Every living creature needs food and energy sources. Glucose plays an important role in this process. When its level in the body rises or falls to a critical level, dangerous conditions arise - hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is a drop in sugar levels that occurs not only in humans, but also in dogs. This is a condition that indicates a metabolic disorder. The causes of hypoglycemia vary. But without timely assistance, it can lead to irreversible consequences.
What is hypoglycemia and how is it dangerous for a dog?
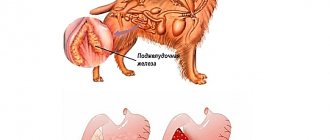
Hypoglycemia is the term for low blood glucose levels. If a dog's concentration is below 3 mmol/l, this is a cause for concern. The normal level of the substance is maintained by hormones that are synthesized by the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and pancreas. The entire process is under the control of liver enzymes. A deficiency of some of them leads to excessive storage of glycogen in the liver. The organ is unable to maintain glucose levels normally.
Glucose is the main source of energy for dogs. Some amount of it must always enter the brain, since the substance is not synthesized by the body and does not accumulate in nerve cells. If an animal does not receive enough glucose, the central nervous system is primarily at risk. Miniature breeds have a faster metabolism than large breeds, so they have a higher chance of developing hypoglycemia.
If normal blood sugar levels are not maintained, this can cause seizures, hypoglycemic coma, and even death in the dog.
Causes of hypoglycemia
Veterinary specialists associate most cases of hypoglycemia with disruption of the pancreas. Increased production of the pancreatic hormone insulin leads to the development of diabetes mellitus.
There is also juvenile hypoglycemia , diagnosed in puppies at 2.5-5 months of age. The main reason for juvenile hypoglycemia is the lack of fully formed systems that effectively regulate the level of sugar in the bloodstream.
Among the reasons for the development of hypoglycemia in puppies are also stressful conditions, prolonged fasting, repeated eruption of gastric contents, profuse diarrhea and hypothermia.
Causes and predisposing factors
More often, the development of hypoglycemia in dogs is associated with excess insulin and the presence of diabetes mellitus. But in reality, there can be many reasons for low sugar levels. Juvenile glycemia is common in puppies 3-4 months old. Their body is not yet fully formed and cannot effectively regulate glucose metabolism.
Learn about the early signs and symptoms of endometritis in dogs, as well as how to treat the inflammatory disease.
Read about the peculiarities of keeping and raising a dog of the Moscow Smooth-haired Toy Terrier breed at this address.
Hypoglycemia in puppies can be caused by:
- stress;
- hunger;
- hypothermia;
- vomiting, diarrhea;
- worms.
Factors that can provoke hypoglycemia in adult animals:
- unbalanced diet, malnutrition;
- excessive physical activity;
- Addison's disease;
- liver dysfunction;
- excessive administration of insulin in diabetes mellitus;
- impaired intestinal absorption, due to which glucose supplied with food does not enter the blood;
- insulinomas and other tumors that produce insulin;
- portosystemic shunts;
- sepsis is a bacterial infection;
- traumatic brain injuries.
More often, hypoglycemia is diagnosed in small dogs with low weight: Spitz, toy terriers, Yorkies, Chihuahuas and others.
Treatment method and prognosis
The basis of treatment is a timely increase in the level of glucose in the dog’s bloodstream. To do this, you need to inject glucose into the dog, but this must be done gradually, initially increasing to the minimum values, raising the bar higher. With a sharp increase in blood sugar levels, the animal can fall into a coma.
In life-threatening conditions for the pet, glucose is administered intramuscularly or via intravenous drip. Mild forms of hypoglycemia allow glucose to be administered directly into the mouth. This could be sweet candy or sweetened plain water.
After the specialist has determined the amount of glucose in the patient’s blood and identified the main cause of hypoglycemia, a further treatment regimen is developed. For diabetes mellitus, injections of the hormone insulin are prescribed.
For dogs, the dosage of the drug is selected individually and will depend on the age, body weight of the animal and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
If the cause of a sharp decrease in blood sugar levels lies in oncological pathology, surgery and a course of chemotherapy are prescribed.
The prognosis for most cases of diagnosed hypoglycemia in dogs is favorable. But this takes into account the timely implementation of diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
Let's see what prognosis is relevant for dogs with the disease we are interested in, depending on what disease caused it.
