Bronchitis is a diffuse inflammatory disease of the respiratory system, affecting the bronchial mucosa. Often the disease can be complicated by tracheobronchitis, where the trachea is additionally affected. This disease is a consequence of a complication of any disease, if proper treatment is not taken, or develops against a background of weakening of the animal’s body. Bronchitis in cats is one of the dangerous diseases and requires urgent diagnostic examination and therapeutic therapy. Symptoms, treatment, diagnosis - we will talk about this in this article.
Bronchitis in cats: symptoms and treatment
What is bronchitis in cats?
A cat of any age can get bronchitis, but weakened pets mostly get sick.
Table 1. Classification of bronchitis according to the course of the disease
| Types of bronchitis | Description |
| Spicy | A sharp inflammatory process, one of the forms of diffuse damage to the bronchial tree |
| Chronic | A progressive inflammatory disease of the respiratory system that disrupts the protective and cleansing function of the bronchi |
Table 2. Classification of bronchitis by damage to the bronchi
| Types of bronchitis | Description |
| Macrobronchitis | The inflammatory process spreads in the large bronchi |
| Microbronchitis | Inflammation of the small bronchi |
| Diffuse | Inflammation of the entire bronchial tree |
Differences between healthy bronchi (right view) and inflamed bronchi with bronchitis (left view)
Table 3. Classification of bronchitis by type of inflammation
| Types of bronchitis | Description |
| Catarrhal | Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory system |
| Fibrinous | Inflammation with a high content of fibrin in the bronchial secretion - fibrous protein or blood |
| Purulent | Inflammatory changes in the bronchial tree with discharge of purulent secretions |
| Putrefactive | A form of chronic bronchial inflammation, which is accompanied by the development of putrefactive flora |
| Hemorrhagic | Inflammation with bleeding, decreased blood clotting |
Table 4. Classification of bronchitis by origin
| Types of bronchitis | Description |
| Primary | Inflammation of the bronchi, spreading to the entire bronchial tree |
| Secondary | Inflammation complicating another respiratory disease |
If your cat develops gurgling sounds in the chest area, difficulty breathing with wheezing, or coughing, take her to a veterinary clinic immediately.
Symptoms of bronchitis in cats
The pathogenesis of the disease lies in the fact that the influence of an irritating factor is accompanied by a disruption of the neurohumoral mechanism due to the effect on the receptors of the mucous membrane. Small blood vessels reflexively contract, which is accompanied by drying out of the mucous epithelium.
The body responds to this process by producing exudate, which contains fibrin, epithelial cells, blood and various microorganisms. Inflammation leads to swelling of the bronchial mucosa, and their lumen decreases. The pathological process leads to disruption of gas exchange in the animal.
Diseases of the upper respiratory tract in acute form do not go unnoticed by the owner and household members. Bronchitis in furry pets is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Cough is one of the main clinical manifestations of bronchitis. At the beginning of the development of the pathological process, the owner observes a dry cough.
As exudate accumulates in the lumen of the bronchi, the cough becomes wet and painful.
- Sputum is released when the dry form of cough changes to wet.
- Rapid breathing. Normally, a cat makes 20 - 30 breathing movements per minute. With bronchitis, breathing increases to 60 - 70.
- Shortness of breath . Difficulty breathing occurs due to a serious violation of gas exchange function. A cat, lacking oxygen, stretches its neck and head forward, spreading its forelimbs wide to increase ventilation.
- Blue color of mucous membranes.
- An increase in body temperature is associated with the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Discharge from the nasal cavity and eyes.
- If the animal has severe coughing attacks, the owner may experience bouts of vomiting .
- Depressed state . The pet moves little and sleeps a lot.
- Loss of appetite or complete refusal to feed.
In the chronic form of the disease, the clinical signs are subtle and may go unnoticed by the owner for a long time. The cough is usually rare and occurs after swimming, stress, or hypothermia. In advanced cases, gurgling sounds and wheezing in the chest may be heard. The temperature, as a rule, is within the physiological norm. A cat may have such symptoms for 1 to 2 months.
Mechanism of disease development
The disease originates from damage to the bronchial mucosa, producing an irritating and inflammatory effect with the release of fluid, which begins to accumulate in the tissues of the respiratory system. As a result, the mucous membrane succumbs to a strong irritant effect and coughing, swelling appears, and exudate provokes shortness of breath.
What other diseases can be diagnosed when a cat coughs ? Read about this in our article.
