws is either completely normal or very slightly reduced.
Ataxia can be static or dynamic. In the first case, the animal is not able to maintain balance even while standing still, and in the second, the cat is thrown from side to side, but only while moving. It is divided into 3 broad groups depending on the location of the lesion.
There are several reasons why you can directly encounter ataxia. Some can be prevented, the likelihood of others depends little on us, but we need to know about them at least in order to quickly respond if necessary:
- genetic inheritance;
- infectious diseases causing pathologies of the central nervous system and brain;
- cerebral edema;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- severe poisoning with toxins, household chemicals;
- hunger or systematic malnutrition;
- acute deficiency of B vitamins and folic acid.
Ataxia is a motor coordination disorder resulting from damage to the brain and nerves. The pathology does not affect mental characteristics, but does not allow the pet to lead a full life. The animal cannot make the simplest movements - turns, jumps, has difficulties when trying to get to the tray or feeder, and becomes completely dependent on the owner.
The following types of disease are distinguished:
- Cerebellar - occurs with traumatic damage to the medulla oblongata and cerebellum or is a congenital anomaly.
- Vestibular - occurs during pathological processes in the area of the medial ear.
- Sensitive - when the peripheral nerves responsible for sensitivity are affected.
- Spinal.
Loss of motor coordination in cats is the main symptom of ataxia. The pathology causes great discomfort to the animal, as it is expressed in a disorder of motor function due to damage to the central nervous system. Only a veterinarian can give recommendations on what to do if a cat has poor coordination of movement. If pet owners are faced with such a problem, they should immediately seek help.
The main stage in diagnosing pathology is a complete history taking. The veterinarian must determine whether the animal had injuries or whether it suffered from infectious diseases. If possible, find out information about heredity and the course of pregnancy if we are talking about pathology in a kitten.
The animal's nervous system is assessed and tests are taken to identify viral pathogens. It is recommended to do an MRI of the brain to see tumors or areas of bruising. It is necessary to examine the ears using an otoscope.
As soon as there is a suspicion that infection is occurring in the area of the brain or spinal cord, a test for leukocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid is required.
Diagnosing disease in pets
The chances of recovery and treatment methods for feline ataxia depend on the general condition of the animal and the reasons that caused the development of the pathology. The cat has the opportunity to fully recover and return to a healthy lifestyle if the owner consults a veterinarian in a timely manner.
The measures taken by veterinarians when diagnosing ataxia may be as follows:
- If the pathology is caused by a tumor, surgery is used. After its removal, the symptoms disappear.
- In case of poisoning, measures are taken to relieve intoxication. The animal is prescribed IVs, injections of vitamin B1, and diet.
If the pathology occurs against the background of brain defects, it can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. The disease cannot be cured, but in mild cases it is possible to save the kitten. This will require full-time care.
Kittens are prescribed the drug "Gamavit" to strengthen the immune system. To improve the functioning of brain tissue, Glycine is recommended at a dosage of 250 mg, 1 tablet per day. The course of admission is 14 days.
Most often, the condition stabilizes after the kitten turns one year old.
Treating a pet for poisoning
Common clinical features of vestibular disease
The most common clinical symptoms of vestibular disease include: sudden falls of the animal on a completely level place, an unexplained body roll in one direction or another, a clear and constant curvature of the neck, as well as nystagmus - a rapid and involuntary oscillatory movement of the eyeballs.
The causes of this pathology can be extremely diverse, ranging in severity from spontaneously resolving to fatal. Very often the disease develops against the background of advanced meningococcal infection; its cause can be any inflammatory disease. Also in veterinary practice, there are often cases of vestibular syndrome occurring against the background of the willful use by animal owners of certain “human” antibiotics that are toxic to cats.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyde
Diagnosis of vestibular syndrome itself is quite simple, since the diagnosis is made based on clinical signs. The difficulty lies in identifying the disease that caused it all to begin.
Your veterinarian will need a comprehensive medical history; the specialist will conduct a full examination of the pet, including neurological and otoscopic examination, which are needed to identify infectious diseases, identify inflammatory processes, and tumors. Please note that in complex or doubtful cases, MRI is strongly recommended.
