Leptospirosis in cats is a rare but very serious disease. It is a bacterial infection caused by microorganisms of the genus Leptospira and affects most of the internal organs of the animal (liver, kidneys, lungs, etc.). Without timely treatment, leptospirosis leads to severe consequences, including death.
See this article:
Causes of leptospirosis Symptoms of bacterial infection Stages of the disease: how does leptospirosis develop in cats? Diagnosis of the disease How is leptospirosis treated? Features of caring for a cat with leptospirosis Are cats vaccinated against leptospirosis? Is leptospirosis transmitted from cats to humans?
Causes of leptospirosis
The causative agent of the infection is bacteria of the genus Leptospira. They enter the animal’s body through damaged soft tissues or mucous membranes. Leptospira survive for a long time in stagnant water, as well as in other warm and humid environments.
Most often, cats become infected with leptospirosis if they come into contact with dirty standing water or other animals that carry the bacteria (for example, rodents). Most infestations occur in spring and autumn.
Leptospira is transmitted through the placenta, secretions from the lungs or genitals, or insect bites (for example, ticks). Infection often occurs after animals come into contact with the urine or feces of infected pets.
After infection, the animal remains a carrier of the pathogen for up to 3 months.
Pathogen and methods of infection
The disease is caused by the bacterium leptospira, which is a long microscopic worm with a spiral-twisted body. All varieties of the parasite are characterized by poor resistance to direct sunlight, temperature fluctuations, humidity fluctuations, and disinfectant solutions. However, viral cells in an aquatic environment can survive for up to 1 month, and soil saturated with moisture ensures their vital activity for up to 3 months.
Penetration of Leptospira microorganisms also occurs through damaged mucous membranes or skin. It should be noted that this method of transmission seems unlikely. Cats very rarely drink water from untreated reservoirs. More often, experts detect infection through contact with the urine of dogs or cats living in the same area.
Scientists have been conducting research on the distribution of microorganisms in the urine of pets for several decades in a row. It was found that almost 85% of stray animals that were subsequently placed in shelters excreted dangerous bacteria.
Wild representatives of the cat family are also susceptible to infection, excreting the pathogen in urine.
Symptoms of a bacterial infection
Pathogenic microorganisms (leptospira) enter the circulatory system through damaged soft tissue. Gradually they spread throughout the body, affecting the main systems: nervous, visual and reproductive, as well as the cat’s brain.
The severity of the infectious disease depends on the general condition of the body. If the animal’s immunity is weakened, then the likelihood of developing severe leptospirosis and complications increases significantly. At the same time, the risk group includes small kittens up to 5-6 months and pregnant cats.
On average, the incubation period lasts from 3 to 10 days. The main signs of leptospirosis:
- increase in body temperature (normal body temperature in adult cats ranges from +38 to +39.5 °C),
- a shaky and uncertain gait, as well as muscle stiffness in the pet’s hind legs, which makes it difficult for him to make any movements,
- complete lack of appetite in the animal and loss of body weight,
- dyspeptic disorders (most often there is profuse diarrhea with blood clots, vomiting is possible),
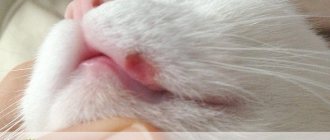
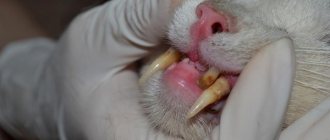
- icteric tint of the mucous membranes and conjunctiva of the eye,
- apathetic and lethargic state,
- dyspnea,
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The first thing many owners pay attention to is the deterioration of the pet’s general condition. The cat moves less and refuses to eat. Many animals have difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). Without timely treatment, the pet begins to experience repeated bouts of vomiting, with the vomit consisting of bile and gastric juice.
Penetrating into the body, Leptospira affects many internal organs, so the clinical picture of the disease is extensive. If even 1-2 signs of infection are detected, you should immediately contact a veterinarian in Moscow and undergo an examination. This is the only way you can find out if your cat has leptospirosis and begin treatment for the disease.