During chronic bronchitis, the mucous membrane is completely exposed to the harmful effects of microbes, and along with it, inflammation of the bronchial wall occurs. As a result, muscle fibers are replaced by connective tissue cells, causing the bronchi to lose elasticity and contractile function.
What is feline bronchitis and what should it not be confused with?
The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the bronchial mucosa and copious secretion of fluid that accumulates in the lung tissue. As a result of irritation of the respiratory tract, the patient develops a cough and shortness of breath.
Advanced inflammation becomes chronic. The damaged mucosa becomes maximally vulnerable to microbes, and muscle fibers are gradually replaced by connective tissue. The bronchi lose their elasticity and cannot cope with their functions (cleansing, humidifying and warming the air).
The resulting symptoms are similar to the following pathologies:
- pulmonary parasitosis;
- pneumonia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system and pleural cavity;
- bronchial asthma and allergies;
- foreign object stuck in the upper respiratory tract.
For this reason, before starting treatment, it is necessary to ensure that the intended diagnosis is correct. To do this you will have to go to a veterinary clinic.
Causes
The main causes of bronchitis in cats are:
Non-infectious:
- Hypothermia of the animal (being in drafts, washing in too cool water, excessive exposure to rain or sleet, absorption of frosty or cold air, being on a chilled surface - ground, concrete, tiles).
Hypothermia can cause bronchitis
- Vitamin deficiency - a lack of essential vitamins weakens the immune system, resulting in illness.
- Inhalation of vapors of hazardous chemicals (tobacco smoke, household chemicals).
- Allergic reaction (dust, pollen from indoor plants, medications).
Infectious in nature: damage to the body by parasites (toxocariasis, hookworm), fungi, bacteria, viruses. Inflammation of the bronchi is provoked by parainfluenza viruses, rhinotracheitis, and adenoviruses. A large number of tissues become infected, so diagnostics are indispensable.
Path of infection of a cat with toxocariasis
What do you need to know? If your cat does not have proper nutrition, it may develop bronchitis. A balanced diet and consumption of essential vitamins strengthens the cat’s immune system and allows the body to fight infections.
Causes of bronchitis in cats
Responsible breeders and veterinary specialists believe that before studying the symptoms of the disease, the owner should have an understanding of the reasons for the development of bronchitis in a cat. It is generally accepted that the disease can be infectious in nature and not be associated with a microbial cause.
Infectious
Toxocar
The causative agent of the infectious form of the disease is numerous microorganisms: bacteria, including pneumococci, viruses, fungi, rickettsia. Pathological agents can cause both primary and secondary bronchitis.
Often the owner is faced with inflammation of the bronchi due to infectious diseases such as parainfluenza, rhinotracheitis, and adenoviral infection. These pathologies lead to the development of a secondary form of bronchitis.
Experts also include invasions as the causes of the infectious form of the disease. Some parasites, for example, Toxocara, hookworm, when parasitizing in the upper respiratory tract, cause inflammatory processes in the mucous and submucous membranes.
Non-infectious
The group of non-infectious causes leading to the development of bronchitis includes the following factors.
| Non-infectious causes of bronchitis | Rationale |
| Allergic substances | Numerous allergens - plant pollen, household dust, pesticides used in everyday life and agriculture, medications - are a common cause of the development of allergic inflammation of the bronchial tree. |
| Aerogenic substances | They have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. Most often, cats suffer from household aerosols, perfumes, paints, solvents, and toxic emissions. |
| Smoke, including cigarettes | Smoke and being kept in a smoky room often leads to the development of chronic bronchitis due to constant irritation of the bronchi. |
| Heart diseases | Diseases of the cardiovascular system, characterized by congestion in the pulmonary circulation, often lead to chronic bronchitis, especially in elderly animals. |
| Hypothermia | Keeping your pet in cold, damp, drafty rooms is a common cause of the disease. The risk group usually includes homeless animals, as well as cats with free access to the street. |
Factors that provoke diseases of the upper respiratory tract include stress and errors in feeding. Stressful situations aggravate the effect of other negative factors and contribute to a decrease in the body's defense mechanisms.
Inadequate feeding is important in the development of bronchitis. A deficiency in the diet of vitamins, minerals, trace elements, and amino acids reduces the pet’s immunity. For weakened and sick cats, this factor is often decisive in the etiology of bronchitis.