From a clinical point of view, the anatomical components of the vestibular apparatus are divided functionally into peripheral and central components. The peripheral part of the vestibular apparatus is located in the inner ear (Fig. 1A) and consists of receptors, ganglion and peripheral axons of the vestibular branch of cranial nerve VIII.
Receptors of the vestibular system are located together with receptors of the auditory system in the bony and membranous labyrinth of the petrous part of the temporal bone (inner ear). The bony labyrinth is divided into three main adjacent regions: the semicircular canals, the vestibule and the cochlea. The lumen of each of these structures is filled with perilymph.
The bony labyrinth contains the membranous labyrinth, which contains 4 endolymph-filled communicating structures called the (1) semicircular canals, (2) utricle, (3) spherical sac, and (4) cochlear canal (Figure 1A). The semicircular canals are located inside the bony semicircular canals, the utricle and spherical sac are located inside the vestibule, and the cochlear canal is located in the bony cochlea.
Each of the semicircular canals is oriented at right angles to the others, that is, located in three planes. 2 At one end of each of the membranous semicircular canals there is an extension called an ampulla, and on one side of each ampulla are structures called otic ridges, each of which is lined by ciliated neuroepithelial hair cells.
Rice. 1. Schematic representation of the neuroanatomy of the peripheral (A) and central (B) components of the vestibular system. (Illustration by Terry Lawrence, Virginia-Maryland Regional Veterinary College, Department of Biomedical Illustration. Published with kind permission of the Virginia-Maryland Regional Veterinary College, Department of Biomedical Illustration.)
The ampullae and scallops, together with the terminal part of each semicircular canal, are called ampullary scallops. Neural activity in these hair cells is continuous, such that movement of the head in any direction of angular rotation results in a displacement of the fluid endolymph and a change in the tonic effect on the semicircular canals by deflecting the hair cells in the corresponding ampullary ridges.
READ My Darling CatsWhat to feed a cat so that it gains weight nutrition rulesHow and what to feed a cat so that it gains weight nutrition rules and dietWhat to feed a cat to gain weightHow to feed a cat
The dendrites of neurons in the vestibular portion of cranial nerve VIII form synapses on these hair cells, and deflection of the hair cells stimulates the vestibular neurons. Three types of crest ampullary receptors respond preferentially to acceleration, deceleration, and rotation (i.e., dynamic equilibrium) but are not activated at constant speeds.
1,2 The semicircular canals are organized in such a way that movement in the plane that activates vestibular neurons in the ampullary crests of the semicircular canals simultaneously inhibits neurons in the synergistic canal on the opposite side of the head. This paired and complementary system of innervation of the channels functions to continuously activate the corresponding muscles involved in maintaining posture in accordance with the forces of gravity after turning the head, thereby preventing abnormal posture. 4
Maculae are receptors located in the membranes of the utricle and sac (Fig. 1A). The macula of the spherical sac is oriented in a vertical plane, while the macula of the utricle is oriented in a horizontal plane. The surface of each macula is covered with neuroepithelial hair cells, the fibers of which project into the otolithic membrane covering the neuroepithelial surface of each macula.
Movement of the otolithic membrane causes deflection of the cilia of the hair cells of the macula, which creates an action potential in the dendritic zone of the vestibular neurons that form synapses in each macula. 2,3 The macular receptors of the utricle and saccule provide a continuous supply of tonic nerve impulses, the main functional effect of which is to maintain static balance (the sense of the static position of the head in relation to the forces of gravity), as well as the response to linear acceleration, involved in maintaining a normal upright posture heads and bodies. 3
The vestibular branch of cranial nerve VIII forms dendritic connections with the crests and macula, and its axons project through the internal auditory canal. The bodies of bipolar vestibular axons are located in the vestibular ganglion (Fig. 1A), located in the petrous part of the temporal bone. 5
After leaving the internal auditory canal, the axons of the vestibular apparatus project to the lateral part of the medulla, where most of them terminate in the vestibular nuclei (Fig. 1B), while a smaller part goes to the flocculonodular lobe of the cortex and the cerebellar medulla along the caudal cerebellar peduncle .
2,5 On each side of the midline, near the lateral wall of the fourth ventricle, there are four vestibular nuclei, forming the vestibular triangle. The neurons of these nuclei are interneurons that generally excite local interneurons in other parts of the central nervous system.
