The essence of allergies, causes and their classification
An allergy is a complex reactive process in a cat’s body when an ordinary and completely safe substance is perceived as something foreign and dangerous. This substance is called an allergen.
Immunity against allergens works in such a way that the “harmful” substance is not immediately eliminated from the body, but first an inflammatory process is provoked around it. Next, a substance such as histamine is released into the blood, which, acting on certain cellular receptors, becomes the culprit for the entire spectrum of clinical manifestations of the reactive state. A feature of all such reactions is the individual set of allergens and the unpredictability of symptoms.
Allergies can be caused by absolutely any substance:
- food (each cat has its own individual allergens);
- chemicals (shampoos, powders, cleaning agents and detergents, etc.);
- dust, mold, pollen;
- medicines;
- cat litter;
- saliva and waste products of blood-sucking insects and skin parasites;
- hair of other animals, dander or other gland secretions;
- the body's own cells.
Main types of allergies
Protein components perceived by the animal’s body as foreign are usually divided into two groups – exogenous and endogenous.
Exogenous allergens are those that enter the body from the environment. Various foods, medications, pathogenic bacterial and fungal microorganisms that penetrate the body through the respiratory tract, epidermis or digestive system can cause allergies.
Endogenous allergens are produced by the pet’s own body. This type of allergic reaction, provoked by internal biological systems, is diagnosed quite rarely. It occurs as a result of complex biochemical changes that provoke the breakdown of cellular structures and tissues. As a result of the malfunction, the immune system recognizes its own healthy cells as foreign and begins to attack them.
There are also a number of factors that provoke the onset of a specific reaction in the body. Among them are:
- predisposition at the genetic level;
- violation of the general environmental situation;
- intolerance to certain substances by animals at the individual level;
- toxic substances injected by blood-sucking insects that parasitize the animal’s skin;
- pollen of flowering plants;
- household and street dust;
- household chemicals.
The most commonly diagnosed types of allergies in cats in veterinary clinical practice are:
- Food allergies. Allergies to food in cats occur more often than other types of specific reactions of the body. The owner of the animal may not suspect for a long time that his pet is experiencing pathological processes in the body. This is primarily due to the fact that food allergies develop quite slowly, without making themselves felt for a long time. Cats are less likely to be allergic to chicken than to beef, pork and river fish. Food allergies can be caused not only by animal fats, but also by plant proteins. Due to the fact that the threshold of sensitivity to the allergen is different for all animals, the manifestation of food allergy symptoms may occur several weeks or months after eating one type of food. The reaction develops when the amount of allergen in the bloodstream begins to exceed the norm.
- Flea allergy. Often the cause of a pet's constant itching is a reaction to flea bites. Some cats tolerate bites normally, while others experience inflammatory processes on the skin, characterized by hyperemia and other serious damage, including the formation of ulcers. Flea allergies are provoked by toxic substances contained in the saliva of ectoparasites. During the injection of saliva during a bite, toxic substances enter the cat's systemic bloodstream, which can cause serious imbalances in the body's balance.
- Atopic dermatitis
. One of the most serious types of allergic reaction, which is chronic. This type of allergy can occur in response to a wide variety of irritants - medications, household chemicals, street dust, gases and pollen. Allergy to wood filler in a cat also refers to an atomic (chronic) type of disease. It is difficult to identify a foreign agent in a timely manner, so the animal continues to be in contact with the pathogen for a long time. During the stage of exacerbation of allergic dermatitis, the cat itches severely, the skin becomes red and swollen, and weeping eczema appears on the body. As a result of severe scratching, as a rule, pathogenic bacterial microflora is added, complicating the course of the disease and further treatment. It is worth noting that there is no complete cure for atopic dermatitis. Treatment of the pathology is based on eliminating the main symptoms that cause discomfort to the pet.
Types of allergic manifestations
Atopic
This is an idiosyncrasy or allergy to any allergens exposed in any of the following possible ways:
- food allergies in cats;
- reaction to medications;
- reaction to dust, pollen, mold.
Infectious
Occurs on substances that are produced in the body during the life of fungi, viruses or bacteria):
- fungal;
- bacterial;
- viral.
Parasitic-insect
This is a reaction to saliva and the vital activity of cutaneous or intradermal parasites, as well as worms.