We recommend reading about pneumonia in cats. You will learn about factors contributing to the disease, classification of pneumonia, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods. And here is more information about the symptoms and treatment of distemper in cats.
Symptoms
Early detection of signs of bronchitis will prevent the spread of the disease, which can spread to the lungs with serious consequences, for example, the pet will get pneumonia.
Common symptoms of the disease:
- Cough, which can be dry or immediately with sputum, accompanied by a whistling sound. It is very difficult to detect the presence of a cough because in cats it sounds like sneezing or gagging.
- Hypoxia, which occurs with severe coughing and lack of oxygen. Often accompanied by blue discoloration of the gums and oral mucosa.
- Vomiting. They can be caused by an excessively strong cough.
- Rhinitis, conjunctivitis, enlarged lymph nodes.
- Loss of appetite occurs during intoxication of the body.
- Lethargic, weakened state of the pet.
- Fever and chills.
- Disorder of the digestive system due to viral infection.
Bronchitis can lead to pneumonia
Treatment of bronchitis in cats
Therapeutic measures for any form of bronchitis should be determined only by a veterinarian, taking into account the cause of the disease and the condition of the pet.
Owner actions
If signs of bronchitis are detected, the owner must first provide the sick animal with a warm, draft-free room. The pet needs peace and absence of stressful situations. It is important to completely stop your cat's access to the street, even in the warm season.
Licorice root syrup
The owner should provide the pet with plenty of warm drinks. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are effective for bronchitis: chamomile, sage, linden, plantain, coltsfoot. Excellent results are achieved by using licorice root syrup.
On the recommendation of a doctor, the animal can be given expectorants and bronchial dilators, for example, Lazolvan, Flavomed, Acetylcysteine, Mucaltin, plantain syrup. In order to dilute the exudate in the bronchial lumen, enzyme preparations can be prescribed: Trypsin, Chymotrypsin.
If a cat has signs of heart failure, heart medications are prescribed, for example, Adoniside, tincture of lily of the valley.
To strengthen the immune system of weakened animals, immunomodulators are used, for example, Gamavit, Gamapren, Anandin. The use of vitamins – retinol (vitamin A) and ascorbic acid – has a good effect.
Immunomodulators
Medicines in the complex treatment of bronchial inflammation are complemented by thermal physiotherapy: diathermy, UHF therapy, Sollux lamp, IR heating.
A sick animal should receive a nutritious diet rich in proteins, vitamins and minerals. Your pet should be fed warm food.
Treatment with antibiotics
When bronchitis is complicated by pathogenic microorganisms, the veterinarian decides to include antibiotics in therapy.
The best option would be to select antibacterial agents based on the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora in cultures obtained from bronchial washings.
In veterinary practice, penicillin antibiotics, cephalosporins, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones are used to treat diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
Of the penicillin series, ampicillin and amoxiclav give good results. Among the drugs of the cephalosporin group, Cefazolin and Cephalexin are effective. Macrolides, for example, Sumamed, block the proliferation of bacteria. Among the fluoroquinolones, Ofloxacin is used.
Antibiotics
In addition to antibiotics, sulfonamide drugs are also successfully used in the treatment of bronchitis in cats: Norsulfazole, Sulfadimezin, Sulfalen, Sulfapyridazine.
We recommend reading about peritonitis in cats. You will learn about the types of peritonitis, routes of infection, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention. And here is more information about how to treat urolithiasis in cats.
Prevention
In order to prevent your pet from getting sick, you need to regularly carry out preventive work, which is actually not as difficult as it seems. You can avoid many diseases, including bronchitis, by following simple rules:
- make sure that the cat does not become overcooled;
- eliminate drafts;
- make your pet a warm bed or buy houses so that the cat does not sleep on the cold floor.
- place the sleeping area away from doors and windows, which can be sources of drafts;
- feed your pet a balanced diet enriched with the necessary vitamin and mineral complex;
How to feed a cat natural food?
- give water only at room temperature;
- Make sure that your pet does not have access to household chemicals and do not spray aerosols harmful to your pet in the room;
- carry out weekly cleaning with a damp cloth;
- do not bathe your cat during the cold season;
- Avoid keeping your pet out in the rain or wet snow.
What do you need to know? The most common respiratory disease in cats is bronchitis. If you notice symptoms indicating the presence of a disease in your pet, immediately show it to a specialist in order to begin treatment on time.