Diseases of the vestibular system cause balance and posture disorders of varying severity, as well as vestibular ataxia. Clinical signs may result from dysfunction of the peripheral or central component of the vestibular apparatus (Fig. 1A and B). Clinical symptoms of vestibular dysfunction usually reflect unilateral involvement, but are sometimes bilateral.
Diseases affecting the peripheral or central components of the vestibular system are accompanied by a set of basic clinical signs, often visible from the outside or easily evoked during neurological examination (Table 1).
Rice. 2. Horner's syndrome.
Peripheral vestibular disease does not affect the degree of general proprioception; thus, peripheral disease results in asymmetric ataxia and loss of balance in the apparent absence of paresis or proprioceptive impairment. With peripheral vestibular disorders, spontaneous or positional horizontal or rotational saccadic nystagmus is possible, with movements in the fast phase directed in the direction opposite to the lesion.
With all types of pathological nystagmus, the direction of movement does not change when the position of the head changes. Although this issue is controversial, it is generally accepted that vertical nystagmus in peripheral vestibular diseases occurs rarely (or not at all). 2,7 In peripheral vestibular diseases, damage to the facial nerve and postganglionic sympathetic innervation (Horner syndrome) of the head is possible. Both of these structures of the nervous system are closely connected with the inner ear and vestibular receptors.
READ Causes of umbilical hernia on the abdomen of a cat and its treatment
Sometimes there are bilateral peripheral vestibular disorders, clinically characterized by the absence of head tilt and pathological nystagmus and the absence of the vestibulo-ocular reflex due to the fact that information from the vestibular receptors ceases to arrive on both sides. Affected animals usually crouch to the ground, move hesitantly, and may fall in any direction.
Damage to the pons and medulla oblongata most often leads to regional disorders not limited to a specific nerve or nucleus. Thus, damage to the vestibular nuclei region also involves the reticular formation, including the ascending general proprioceptive (AP) and central motor neurons (CMN) of the descending pathways in the white matter, the reticular activating system (RAS) and peripheral motor neurons (PMN) of cranial nerve V -XII.
Thus, vestibular symptoms accompanied by a decreased level of consciousness (LAC), spastic hemiparesis (disorder of the descending pathway of the central nervous system), disorders of the cranial nerve V-XII, or general proprioceptive disturbances (ascending OP pathways) on the same side as the vestibular disorders , should be considered a sign of central vestibular disorder.
2,7 The presence of hemi- or tetraparesis in an animal with vestibular symptoms is the most reliable indicator of a central vestibular disorder. 2,7 In addition, spontaneous vertical nystagmus or pathological nystagmus that changes direction (eg, from horizontal to vertical with changes in head position) indicates central vestibular disease. 1.2
Diagnosis of ataxia in a cat
The most common cause of loss of coordination of movements is infectious diseases affecting the nervous system and brain. These, in most cases, include panleukopenia.
Cerebellar - often the cause of ataxia is aplasia of brain structures. This disease is congenital in nature and can arise both from a hereditary genetic predisposition and from developmental disorders in the prenatal period. Typically, sick kittens are born when the mother has panleukopenia. Also, the cause of damage to the cerebellum and the subsequent development of ataxia can be traumatic brain injury, inflammatory processes and cerebral edema.
With vestibular ataxia, there are two options for the development of the disease:
- The structure of the inner ear - the cause is its damage due to otitis media, neuritis of the craniofacial nerves, idiopathic vestibular syndrome and tumors.
- The medulla oblongata and brain stem are tumors.
Possible causes of disorders in spinal ataxia are intervertebral hernias, inflammatory diseases and spinal cord trauma.
Prerequisites can be inherited or acquired. Congenital predisposition is characteristic of cerebellar ataxia. Pathological signs appear by six months of age. However, the cerebellar variety can also be acquired.
The most likely causes of uncoordinated movements include the following:
- viral infections: with panleukopenia, kittens predisposed to ataxia are born in mature females;
- back or skull injuries;
- otitis of parasitic, allergic or infectious origin;
- poisoning
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to give an injection to a cat at home?