Chemical
This is an allergy to care products, household chemicals, cat litter, etc.
According to the method of exposure to allergens, the classification is as follows:
- contact (by direct contact with the allergen);
- respiratory (by inhalation);
- autoimmune (internal allergic reaction to the body’s own cells).
Treatment
You can cope with allergies only if you limit contact with animal litter. Many accompanying factors can aggravate a person’s condition:
- presence of animals at home;
- dry air in the apartment;
- aggressive household chemicals;
- a lot of upholstered furniture and carpets that collect dust.
Daily cleaning and an air purifier will help reduce symptoms. During treatment, you can transport the animals to friends.
Drug therapy
Allergies are treated in several ways:
- Antihistamines. They are prescribed during periods of exacerbation of allergies. They relieve symptoms, but are not able to completely cure a person.
- Decongents. These are vasoconstrictors that make breathing easier.
- Corticosteroids. Hormonal drugs are prescribed for severe allergic reactions that pose a threat to life.
- ASIT. This is a specific immunotherapy in which a person is injected with an allergen in small doses (see in more detail “The effectiveness of using allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) in the treatment of allergies in adults and children”). Thanks to this, the body begins to get used to the irritant and unpleasant symptoms do not occur.
After ASIT, a person can forget about allergies for a year or more, and in some cases it is possible to completely cope with the disease.
Folk remedies for treating allergies
Nasal congestion, itching and sneezing are relieved by inhalation. You can quickly relieve an unpleasant symptom using ordinary water vapor. To do this, pour boiling water into a bowl and bend over it. To contain steam, it is advisable to cover yourself with a towel. Inhalation is carried out for no more than 10 minutes. You need to act carefully so as not to get burned. To improve the effect, you can add eucalyptus essential oil to the water.
If your eyes are watery due to allergies, you can relieve the irritation with a decoction of chamomile. To do this, you need to brew the flowers of the plant and blot cotton pads with the liquid. The compress is applied to the eyes for 15 minutes. You can quickly relieve pain in the eyes with a towel dipped in cold water.
Skin irritation will decrease if you take a bath with the addition of a herbal decoction. Anti-inflammatory plants include:
- pharmaceutical chamomile;
- series;
- oregano;
- nettle;
- Bay leaf.
Green tea will provide quick relief from an allergic reaction to the filler. It will help relieve the symptom if you don’t have an antihistamine on hand. During an attack of allergic cough, you can drink herbal tea from the series.
An allergy to pet litter can manifest itself in a variety of symptoms. To alleviate the condition, you need to replace the mixture with a hypoallergenic composition as quickly as possible.
Symptoms of allergic manifestations
Regardless of the type of allergy, common signs of the body's reaction to allergens are:
- redness of the skin or skin rash of various locations;
- itching, visible scratching, baldness, swelling of certain areas of the body;
- sneezing, discharge from the nose and/or eyes;
- peeling of paw pads, eczema in the interdigital space;
- dyspnea;
- vomit;
- sometimes increased body temperature;
- possible swelling of the respiratory tract;
- anaphylactic shock (in very rare cases).
An allergy in a cat can manifest itself as one symptom, or perhaps as a whole symptom complex of several phenomena. Reactions are observed both immediately after interaction with allergens and after some time (which usually makes diagnosis difficult).
Features of symptoms for various types of allergies:
|
|
| classic signs of allergy accompany the underlying fungal, viral, bacterial or helminthic disease. |
|
|
|
|
| damage mainly to the respiratory tract (discharge from the nose and eyes, swelling of the larynx, shortness of breath). |
|
|
|
|
Symptoms of pathology
When a cat food allergy develops, symptoms begin to appear gradually. Initially, you can notice how the animal has changed its behavior. The cat begins to rub its nose, chews its paws or other objects in the house. Some animals can pull out their fur on their own.
If the fur becomes foul-smelling, and scratches, spots or sores appear on the body, then such symptoms are not always characteristic of an allergic reaction. Fungal infections are also diagnosed using these signs.
Swelling of the skin, the formation of inflamed red areas on the skin and bleeding ulcers often become the cause of a flea attack. The resulting severe itching provokes scratching. Places of damage entail another danger: infection can penetrate into the resulting wounds, which will further complicate the situation. The first thing that is recommended to do when a pet develops health problems is to examine it for the presence of parasites.