The cat should have a specially designated place, located in a warm, dry place without drafts, preferably soft bedding or a house
Prevention of bronchitis in cats
In order to prevent upper respiratory tract diseases in pets, veterinary experts recommend that owners adhere to the following rules:
- keep animals in a warm, not damp, draft-free room;
- do not allow the cat to stay on the cold floor or tiles;
- arrange a sun lounger, a house or a warm sleeping place for your pet to sleep and relax;
- limit access to the street during cold and damp seasons;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning of the premises;
- do not keep the cat in a smoky or smoky room;
- do not use aggressive chemicals, perfumes, or household chemicals in the presence of an animal;
- Give your cat water at room temperature;
- do not bathe the animal in the cold season;
- Boost immunity with a nutritious diet and vitamin supplements.
Bronchitis in cats is one of the common respiratory diseases. Despite the apparent frivolity, the disease can have serious consequences for a sick pet. In this regard, at the slightest symptoms of the disease, the cat should be shown to a veterinarian and strictly follow the specialist’s instructions. Self-medication of bronchitis is unacceptable.
Similar articles
- Pneumonia in cats: symptoms of pneumonia, how...
Dangerous bronchitis in cats: signs of presence, treatment and prevention. What causes and how to treat anemia in cats. Read more - Peritonitis in cats (viral, infectious, dry...)
Dangerous bronchitis in cats: signs of presence, treatment and prevention. What causes and how to treat anemia in cats. Read more
- Treatment of otitis media in cats: symptoms of purulent and fungal...
Dangerous bronchitis in cats: signs of presence, treatment and prevention. What causes and how to treat anemia in cats. Read more
- Gastritis in cats is uremic, chronic, acute...
Dangerous bronchitis in cats: signs of presence, treatment and prevention. What causes and how to treat anemia in cats. Read more
- Endometritis in cats: symptoms, treatment, actions after...
Dangerous bronchitis in cats: signs of presence, treatment and prevention. What causes and how to treat anemia in cats. Read more
Why is bronchitis dangerous?
If the disease passes in a latent form and is not diagnosed in time, then it is very dangerous and can threaten the life of the pet. Often, chronic bronchitis can trigger asthma in a cat. If the inflammatory process of the respiratory mucosa is not treated for a long period of time, then bronchoconstriction and then asthma develop. The danger is that inflammation easily spreads to the lungs, leading to pneumonia, a more dangerous and difficult-to-treat disease. Therefore, if the slightest symptoms of bronchitis are detected, it is necessary to show the cat to a veterinarian and begin therapy as quickly as possible.
Diagnosis of bronchitis in cats
At the initial stage of diagnosis, a veterinarian, already at the stage of clinical examination, history taking, auscultation and percussion of the chest, may suspect bronchitis in a furry patient. Veterinary medicine has modern diagnostic methods that allow you to correctly diagnose:
- General and biochemical blood test. An increase in neutrophils and leukocytes is an indirect indicator of respiratory disease.
- Scatological analysis . A stool examination can identify an invasive form of bronchitis when pulmonary parasites are detected in the feces.
- Chest X-ray . With bronchitis, your veterinarian may detect signs of diffuse inflammation.
X-ray of a cat with bronchitis
- Bronchoscopy allows you to see a more accurate picture of the inflammatory process in an animal. It is performed under general anesthesia.
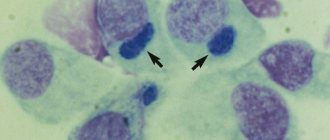
- Bronchial washings are used for subsequent cytological examination, as well as for seeding pathogenic microorganisms. The procedure is performed during bronchoscopy.
Diseases of the respiratory system of domestic animals are characterized by similar clinical signs and require a differential diagnosis. Bronchitis should be distinguished from the following diseases with similar symptoms:
- heart failure;
- pulmonary invasions;
- entry into the upper tract of a foreign body;
- various forms of pneumonia (infectious, non-infectious);
- allergic reaction;
- pathologies of the pleural space;
- asthma.
To make a differential diagnosis, the veterinarian may prescribe echocardiography, parasitological studies, and allergy tests.
The danger posed by chronic bronchitis
Unclear symptoms of the chronic form of the disease often lead to the fact that the pathological process occurs in a latent form and leads to negative consequences for the cat’s health.
Chronic bronchitis often provokes the development of asthma. As a result of prolonged inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi (bronchoconstriction) often develops, which leads to asthma.