The main cause of impaired motor coordination in cats is infections that affect the central nervous system and brain. Most often, ataxia develops against the background of panleukopenia.
Loss of coordination is the main sign of pathology
Cerebellar ataxia in cats is a hereditary disease with a genetic predisposition or develops as a congenital form. It can appear as a result of an intrauterine developmental disorder in kittens.
Also reasons may be:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cerebral edema;
- inflammatory processes;
- damage to the inner ear due to otitis media;
- neuritis of the craniofacial nerve;
- tumors.
Veterinarians include hernias between the vertebrae and spinal cord injuries as possible causes of incoordination in cats.
Causes
There are a large number of reasons that can lead to the development of nystagmus in dogs.
. Most of them are associated with central nervous system disorders and related diseases. In some works devoted to this problem, one can find such a definition as “a disorder of the balancing system,” that is, a disruption of the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and the part of the brain responsible for maintaining proper balance of the head and body.
Also possible causes of the development of nystagmus in dogs can be, for example, hypothyroidism, traumatic injuries (for example, due to a car accident), various tumors, thiamine deficiency, viral infections (for example, carnivore distemper), and, as a result, inflammation, heart attacks, hemorrhage in the heart, exposure to poisons and toxins (for example, lead).
General symptoms
Despite the similar symptoms of all types of ataxia, there are different signs that depend on the cause of the disease.
All types of violations are characterized by:
- Staggering "drunk" gait. The cat walks with its hind legs widely spaced, raising them high.
- Changes in head position - usually it is tilted to the side or down.
When the spinal cord is damaged, pain occurs when walking, and the animal tries to move less. Very often there is no loss of coordination of the head.
Cerebellar ataxia is characterized by the presence of tremor during movement - when walking or running, the animal’s body trembles slightly, often only the back part. There may also be nystagmus, which is rapid eye movements that are independent of where the cat is looking or what the cat is observing.
If there is damage to the vestibular apparatus, then nystagmus is also observed, severe pain in the head is possible (the cat meows, sits in the corner with its forehead pressed to the wall).
In addition to individual signs of the disease, characteristic only of one of its forms, there are several general symptoms by which ataxia can be identified:
- The cat has a wobbling gait with drifts to the side.
- When walking, the paws are widely spaced; The animal seems to be constantly afraid of falling.
- Often falls while walking or running.
- Rarely holds head straight; more often - with an inclination to the side or down.
- Does not control her body: even with fairly confident walking, she is not able to jump, go down/ascend, or turn around a turn.
- In severe cases, he cannot consistently perform the simplest movements. Remains in one place, but wobbles a lot and falls.
- Partially or completely not oriented in space. Bumps into objects and does not know how to calculate real distance.
The disease has species-typical and generally similar symptoms. The different symptoms depend on the causes. All types of pathology are characterized by:
- the cat holds its head atypically, it can tilt it to the side or lower it down;
- a staggering gait is observed, the animal loses coordination, the cat can walk, raising its hind legs high.
If the animal's spinal cord is damaged, it will experience pain when walking. Such cats try to hide in a quiet place and move less.
Attention! In severe forms, paralysis of the hind limbs can develop in cats.
With cerebellar ataxia, tremor occurs when running or walking. The kitten will often tremble, and most often the trembling is noticeable only in the back of the body. The cat also has dilated pupils and poor coordination.
If the vestibular apparatus is affected, the cat will suffer from severe headaches. Such animals constantly meow, hide in the corner, pressing their foreheads against the wall.
Hind limb paralysis
Diagnostics
One of the first diagnostic methods will be a thorough history taking. It is important to know about the cat's previous injuries, infectious diseases and nutrition. If possible, family heredity and the peculiarities of pregnancy in the mother cat are determined.
The animal is examined by a neurologist to assess the functionality and disorders of the nervous system.
Determine serological reactions to dangerous feline viruses - immunodeficiency virus, panleukopenia and leukemia.
If the clinic has the opportunity, then they conduct an MRI diagnosis of the brain; tumors, aplasia of areas, hemorrhages and edema are clearly visible on it. It is also possible to use ultrasound and radiography.
The ear is examined using an otoscope.