Itching of the skin combined with dryness is characteristic of dermatitis.
The danger of this form of pathological process is that it can rarely be cured. The veterinarian prescribes symptomatic treatment, which is aimed at reducing symptoms of itching and treating scratching.
It is quite difficult to predict exactly how an allergic reaction to a particular irritant will manifest itself. The most common symptoms that signal the presence of a foreign agent include:
- formation of swelling and redness in certain areas of the epidermis;
- debilitating itching that makes the animal scratch all the time;
- prolonged sneezing;
- skin rash;
- severe shedding;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- bad breath;
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- shortness of breath and other breathing problems;
- vomit.
The main signs of allergies in cats can be seen in the photo
| Flea allergic dermatitis | Allergy tests |
| Atopic dermatitis | Hives |
| Autoimmune pemphigus foliaceus | Allergic lacrimation |
| Autoimmune lupus erythematosus | Contact allergy to detergents |
| Food allergies | Allergy to meat protein |
Types of allergies in cats
Hair loss can be one of the symptoms of allergies in a cat.
Often, owners complain about hair loss in their pets, eye diseases and other characteristic symptoms, which are ultimately caused by allergies. But to make an accurate diagnosis, you should always contact a veterinarian.
Allergies in cats are generally divided into two main types: food and non-food.
This classification is very conditional, because there are also frequent cases of allergic reactions to household chemicals, perfumes, plastic and rubber products, indoor plants, and toilet filler.
Food allergy (allergy to food)
Manifestation of food allergies
Food allergies arise due to the sensitivity of the animal’s body to one or another component of the diet or to the composition of the bark as a whole.
Often this component is protein . It is believed that the most common allergenic foods for cats are chicken, milk, eggs, cereals, beets, carrots, and pumpkin. If they are present in a ready-made coma or added to food, the owner of the animal must be especially careful.
There are also frequent cases of allergic reactions to food from a particular manufacturer. This can be signaled by symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction: diarrhea, vomiting or constipation. You must also be careful when taking herbal medicines .
Non-food allergies
A cat is allergic to a wasp sting on its nose.
Non-food allergies are often the result of insect bites such as fleas, bees and wasps, and mosquitoes.
Sometimes flea bites are accompanied by a severe allergic reaction of the body due to the protein contained in the flea's saliva and enters the body during the bite. But one flea can cause up to 200 bites per day.
The cat begins to scratch the area where it is allergic.
The animal begins to scratch the bite sites, which aggravates the reaction due to the release of biologically active substances. This condition is called flea dermatitis.
But also allergies, mainly of individuals living on the street, can be caused by bites of snakes or other poisonous creatures. A common cause of non-food allergies can be litter trays. This usually happens after changing the type of litter, which can cause the animal to refuse to go to the tray.
Features of allergy diagnosis
The diagnosis of “allergy” can only be made by a veterinarian after a personal examination and interview with the animal owner. This disease very successfully disguises itself as many other infectious and internal non-communicable diseases, so only a specialist will be able to differentiate one from the other.
As a rule, cats are not subject to allergy testing. The process is quite expensive and not always informative. Usually performed under general anesthesia, because It is impossible to introduce up to 20 allergens intradermally to an animal without additional effort. Substances included in the anesthesia come into contact with reactive test allergens, showing a false local reaction. Those. the test shows an allergy to something that in fact is not.
There are also no special tests for mustachioed pets, and in practice human test kits are used. Considering the peculiarities of the course of allergic reactions in humans and cats, the likelihood of false results is also very high.
Determining the source of an allergy is carried out exclusively experimentally by the method of exclusion. In this case, all potential allergens are consistently excluded from the cat’s environment until the true cause of the body’s increased sensitivity is identified. This method works great for food allergies.
With seasonal allergies, the source of the reaction is often not looked for at all. If it is noticed that signs of hypersensitivity to something appear once a year for a certain period, then for this period of time it is enough to give antihistamines until the allergen disappears on its own after this period.
Treatment of allergic (atopic) dermatitis
Eliminating the cause or contact with the cause
Drug treatment will be ineffective if the allergen continues to affect the body. This point usually coincides with preventive measures for the occurrence of allergies, depending on the substances that cause the reaction:
Dust |
|
Mold |
|
Pollen |
|
Cutaneous blood-sucking parasites |
|
Household chemicals |
|
Application of local therapy
As a local antiallergic agent in cats, the use of only shampoos with hydrocortisone is justified. The effect is short-term, but immediate.