The prognosis for hypoglycemic dogs may vary.
Table. Forecasts for the disease in question, depending on the cause of the disease
| Positive outlook | Negative Outlook |
| Juvenile hypoglycemia has an extremely positive prognosis, provided that you get your bearings in time and take the animal for examination to a veterinarian | A veterinarian will probably give a bad prognosis for a dog with insulinoma, since this tumor is not benign, and most likely, at the time of its discovery, there may already be metastases in the animal’s lungs |
| Hypoglycemia associated with malnutrition is also quickly eliminated, since its treatment only requires proper feeding and nutritious food, which will improve the dog’s health | A negative or unclear prognosis will be indicated for an animal that is suffering from any severe or moderate illness that causes the development of hypoglycemia, for example, liver pathology, impaired intestinal absorption of nutrients, sepsis. She may have portosystemic shunts or hereditary diseases. In this situation, the forecast will depend on: |
| Hypoglycemia associated with increased physical activity is also considered harmless, since to restore the desired level of sugar in a dog’s blood, it is usually enough just to reduce the animal’s activity and help it with medication in the first stages |
You will be able to defeat the disease if you react to it in a timely manner
Signs and symptoms
Although hypoglycemia can only be diagnosed through laboratory tests, the following symptoms may indicate a dog's glucose deficiency:
- increased salivation;
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- a sharp decrease in appetite or, conversely, gluttony;
- chills;
- indigestion.
With a critical decrease in sugar, acute hypoglycemia develops; the dog may have:
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness;
- paralysis of limbs;
- coma.
On a note! Manifestations of hypoglycemia in dogs can be expressed differently, depending on the form and level of glucose deficiency.
Symptoms of diabetes in a dog
If you notice clusters of ants there, where the pet is in the habit of relieving itself, be wary. This is one of the signs of diabetes mellitus. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- thirst: in order to remove excess glucose with urine, you need to drink as much as possible; In diabetes, thirst develops.
- increased appetite: the cells require nutrition, the dog eats more than before, the starch contained in the food is hydrolyzed to glucose, but the tissues do not absorb it;
- weight loss is explained by the fact that the body synthesizes glucose first from fat depots, then from muscle proteins;
- weakness due to tissue starvation, gait becomes unsteady;
- convulsions; loss of consciousness, diabetic coma;
- death of peripheral tissues due to starvation leads to pyoderma, inflammation of the bladder;
- the lens becomes cloudy, the dog may go blind;
Diabetes causes blindness.
The most dangerous condition in diabetes is ketoacidosis. Pathology develops when the body begins to extract glucose from fats and proteins. Under-oxidized products are formed - ketone bodies, which shift the pH of the blood to the left. The work of enzymes is blocked, toxins accumulate.
Ketoacidosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the mouth smells like acetone;
- signs of intoxication occur - diarrhea, vomiting;
- the slightest physical exertion leads to shortness of breath;
- skin deprived of nutrition dies, ulcers form, which are infested with secondary microflora, and pyoderma develops.
Pyoderma.
Additional mechanisms to combat high glucose concentrations are activated. The level of monosaccharide in the blood drops below normal, hypoglycemia develops, accompanied by symptoms of approaching death: hypothermia and falling into an unconscious state - coma. The skin emits a stench and attracts flies, the appearance of which signals imminent death.
Diagnostics
The listed symptoms are characteristic not only of hypoglycemia. To verify the presence of this condition, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests for the dog:
- clinical and biochemical analysis of blood and urine;
- ACT hormone test;
- determination of the level of bile acids in the blood.
Additionally, hardware diagnostics are performed to determine the condition of internal organs: ultrasound, radiography. A comprehensive diagnosis is necessary to accurately determine the causes of hypoglycemia.
Treatment
Therapy should be based on 2 principles:
- bringing glucose concentration to normal;
- relief of the root cause of the pathological condition.
Urgent Care
When the first signs of glucose deficiency appear, the dog needs to be helped as soon as possible to avoid complications. At home, give the puppy a 5-10% glucose solution. It can also be water diluted with sugar or honey.
In severe cases, the dog must be taken to the clinic, where it will undergo emergency infusion therapy:
- 5% glucose solution and hypertonic solution;
- Ringer Lactat + 0.45% NaCl + 5% Dextrosa;
- Glucagon, Diazepam intramuscularly;
- Methylprednisolone;
- Hydrocortison hemisuccinat.