If there is a suspicion of infection of the brain or spinal cord, cerebrospinal fluid is taken to analyze leukocytes and protein, and a bacteriological examination is also carried out.
Often, to a professional veterinarian, ataxia is obvious upon initial examination. But to fully understand the situation, it is necessary to collect all the anamnesis data. Have there been any injuries (even several years ago), how and what does the cat eat, what severe infections has it suffered? If possible, how her mother’s pregnancy progressed. Examination of the ears with an otoscope is mandatory.
X-rays, ultrasound, or even an MRI will be needed to confirm the diagnosis and identify or rule out tumors, hemorrhage, or swelling of the brain. In some cases, if a brain or spinal cord infection is suspected, a cerebrospinal fluid test may be necessary.
Ataxia in cats: symptoms and treatment
The tactics of the prescribed treatment depend on the causes of ataxia. B vitamins, especially B12, are mandatory. Gamavit is used to strengthen the immune system and the body as a whole.
The medicinal substance Proserin also penetrates well through the blood-brain barrier and helps restore nerve conduction.
With cerebellar ataxia, treatment of the disease is extremely difficult. After all, the basis of the disease is degenerative changes in the brain. Cerebrolysin (Cerebrolysate) is used to improve cerebral circulation and tissue regeneration.
To improve the functioning of brain tissue, glycine is used 0.25 t once a day for 2 weeks, piracetam 0.3 ml IV and caviton 0.25 t 3 times a day for a week.
In case of spinal cord damage, surgical treatment is prescribed in most cases. Physiotherapy is also used - UHF, UMI (pulse therapy), massage.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Top 10 biggest cats in the world: description and photo
If there is an infection, then antibiotics are used - ampicillin, vancomycin. Often the cat will require anti-toxic therapy. To do this, use a drip infusion of saline solutions - saline solution with glucose. Glucocorticosteroids – prednisolone – are also administered.
If there is cerebral edema or hydrocephalus, diuretics are prescribed - furosemide, veroshpiron.
Severe tremor can be relieved by using diazepam, but in this case it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the liver and prescribe minimal doses of the drug, as it is toxic to the liver.
Owners of kittens with cerebellar ataxia should remember that after the animal reaches the age of 1 year, its condition stabilizes, and the pet can continue to live happily. Such pets have extraordinary intelligence and kindness, but they require the safest possible life and good care, and, of course, love and affection.
Now in the United States there is even a special queue where residents sign up to shelter animals with this diagnosis.
The entire treatment regimen for ataxia, if possible and relevant, always directly depends on the root cause of the disease. Therefore, the list of prescriptions and dosages of drugs are never the same, even for the same form. And in this section we will provide only generally accepted medical recommendations in practice:
- Vitamin complexes following the example of Gamavit and especially B vitamins are always required;
- antibiotics will be needed if the cat is fighting an infection;
- diuretics - Furosemide, Veroshpiron - will help in the outflow of excess fluid during cerebral edema;
- in case of damage to the spinal cord (sensitive ataxia) - surgical intervention;
- for intoxication - droppers of saline solutions and glucocorticosteroids;
- severe muscle tremors can be treated with caution with Diazepam;
- Cerebrolysate - to improve cerebral circulation;
- Physiotherapy - UMI, UHF, massage;
- Piracetam, Cavinton and Glycine - to restore cerebral functions.
Please remember that any information on the Internet is for informational purposes only. Never prescribe medications to your cat without first examining and consulting a veterinarian.
The treatment strategy is determined by the cause of the ataxia. In all cases, to restore the conduction of nerve impulses, group B drugs are injected. The specialist prescribes medications that improve cerebral circulation and normalize metabolic processes in nerve tissues.
If a tumor is found, it is removed. Prescription psychotropic medications are used to stop tremors. If the disease is accompanied by cerebral edema, diuretics are prescribed. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed, as well as rehydration therapy. In some cases, the specialist offers the owner a choice between continuing treatment and euthanasia.
If ataxia is detected in a kitten, the pathological symptoms may disappear upon reaching one year of age.
It is important that therapy is carried out comprehensively. The treatment regimen is developed depending on the cause that caused the development of the disease. In this regard, the dosage of drugs may differ even if we are talking about the same form of pathology.