The use of ointments with hydrocortisone is justified only in the presence of itching and in small, hard-to-reach areas for licking. Ointments have virtually no adverse reactions due to the fact that they are practically not absorbed into the blood.
Prescription of biotin (vitamin B7) and preparations containing it
It has been proven that this vitamin in combination with omega fatty acids gives a noticeable effect in eliminating allergic dry skin, itching and seborrhea. With long-term use of the biotin + fatty acid complex by a cat in combination with antihistamines and diet, the need for steroids is significantly reduced.
Antihistamines
They are used as emergency aid and for long-term use to eliminate allergic symptoms or reduce their intensity. The dosage is always calculated individually.
Steroids
This group of drugs for systemic use is used in extreme cases, when all possible methods have been tried, but the effect is minimal or completely absent. Corticosteroids have many contraindications and side effects for cats, so it is important to follow the exact dosages and administration schedules that will be prescribed by your veterinarian. It is best to use injectable steroids (flumethasone, betamethasone, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone).
As for atopic dermatitis, unfortunately, it cannot be completely cured. All therapeutic measures are aimed at maximizing the relief of the animal’s condition and reducing the number of exacerbations. Those. this pathology is controllable. The treatment scheme is similar to the treatment of ordinary allergic dermatitis, only it is carried out almost constantly throughout the animal’s life.
Treatment of food allergies
- Eliminating the cause. After determining what type of product the cat is allergic to, it will have to be excluded forever.
- Consumption of a complex of fatty acids + biotin.
- Use of antihistamines.
- The use of steroids for food allergies is indicated when there is no relief in symptoms after all possible treatments. Until the cause is identified, it is usually not prescribed.
Treatment of infectious, parasitic and insect allergies
- Treatment of primary infectious disease. Before you begin direct treatment of allergies, you need to cure primary fungal, infectious or parasitic diseases. Treatment of the primary disease will be considered the elimination of the cause of the allergy.
- Destruction of blood-sucking parasites not only on the cat, but also in the premises where it lives.
- Deworming.
- Antihistamine therapy.
MAIN CAUSES OF ALLERGIES
The cause of an allergic reaction can be a variety of substances:
- Certain types of trees and grasses, fungus, mold stains, pollen and dust accumulations;
- Foods the cat eats;
- Lice, fleas and means to eliminate them;
- Medications;
- Cigarette smoke;
- Household chemicals, mainly cleaning products;
- Some types of materials such as plastics and rubber;
- Perfumes;
- Some types of fabrics.
Video: primary signs
Main symptoms of allergies in cats
Depending on what irritant caused the allergy, the body's reactions will be completely different. A common symptom for any allergy is itchy skin , as well as the following manifestations:
- Attacks of coughing and sneezing, while breathing is accompanied by whistling;
- Eyes water;
- The cat scratches its back and near its tail;
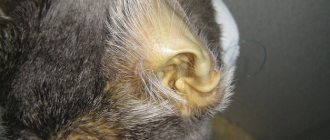
- Itchy ears and an ear infection may occur;
- Attacks of vomiting, defecation occurs in liquid masses;
- Paws become swollen;
- Snoring occurs as a result of inflammation of the throat.
Drugs for allergies in cats (a brief overview of systemic antihistamines)
Any antihistamine has its own exact dosage, exceeding which turns the medicine into a substance harmful to the cat with a lot of adverse reactions. This is the main reason why such medications should only be prescribed by a veterinarian.
Along with veterinary antihistamines, human drugs are effectively used for treatment according to long-developed and effectively implemented regimens.