Home care
After stabilizing the animal's condition, it is necessary to provide proper care so as not to cause a drop in glucose again. The dog needs to be fed every 3-4 hours. Create a clear schedule and diet. The pet should not feel hungry and eat on time.
Healthy foods:
- boiled veal or chicken;
- rice and other grains;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir.
If you have hypoglycemia, you should limit physical activity. Leave short walks to the toilet.
How to cut your Yorkie's hair at home? Look at the step-by-step algorithm of actions.
An overview of the lines and types of Orijen elite food for small breed dogs can be seen in this article.
Follow the link to learn about the symptoms of Malassezia in dogs and how to treat a yeast infection.
Treatment of hypoglycemia in dogs
Treatment is designed to restore the required level of glucose in the blood, and then to determine the cause that led to this condition. It is necessary to increase the sugar concentration gradually so as not to cause a coma in the animal. After removing the dog from a critical situation, the doctor must determine what caused this condition and further treatment will depend entirely on the detected problem. There is no single method of treating the disease. The doctor develops it individually.
What helps with low glucose
Glucose injections can help a dog with low blood sugar. In mild cases it is increased orally. The animal is given sweetened water (maybe with honey) or candy. Most often, this method of administering glucose is used for small breeds.
If the pet does not want to drink the solution, it must be forcibly poured into the mouth. To do this, you need to unclench your jaws and carefully introduce sweet water so that the dog does not choke. During an attack, the animal should be given a drink every five hours. Heart function must be supported with vitamin B1 and carboxylase.
Important! It is prohibited to pour sugar solution into the mouth of an unconscious pet during an attack of hypoglycemia. Such actions may result in liquid entering the respiratory system.
Care and nutrition of a sick pet
During illness, the owner must provide the animal with good care and feeding small portions of high-quality food every 3-4 hours. Short walks should be allowed, but physical activity should be excluded. If the animal is in serious condition, it is better to place it in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor. If the body temperature drops, the dog should be warmed up. Newborn puppies suffering from juvenile hypoglycemia should not be given to inexperienced owners until the attacks disappear. By 4 months of age, the disease usually resolves.
Forecast
The prognosis for hypoglycemia depends on what causes it. Positive dynamics can be expected with juvenile hypoglycemia, as well as with a decrease in sugar due to excessive physical activity and malnutrition.
If an animal is diagnosed with insulinoma, the prognosis for recovery is usually disappointing. In a malignant process, metastases are usually detected, which accelerate death. In such serious diseases as renal failure, intestinal malabsorption, sepsis, the prognosis depends on their severity, timeliness of treatment and its result.
Prevention
Hypoglycemia in dogs can be avoided by preventing the progression of the conditions that cause it:
- Feed the animal correctly and in a balanced manner, avoid starvation;
- reduce the impact of stressful situations;
- monitor the health of the liver, as well as the endocrine glands;
- Do not overload the dog with physical activities.
Hypoglycemia in dogs is not an independent disease, but a condition that indicates certain problems in the body. To avoid a critical drop in blood sugar, you need to carefully monitor your animal and regularly check its health with a veterinarian.
Video lecture by a veterinarian-therapist about the symptoms, treatment and prevention of hypoglycemia in dogs:
Share this article with your friends:
Possible causes of glypoclycemia in dogs
In general, hypoglycemia is caused by either decreased glucose production or too high a rate of glucose utilization. However, such changes in the process of assimilation or production of such a valuable resource as glucose are always caused by any significant negative changes in the functioning of the animal’s body.
This is what makes diagnosing hypoglycemia very difficult. However, dog owners should be aware that a decrease in glucose production can be caused by various diseases of the liver and endocrine system, for example:
- hypoadrenocorticism, also known as Addison's disease;
- liver circulatory abnormalities (portosystemic shunt);
- disturbance of metabolic processes in liver cells.
Read also: Emergency care for hypoglycemia
As for the too rapid absorption of glucose, it often occurs for the following reasons:
- with an excess amount of insulin, which affects metabolic processes in many tissues of the body;
- with too much consumption of sugar and sugar-containing products;
- after a long fast.
Factors that can also provoke hypoglycemia in dogs include:
- severe or permanent stress;
- violation of balanced nutrition;
- constantly low body temperature;
- a sharp transition from one dish to another;