The following medications are most often prescribed:
- vitamin complexes, B vitamins;
- to eliminate infections - antibiotics;
- for swelling of the brain - diuretics;
- Hepatoject for liver dysfunction;
- to improve blood circulation in the brain - Cerebrolysate;
- saline solutions in droppers to relieve intoxication.
Physiotherapy and massage are recommended for the animal. If the spinal cord is affected, surgery is required.
Important! You should not try to treat yourself. A sick animal requires professional advice from a veterinarian. The severe form cannot be eliminated using folk methods alone without an integrated approach.
Vitamins for full recovery
Prevention
- Mandatory vaccination against panleukopenia, rhinovirus and feline leukemia virus.
- To avoid injury to the animal as much as possible, it is advisable to limit free access to the street.
- Careful protection of the health of a pregnant cat, a ban on its communication with other animals.
- When planning a mating, be sure to check the cat for panleukopenia.
- Timely treatment of otitis and inflammatory ear diseases.
- Urgent hospitalization of a cat if a traumatic brain injury is suspected.
- Check with the breeder about genetic diseases in relatives and about the mother’s pregnancy history.
Despite the fatality of this disease, you still have too many conditions in your hands for a full and healthy life for your pet.
- Eliminate all factors that could cause serious serious injury. It is advisable to limit unsupervised walks on the street. And if you live in a multi-story building, a mosquito net on the windows will simply save the animal’s life.
- If you suspect a traumatic brain injury, immediately take your cat to a veterinary clinic or, at a minimum, immediately consult a doctor by telephone.
- Strictly follow the vaccination schedule against panleukopenia, rhinovirus and leukemia.
- Do not under any circumstances start treatment for otitis media or any inflammation in the ears.
- When planning a mating, pre-examine the cat for panleukopenia.
- During pregnancy, protect her from any contact with other animals.
- When purchasing a kitten from breeders, try to find out in as much detail as possible the course of the mother’s pregnancy and possible genetic problems along the family line.
We suggest you read: Determining the cause of odor from a cat’s ears
Problematic coordination of movements of a cat with ataxia is very well corrected by physical therapy. Exercise and play with the animal as often and for as long as possible. This not only brings him a lot of positive emotions, but is also a necessity when he is ill.
You should purchase a kitten from a trusted breeder with an impeccable reputation. The cat is immunized before mating. The kitten is vaccinated according to the vaccination plan. Monitor the health of the ears and promptly treat otitis media.
Despite the complexity and severity of the pathology, pet owners can create the necessary conditions to avoid its development. First of all, it is necessary to avoid any factors that could lead to injury. It is not recommended to let your animal go outside unattended.
The following should be used as preventive measures for the development of ataxia:
- Timely contact a veterinarian if there is a suspicion that the animal has a traumatic brain injury.
- Vaccinations in accordance with the schedule against leukemia, panleukopenia.
- Treatment of inflammation in the ear canals is mandatory.
- Examine the cat for panleukopenia before mating is planned.
- During pregnancy, protect the cat from contact with other animals.
Important! Loss of coordination can be effectively treated through physical therapy. Veterinarians recommend working with your pet and provoking it to play. Activity is very necessary for a kitten with ataxia.
Ataxia in cats is a complex disease, but with a competent and timely approach, the pet owner can return it to normal life. Caring and adherence to preventive measures effectively influence the healing process.
Treatment of cerebellar ataxia in cats
In this case, the motor pathology was provoked either by a genetic factor with a developmental defect in the brain structures, or by a mother cat who developed panleukopenia in late pregnancy.
In kittens, hypoplasia of the cerebellum occurs, which controls coordination and regulates voluntary and involuntary movements.
The unusual nature of the kitten becomes obvious when the babies grow up and begin to move actively. And in some cases, particularly attentive owners can detect violations immediately after birth. Most cats with cerebellar ataxia move sideways or diagonally.
Cerebellar ataxia differs from other types of ataxia: nystagmus - involuntary very rapid movements of the eyes, trembling of the head when the animal is focused on something, and tremor of the back of the body during movement. When the cerebellar vermis is damaged, static-locomotor ataxia develops.