Therefore, it is important for the owner to carefully monitor the slightest changes in the animal’s health status and immediately seek qualified help.
To learn how to make your own spacer for inhalation for bronchitis or asthma in a cat, watch this video:
What to do if cats have bronchitis?
Bronchitis is a serious inflammatory process that affects the bronchial mucosa. At first glance, it seems that this is just a mild cold, but in fact it is not. Everything is much more serious. Symptoms and treatment for bronchitis in cats and dogs are similar.
During the course of the disease, all body functions are disrupted and the immune system is weakened. This contributes to the emergence of other serious diseases. Bronchitis in cats very quickly becomes chronic, so it is important to begin a course of treatment as quickly as possible.
More details about the disease are described in the article.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Prevention
Causes
Types of bronchitis in cats are divided into viral, bacterial, chemical and mechanical. What are the most common causes of bronchitis that doctors determine are the most common, we will consider below:
- Drinking cold water and hypothermia.
- Particles of pesticides and household chemicals entering the bronchi.
- Damage to the body by helminthic infestations.
- Viral, fungal and bacterial infections.
- Consequences after allergies or asthma.
- Hypovitaminosis and vitamin deficiency, as well as reduced immunity.
- Strong odors of perfumes, fresheners and cosmetics.
- Complication due to cardiovascular diseases.
Causes
Bronchitis is a serious inflammatory process that affects the bronchial mucosa. At first glance, it seems that this is just a mild cold, but in fact it is not. Everything is much more serious. Symptoms and treatment for bronchitis in cats and dogs are similar. During the course of the disease, all body functions are disrupted and the immune system is weakened.
Note. Smoking in their presence may also be a cause of the disease in cats. Limit your cat's exposure to tobacco smoke.
Veterinarians distinguish between infectious and non-infectious bronchitis, and its course is defined as acute and chronic. In both cases, the symptoms of bronchitis in cats are almost the same; we will describe which ones further:
- Dry cough with whistling and heavy breathing (shortness of breath).
- Blue color of mucous membranes.
- Depressed state and apathy.
- Decreased appetite or complete refusal of food.
- Nasal congestion, runny nose.
- During the first 2-3 days, there is a slight increase in body temperature.
- With advanced bronchitis, squelching appears in the bronchi. Cough with sputum and profuse nasal discharge. And the temperature may drop to normal. If the cat has severe coughing attacks, then foamy vomiting may occur.
We suggest you read: How to breed oysters at home. Oyster farming as a business. Step-by-step instruction. From juveniles to commercial oysters
In the case of bronchitis caused by allergic reactions, the course of the disease is possible without fever. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should not hope that the cat just sneezed and did not get sick. It is better to consult a doctor to rule out disease and inflammation in the bronchi.
Diagnosis of bronchitis is made using a general and/or biochemical blood test, bronchial washings, examination of cat feces and a chest x-ray. For a more accurate study of the disease, bronchoscopy may be prescribed, which helps to establish an accurate picture of the course of the inflammatory process.
Treatment methods, a list of necessary drugs and their dosage are determined by the doctor, based on test results and the physiological characteristics of the animal. Next, we will consider ways to treat cats for bronchitis and its consequences.
- Providing your cat with a balanced diet; food rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements.
- Expectorants; Ambroxol, Bromhexine, herbal decoctions of violet, licorice root or coltsfoot.
- Broad spectrum antibiotics depending on the type of bronchitis; penicillin series (Ampicillin, Amoxiclav). Cephalosporin group (Ceftriaxone, Cephalexin). Macrolides (Sumamed).
- Anti-helminth medications (in case of bronchitis due to worms); Drontal, Milbemax, Kanikvantel and others.
- If the bronchitis is of an allergic nature, then the cat is prescribed glucocorticoids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone acetate) and antihistamines (Suprastin and others).
- In case of heart failure it is used; Adonizide, tincture of lily of the valley.
- Drugs that dilate the bronchi and relieve spasms; Euphilin.
- If bronchitis is allergic, then it is necessary to eliminate all harmful substances that can aggravate the course of the disease.
- For infectious bronchitis, immunostimulating drugs are prescribed; Glycopene, Roncoleukin.
- Immunomodulators are also prescribed to support immunity; Gamavit, Anandin.
- Nasal drops for discharge from the nose; Isofra, Maxidin.
The use of any drug is carried out only with the permission of a veterinarian. Improper self-medication can lead to irreversible consequences.