What causes the disease?
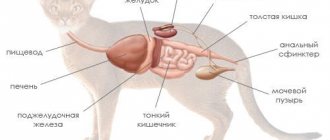
Cirrhosis is a pathological disease that occurs due to destructive changes in the tissues of the liver of cats. A characteristic feature is an increase in the area of expanding connective tissue over the area of the organ. Which, in turn, leads to a malfunction of the system. As a rule, the manifestation of this disease is characteristic of elderly and middle-aged animals.
One of the manifestations of cirrhosis is liver fibrosis in cats. If we decipher this term, it means “overgrowth of connective tissue.” Experts classify fibrosis as a separate group of diseases. In fact, cirrhosis has other symptoms besides fibrosis.
Veterinarians distinguish between primary and secondary cirrhosis.
The causes of the first type of disease are:
- lack of vitamins in the body, in particular B6;
- disruption of glycogen metabolism in the organ;
- poisoning of the body with toxic compounds for a long time (household chemicals, pesticides, medications that have a hepatotoxic effect);
- eating food or other products that have been contaminated with mold fungi.
Factors that provoke cirrhosis and its development are:
- diseases caused by bacteria, viruses and fungi;
- damage to the organ by liver parasites;
- against the background of primary organ ailments (hepatitis, hepatosis).
The causes leading to cirrhosis are heart failure and disturbances in the functioning of the body, accompanied by a disturbance in the outflow of bile.
Causes
Cirrhosis is a progressive pathology accompanied by destructive changes in organ tissues, characterized by diffuse proliferation of connective tissue. The disease leads to the inability to perform numerous organ functions. The disease is more often observed in middle-aged and older animals.
In veterinary medicine, it is customary to distinguish between the primary and secondary forms of the disease. Each of these varieties has its own etiology and provoking factors.
We recommend reading about why a cat is thin. You will learn about the signs of exhaustion of the animal, the reasons for weight loss, and symptoms that should alert owners. And here is more information about how to deworm a cat.
Primary cirrhosis
Primary liver damage occurs for the following reasons:
- Lack of vitamins and minerals in the body, in particular vitamin B6 deficiency.
- Hereditary diseases associated with impaired glycogen metabolism in the liver.
- Chronic intoxication of the body with toxic substances . These could be pesticides used in agriculture, household pesticides, poisoning by petrochemical products, and drug intoxications. Corticosteroid drugs and drugs that have a hepatotoxic effect (anticonvulsants, disinfectants, phenol-based drugs) are especially dangerous.
- Often, intoxication is associated with food contamination by mold fungi (toxins of natural origin). Numerous helminthic infestations lead to the development of toxic cirrhosis due to poisoning of the body with waste products of worms.
Secondary cirrhosis
Secondary organ damage is recorded by veterinary specialists more often than the primary form. The causes of the pathology are:
- Infectious diseases of various etiologies (bacterial, viral, fungal). Pathogenic microorganisms not only enter the organ directly, but also spread through the bloodstream from other foci of infection. Liver damage often occurs due to leptospirosis, an adenovirus infection.
- Worm infestations . Liver cirrhosis in cats is often caused by the presence of liver parasites, such as echinococcus. Opisthorchiasis is a common cause of parasitic cirrhosis in felines.
Multifocal liver necrosis and microhemorrhages secondary to systemic toxoplasmosis
- Against the background of the development of primary liver diseases, for example, hepatosis or hepatitis .
Among the causes of cirrhosis, veterinarians often note heart failure, as well as pathologies accompanied by impaired outflow of bile.
Symptoms of cirrhosis in cats
A disease such as cirrhosis is characterized by a latent and chronic course of the disease. It is almost impossible to identify the symptoms of liver cirrhosis in cats at an early stage. The disease manifests itself when the chance of recovery is unlikely. Late detection of symptoms occurs due to the ability of liver cells to quickly recover and regenerate.
However, if you know some characteristic signs, you can begin treatment immediately. And the sooner the owner pays attention to them, the higher the chances of recovery.
- Decreased appetite.
- Low activity, apathy, fatigue, drowsiness, lethargy.
- Weight loss.
- Abnormal stool (alternating diarrhea and constipation).
- Frequent urination (urine color: orange; discharge of bilirubin from the urethra).
- Vomiting mixed with bile.
- Enlargement of the abdominal cavity.