According to the severity, it can occur in mild, moderate and severe form. With mild, falls occur periodically, the cat actively walks and runs; with moderate, movements are not easy for the animal, the cat often falls, but still moves. And the severe degree does not even allow you to get up on your paws.
Unfortunately, the disease cannot be treated. But with proper care, a kitten has every chance of living as long as an ordinary healthy cat. He does not experience any pain, his intelligence is completely preserved, and after the age of 1 year, movements become more coordinated and consistent. If deterioration begins, this only indicates that another neurological disease with similar symptoms has joined the ataxia.
By nature, cats with cerebellar ataxia are very affectionate and friendly. Owners of such animals note their unusual intelligence, close emotional connection and strong affection. Throughout its life, a cat perceives its owner or mistress as a big mother.
The same litter may produce kittens with varying degrees of cerebellar damage.
What does nystagmus mean?
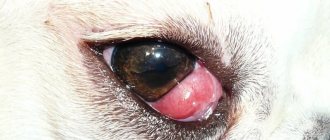
I would like to note right away that if a cat owner discovers such a strange state of the eyes in his pet, when the pupil rotates as if wound up and the cat looks into emptiness, this does not bode well. This kind of phenomenon is not the norm. These rhythmic oscillatory eye movements (usually movements occur in the horizontal plane) indicate serious brain damage.
Where does nystagmus come from?
Nystagmus is an alarming symptom
Let's look at the anatomy. The eyes play a very important role, and it is impossible to imagine maintaining body balance in space without clear vision. After all, there is a close connection between the eyes and other organs of the vestibular apparatus. Thus, it can be argued that the eyes for our brain are sensors that transmit readings to the brain, and it already analyzes it and makes decisions on what to do next. But,
when a cat begins to have nystagmus, this indicates damage to the brain as the main center.
Types of nystagmus
I would like to immediately note that such a disorder can be either acquired or congenital. The latter is typical for representatives of the Siamese breed. Kittens with nystagmus are often born there.
As for acquired nystagmus, the cause may be:
- injury,
- severe stress,
- transferred disease.
And if congenital nystagmus is not treated, then acquired nystagmus can and should be fought. However, not with the symptom of spinning eyes itself, but with its root cause.
Nystagmus can also be pendulum - in this case, the speed of eye movement is the same in all directions. And also clonic - in this case, we can distinguish the slow and fast phases of pupil movement.
Vestibular ataxia
The diagnosis is made in two cases: with an affected structure of the inner ear and with tumors of the brain stem or medulla oblongata.
Adult animals over 10 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The cat has difficulty standing, can walk in circles, or fall over on one side.
The head is either thrown back or tilted towards the affected side. Movements are slow and careful. Concomitant strabismus and nystagmus are often found, and in some cases there is also periodic vomiting.
The appearance of vestibular ataxia is provoked by:
- otitis;
- brain tumors;
- bacterial infections and abscesses of the ear canal;
- excessively intense and traumatic ear cleaning;
- medication overdose;
- use of aminoglycoside antibiotics;
- liver or kidney dysfunction (in rare cases).
A cat with an affected vestibular apparatus may periodically sit in a corner with its forehead pressed against the wall. We often see this exact pose of the animal in a series of “funny” photos. Meanwhile, the pet is suffering from a severe headache and is in dire need of veterinary care.
Reasons for appearance
If this is an acquired phenomenon, then you need to consider the main factors that can lead to a cat getting sick:
- presence of injury that may occur from a fall from a height. A severe blow to the head may also be present. The cat's eyes suffer mechanical damage, or the functioning of the optic nerve is disrupted. In this case, any type of disease may occur;
- heredity, which is determined by genes. If the deviation is within the acceptable norm, then treatment is not required. Cats from birth get used to this pathology and feel great in the future;
- problems with the vestibular apparatus. It causes a distorted perception of the information received by the brain, in particular, the position of the head in space is incorrectly perceived;
- various diseases of the nervous system. The interaction between the eyes and the central nervous system is disrupted. This case also includes brain tumors of various etiologies;
- rabies, in which the pupil dilates greatly and clouding of the cornea is observed;
- otitis media of both the inner and middle ear;
- the presence of dropsy in the brain - hydrocephalus;
- feline leukemia;
- glaucoma;
- encephalitis;
- meningitis.