Stages of the disease: how does leptospirosis develop in cats?
At the first stage, pathogenic microorganisms (leptospira) rapidly multiply in the blood and parenchymal organs: liver, spleen, kidneys, as well as the thyroid and pancreas. At the same time, the permeability of blood vessels sharply increases. Detection of antibodies is possible 5-7 days after a cat is infected with leptospirosis. Signs characteristic of the first stage include an apathetic state, refusal to eat, and increased body temperature.
At the second stage, pathogenic microorganisms (leptospira) disintegrate and their toxins are released, which impair the functions of the liver and kidneys.
This leads to the development of hepatorenal syndrome - acute renal failure (ARF) and severe liver damage. A characteristic condition for the second stage of leptospirosis is capillary toxicosis. It causes the capillary walls to become very brittle and brittle. Numerous hemorrhages occur, and against their background - necrosis of internal organs.
Diagnosis of the disease
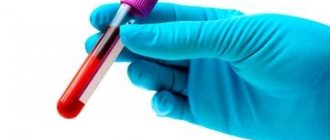
Only a veterinarian can make a diagnosis after a preliminary examination. Leptospirosis has specific symptoms, but diagnosis in any case requires laboratory tests. They are necessary to determine the form and severity of the infectious disease, as well as to prepare a treatment plan.
Methods used to diagnose leptospirosis in cats:
- blood and urine tests (biochemical, general),
- microagglutination (MAT) to detect antibodies to the pathogen,
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR),
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA), etc.
The treatment program for leptospirosis in a cat is drawn up taking into account the stage and form of the disease, as well as its general condition.
How to treat
Leptospirosis in cats is highly treatable if the animal is brought to the veterinary clinic on time. Self-medication is prohibited! Leptospirosis is dangerous for humans, so you should not conduct any experiments or attempts to cure a cat without the participation of a specialist!
The most important link in therapy is the use of antibiotics!
- Antibiotics of first choice to stop the proliferation of Leptospira in the case of a cat’s severe condition (the first three days) are penicillin and its derivatives: amoxicillin (preferably if administered intravenously) 20 mg/kg twice a day at regular intervals or ampicillin 20 mg/kg every 8 hours
- If an animal is allergic to penicillin antibiotics, it is allowed to use chloramphenicol (20 mg/kg subcutaneously) or streptomycin (20 mg/kg intramuscularly) once a day for 3 days.
- The second stage of antibiotic therapy (destruction of leptospira in the body) is tetracycline antibiotics, in particular doxycycline - 5 mg/kg orally. This stage begins only after the animal begins to eat on its own, vomiting goes away and the absence of liver pathologies is confirmed, because Doxycycline has some hepatotoxicity in cats. It is best used as a hyclate salt rather than a monohydrate (drugs: Ronaxan, Paudox or Doxatib).
- If there was no vomiting or signs of severe intoxication when visiting the veterinary clinic, then therapy can be started immediately with doxycycline. Also, this drug is indicated for cats that are healthy in appearance and that excrete the pathogen in the urine into the external environment, and this has been confirmed in the laboratory.
Symptomatic therapy
Mainly aimed at relieving signs of liver and kidney (especially) failure. Therapeutic regimens are drawn up after a blood test and assessment of the animal’s general condition.
Vitamin preparations and immunomodulators
They are administered at the discretion of the treating veterinarian. Considering the specific course of the disease in cats, leptospirosis is either quickly cured with a satisfactory recovery rate, or progresses rapidly with a fatal outcome. The expediency of use is not always justified.
How is leptospirosis treated?
First, and most importantly, do not self-medicate! This is a dangerous infectious disease, which without contacting a reliable veterinary clinic in Moscow can lead to serious and often irreversible consequences for the health of the animal.
If the disease was detected at the first stage, then treatment is aimed at combating pathogenic microorganisms (leptospira) and preventing their further reproduction in the cat’s body. In cases where the infection is detected at a later stage, the main goal of therapy is to remove toxins and maintain the functions of damaged internal organs (liver, kidneys, spleen, etc.).