Veterinary:
Used for allergic dermatitis. Prohibited for diabetes mellitus in cats, pregnant women, heart or kidney pathologies. Do not use for a long time due to the peculiarities of the glucogenic effect (increases blood sugar levels). Intramuscularly at 0.25-0.5 ml/head. every 24-48 hours |
Bravegil (up to 180 rub./amp or up to 120 rub./10 tablets)Widely used for all types of cat allergies. It is administered intramuscularly or given orally in tablet form. Slightly manifests itself in drowsiness. Not used during pregnancy. Dosage: 0.015-0.02 mg/kg once or twice a day (every 12-24 hours) (regardless of the route of administration). Can be used for a long time. |
It perfectly relieves allergic manifestations on a par with diphenhydramine, but has a longer lasting effect. Slightly causes drowsiness in cats. It is administered intramuscularly. Do not use for pregnant individuals. Apply 0.015-0.02 mg/kg twice a day after 12 hours. |
Human:
Effect: antihistamine, analgesic, sedative and hypnotic. The dosage is selected for each animal strictly individually, because It can have completely different effects on different cats, even in the same dosage. It is administered intramuscularly in an amount of 0.02-0.04 ml per 1 animal, in tablets orally the dosage is 1.5-2 more. Maximum twice a day for a week. |
Most often used for allergic reactions to insect bites. There is a hypnotic effect. The action is similar to diphenhydramine. Do not use in lactating animals or during pregnancy. It is forbidden to administer simultaneously with antipyretics. Orally at the rate of 1-4 mg of the drug, without mixing with food. You can repeat no earlier than after 8-12 hours. |
It has an antiallergic, psychotropic, sedative effect, suppresses the emetic effect. Relaxes smooth muscles, dilates bronchi and relieves pain (part of the piperazine range of drugs). Does not provoke addiction. Give orally at a dose of 5-10 mg/cat, repeated after 8-12 hours. |
Chlorpheniramine maleate (RUB 125-500)Works well on feline allergic dermatitis and urticaria. It is better to administer intramuscularly, because when it gets on the surface of the skin, it provokes a local irritant effect. When used orally, combine with or after feeding to reduce stomach irritation. Do not combine with alkaloids. Not suitable for long-term use - only for relief of acute increased individual reactions and no longer than 3 days. Dosage: 1-2 ml/animal intramuscularly or 2-4 ml/animal orally every day or 12 hours. |
Clemastine (Tavegil) (110-220 RUR/pack)Perfectly eliminates allergic symptoms in cats such as sneezing, runny nose and watery eyes. It has a long action time. It enhances the sedative effect of sedatives, so any drug combinations are not recommended. Side effects: diarrhea, thirst, lethargy or increased activity. The dosage does not depend on the weight of the animal: ½ tab. every 12 or 24 hours. |
Why cats can't have milk
It is impossible to do without dairy products in an animal’s diet. Dairy products contain all the necessary nutrients, such as lactose, a set of unique amino acids, protein components, microelements and lipids.
Such a natural carbohydrate as lactose is obtained from other molecules - glucose and galactose. Lactose is present in all dairy and fermented milk products - kefir, cottage cheese, whey. If the body is unable to absorb milk sugar, intolerance occurs. But this condition is not observed in all animals.
Milk also contains:
- Amino acids – there are about 20 amino acids, 8 of which cannot be replaced in the diet with herbal supplements or artificial substances;
- Protein of animal origin - it is not possible to synthesize it in industrial conditions, nor is it possible to replace it with equivalent plant proteins.
- Microelements – microelements in milk are maximally balanced and are absorbed by the body to the maximum. In attempts to replace dairy products with pharmaceutical analogues, the cat owner may develop dangerous diseases such as urolithiasis.
- Fatty acids – give dairy products a characteristic sourness, contain an increased concentration of retinol and ergocalciferol. Without these substances, the body cannot exist normally. Beneficial cholesterol is involved in the activation of hormonal processes in the body.
Veterinary specialists do not have a categorical opinion about the dangers of cow's milk for the cat's body. Each organism is individual, so some cats that reach adulthood retain the enzymatic substance that breaks down lactose. If the pet’s body has a reduced amount of the enzyme that breaks down lactose, serious allergic reactions occur, accompanied by loose stools and indigestion.
In the absence of a specific reaction to receiving cow's milk, the animal can be given milk, but do not exceed the dosage. The recommended amount of milk for a cat is 15 ml per 1 kg of live body weight. Some owners of cats who avoid giving milk argue that in the wild these animals do not drink milk. But it is worth noting that during the course of evolution and the process of domestication, the nutrition of animals has undergone changes.
If the owner wants to feed natural food and wants to give milk, it is recommended to give sheep or goat milk, because these products have significantly lower allergenic properties than cow milk.