- Urination in large quantities.
- The appearance of yellowness on the mucous membranes (characteristic of the late stage).
- Frequent bleeding, low blood clotting.
- The appearance of convulsions, loss of coordination, increased salivation. Pets often meow, indicating that they are in great pain.
Since these symptoms are minor, it is quite difficult to detect cirrhosis at an early stage.
Forecast
When owners ask how long cats with this disease live, doctors answer differently. It all depends on how severely the damage has affected the liver. Normal liver tissue will not be restored, and the more of it was replaced by connective tissue, the worse. The average statistical life expectancy among cats with this disease is 1-1.5 years. Moreover, throughout its subsequent life, the animal must be regularly examined by a doctor and follow a strict diet.
Finally, I would like to say that cirrhosis of the liver is a terrible disease, in most cases ending in the death of the cat. The high mortality rate from the disease is due to the fact that it does not manifest itself in any way in the early stages. You can protect your cat from a terrible diagnosis with timely vaccinations, a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular treatment for worms, and very responsible use of antibiotics in treating the animal. At the first signs of aggravating pathologies such as hepatitis or hepatosis, you should immediately take your pet for examination to a veterinarian.
Liver cirrhosis in cats is a disease in which organ cells die as a result of the proliferation of fibrous (connective) tissue, leading to severe functional impairment. The pathology develops unnoticed by the owner and is practically untreatable.
Diagnosis of the disease
As soon as you suspect the presence of a disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. Whether the prognosis will be comforting or not depends only on the speed of the owner’s reaction.
To identify this disease, the following types of diagnostics are used:
- A doctor examines the abdomen for fluid accumulation (ascites). Ascites manifests itself upon palpation. The specialist conducts a clinical examination in order to identify the boundaries of the organ. Fibrosis causes the organ area to expand and go beyond physiological boundaries.
- Ultrasound. It is considered the most informative diagnostic method. The specialist determines how severely fibrosis has affected the liver, identifies the nodes of regeneration foci, and determines the structure of the organ. Ultrasound examination is also necessary to detect ascites in the abdominal cavity. In addition, an enlarged spleen is a sure companion to cirrhosis.
- General urine analysis. What should not be in urine? Basically, bilirubin and protein. Their concentration in the urethra should be zero. But urobilinogen and bile acids are normally found in microdoses. They should not exceed a certain level.
- Blood chemistry. Cirrhosis contributes to a decrease in the level of protein, prothrombin, cholesterol and hemoglobin. Such studies will show an increase in the concentration of bilirubin and gamma globulins. Using this test, you can determine your blood sugar levels and kidney enzyme concentrations.
- Conducting serological tests to detect the source of infection.
- Study of the functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Organ biopsy. This is done extremely rarely.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis in cats
When a pet owner learns about the diagnosis, he wants to know the prognosis. As a rule, the veterinarian's answer is disappointing. The problem is that connective tissue replaces normal, healthy tissue, and this process, alas, cannot be reversed. Treatment of liver cirrhosis in cats can be successful, but no one can guarantee the animal’s complete recovery.
If cirrhosis is of the secondary type, then the efforts of specialists and the owner are directed towards eliminating the underlying disease.
- Administration of intravenous injections of glucose and calcium borogluconate. This is necessary to maintain an exhausted body.
- At the same time, any medications that could lead to severe damage to the organ are discontinued. This is especially true for hormonal medications.
- In order for the treatment of cats to be successful, “human” drugs are used in veterinary medicine: Essentiale, Phosphogliv, Ovesol, etc.
- Providing animals with a vitamin-mineral complex. B vitamins will be especially important.
- Treatment also involves the administration of albumin at a reduced protein concentration.
- If bleeding is observed, the doctor prescribes hemostatic drugs (Dicinon, Vikasol).
- To protect the animal from ascites, diuretics are prescribed.
- Sometimes the veterinarian prescribes antibacterial medications to prevent and reduce the risk of developing peritonitis and hepatitis.
- If the pet is being treated in a specialized clinic, then fluid from the abdominal cavity is removed through a puncture (laparocentesis).