Treatment methods for leptospirosis:
- Immunotherapy . It involves the use of leptospirosis serum, which strengthens the immune system. It gives excellent results, but only at the first stage of the disease, while there is no serious damage to internal organs.
- Antibiotics . Leptospira are cellular pathological microorganisms, so antibiotics are used to eliminate them. The greatest effectiveness is achieved by combining several drugs at once, but when prescribing them it is important to take into account all contraindications.
- Infusion therapy . Most often, infusion saline solutions with a high concentration of potassium ions are used. Additionally, hemodez with glucose is used to eliminate signs of dehydration and restore the cat’s general well-being.
- Osmotic diuretics . They are used in the second stage of the disease, when renal failure develops. If the process intensifies, the veterinarian may prescribe anabolic hormones.
- B vitamins . Along with them, folic acid (vitamin B9) and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) are prescribed. They restore liver function and prevent the development of liver failure.
- Symptomatic therapy . It is aimed at eliminating the main signs of leptospirosis, which include vomiting, dehydration, numerous hemorrhages, etc. Additionally, medications are prescribed that strengthen the pet’s body.
On average, the course of treatment lasts from 1 to 2 months. During this period, all veterinarian recommendations must be followed. Strictly follow the regimen of taking medications, especially antibiotics. If the cat's condition worsens, immediately contact the veterinary clinic for a secondary examination!
Treatment of the disease
It should be noted right away that cats, unlike dogs, are not specifically vaccinated against leptospirosis. Therefore, try to protect your mustachioed friend from eating rodent meat, and also try to ensure that he does not drink water from puddles or stagnant bodies of water, and does not come into contact with stray brothers. Pets are practically not afraid of such a transmitted pathology as leptospirosis.
At the first signs of infection, protect the cat from contact with members of your family, especially for older people and children. In the near future, you will have to carefully monitor hygiene and sanitize your home much more often. You should use disposable gloves to remove your pet's waste products, and treat the tray itself with disinfectants.
The basis of medical therapy for an animal is a course of antibiotics. Other pharmaceuticals are added to them, depending on the symptoms that appear. The antimicrobial strategy includes two stages:
- Urgently stop the process of reproduction of microorganisms in the cat’s blood fluid, as this significantly reduces the risk of severe damage to internal organs. A vaccine made from Ampicillin or Amoxicillin is ideal for these purposes. It is preferable to administer the medicine intravenously, especially in advanced cases.
- After the animal’s condition returns to normal, you should be concerned about removing the infection from the internal organs. Veterinarians advise using Doxycycline for this. It cannot be administered intravenously, as this can lead the cat to shock, only in the form of a powder or suspension. Unfortunately, this effective remedy cannot be used if the cat has a diseased liver.
It is important to understand that after undergoing treatment, the animal’s body will be weakened, so it will need peace and quiet, as well as a balanced diet. In addition, in particularly difficult cases, the veterinarian may prescribe the cat a course of vitamins and a drip with glucose solution
Finally, I would like to say that leptospirosis is a terrible disease that can be transmitted from cats to humans. The best prevention against it is timely vaccination against leptospirosis. Such a vaccine will protect the pet from the risk of infection with leptospira for the next 12 months, which means that the owner will have no reason to worry about the health of his mustachioed fidget.
Is leptospirosis transmitted from cats to humans?
Yes, leptospirosis is contagious to humans. About 16 leptospira are now known, which are dangerous for both humans and domestic animals. Leptospirosis manifests itself differently in people, but the main symptoms of infection include muscle pain, general weakness and dyspeptic disorders (profuse diarrhea). All this requires immediate consultation with a doctor to avoid the development of inflammatory processes, acute renal failure (ARF) and other consequences.
Leptospirosis is a dangerous bacterial infection. The sooner you seek help from a veterinarian in Moscow, the higher the likelihood that the cat will return to a healthy life and avoid serious consequences for the body.