The prognosis for recovery will be more favorable if the treatment is accompanied by complete rest of the animal and the consumption of special medicinal feed.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease itself is chronic. Therefore, symptoms of cirrhosis in cats do not appear immediately, and they are not too obvious; they often go unnoticed for a long time until the animal becomes very ill. The main symptoms of liver cirrhosis in cats are:
Let's start with the common belief about jaundice in cats - as a symptom. Jaundice, which is characteristic of almost all liver diseases, is practically invisible in cirrhosis. The cat's mucous membranes and the white of the eye turn slightly yellow.
Palpation, percussion
Regarding the enlargement of the organ, everything is also ambiguous. If cirrhosis is hypertrophic, then on the right side of the pet, immediately behind the last rib, you can feel the affected liver. Normally, it does not protrude beyond the ribs! However, if a cat has atrophic cirrhosis of the liver, the organ shrinks, as if it dries out. And the owner himself will not be able to detect anything. This is not hepatitis, so the animal does not experience much pain. And during percussion, the veterinarian may not suspect anything.
Other symptoms
Other symptoms of liver cirrhosis in cats:
| Ascites | The only thing that may still alert a veterinarian is dropsy of the abdominal cavity. And the owner himself will probably notice how the whole family’s pet’s tummy has become rounder, although the pet eats as usual or even less. And it doesn't look like it was fat. If you touch the stomach, it becomes clear that fluid has accumulated inside. |
| Fatigue | The pet gets tired quickly, so it can sleep a lot (although cats already sleep 18 hours a day, but if the cat has cirrhosis of the liver, sleep can be even longer). |
Loss of weight and appetite, extreme thirst
The cat begins to lose weight. And the appetite is noticeably reduced. If the mustache eats, it is with reluctance. But he drinks a lot. Since a large amount of water is drunk, the pet pees often and a lot. Sometimes even past the tray, without reaching it.
If you look at the results of the blood test, you can see that the cat has anemia and leukopenia (albeit minor).
In an advanced form of the disease
Preventive measures
To prevent fibrosis from affecting the liver and contributing to the development of cirrhosis, it is necessary to take care of premature prevention:
- Timely vaccination of the animal.
- Carrying out deworming.
- Avoiding poisoning and intoxication.
- Use of antibiotics and other medications as prescribed by a doctor.
- Reducing the risk of primary pathologies or curing them.
If a doctor has diagnosed fibrosis in an animal and, as a consequence, poor condition of the organ, then the prognosis for recovery from cirrhosis given by the specialist will vary depending on the degree of liver damage in cats. The less healthy tissue left, the less likely the animal is to survive.
Statistics show that animals with damaged livers live no more than 1.5 years. At the same time, all the time the pet will undergo unpleasant procedures to pump out fluid from the abdominal cavity, administer intravenous injections, and strictly adhere to a nutrition plan.
The owner must remember that the sooner he pays attention to the symptoms, the sooner he seeks help from a doctor, the higher the animal’s chances of recovery and future life. It must be remembered that this disease is considered one of the most insidious and serious. Therefore, take care of your animals!
Symptoms of the disease
The insidiousness of cirrhosis is that, unlike simple inflammatory processes in the liver, it has practically no signs in the early stages. Doctors explain this by the fact that the organ cells have high regenerative qualities. However, this positive aspect plays a bad role for the cat’s health, since it ends up on the operating table with an advanced pathology, which is almost impossible to cure.
However, owners, in any case, should carefully monitor symptoms of the disease such as:
- Lethargy, the cat’s loss of desire to walk and play with the owner. The animal prefers to sleep, and with physical activity, even minimal, it quickly gets tired.
- Appetite is significantly reduced, which leads to weight loss and further weakens the mustachioed friend.
- The cat often vomits, and bile impurities are clearly visible in the vomit.
- The process of defecation is disrupted, the cat alternates between diarrhea and constipation.
- The cat absorbs a lot of liquid.
- Uncontrolled urination, sometimes the pet does not have time to get to a place specially designated for this purpose.
- The cat's abdominal cavity swells as excess fluid accumulates there; this is called ascites in medicine (popularly called dropsy).
- In advanced forms, a clear sign of cirrhosis is yellowing of the mucous membranes of the animal.
- The coagulability of blood fluid decreases, and frequent bleeding is possible.
- Constant intoxication of the body causes encephalopathy, which provokes a loss of coordination of the cat's movements, increases the secretion of saliva and leads to a change in its behavior from calm to aggressive. A sick furry friend can meow loudly, thereby attracting the owner's attention to his problem.
- The color of the urine becomes significantly darker.