What is fungus in cats?
Mycosis in cats is a type of disease of the skin and internal organs, which is caused by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms on the body of animals. All cats are susceptible to fungal infections. Living conditions and quality of food do not greatly affect the possibility of infection.
Most often, animals become infected from each other through contact. Although domestic cats that never leave the premises can encounter fungal infection pathogens found on the owners’ outdoor shoes and clothes. The fungus is constantly present on cat fur, but in a healthy animal the pathogenic fungus does not develop and does not lead to the development of infection.
High indoor humidity can contribute to the growth of fungus in cats.
is most often found in kittens and elderly animals, since their immune system does not function fully.
The danger of cat fungus for humans
Fungal infections in cats can be easily transmitted to people if precautions are not taken. Fungal spores easily enter the human body from the fur of an infected animal. And this happens not only from tactile contact, pathogenic fungi are spread throughout the room with the air when scratching.
In addition to the danger of direct contact with an infected animal, human infection can occur through soil, sand or objects on which there may be a source of infection. It is also possible to become infected from a healthy cat, without the presence of pronounced symptoms due to the stable immunity of the animal, which is only a carrier of the fungus.
Fungus prevention
First of all, to prevent the onset of the disease, preventive vaccinations should be used, which are carried out once a year. Also, to maintain the health of the animal, it is important to provide it with adequate nutrition, sufficient physical activity and high-quality skin care with regular washing at least once every 3 months and no more than once every 2 months, unless otherwise indicated.
Since any cat can become infected with a fungus, even one living only in an apartment, it would be a good idea to regularly examine the animal’s body to detect the beginning of the formation of bald spots and weeping wounds. Your cat's ears should be cleaned at least once every 10 days.
Organs susceptible to fungal infection
Fungus in cats can affect various organs, but there are general symptoms of fungus in cats , characteristic of all types of fungal infections:
- Coughing;
- depressed state;
- lack of appetite;
- prolonged scratching of a certain area;
- head shaking with ears back;
- dull coat and flaky skin.
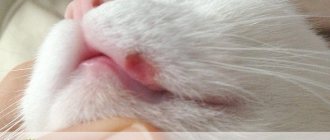
Skin fungus
The skin is most susceptible to infection, including fungi, since the skin is the body's primary protective barrier.
Infection with the fungus is possible through the air, orally, or through wounds. The cat's skin becomes covered with scabs, and constantly causes the desire to itch. A characteristic symptom of a skin infection is a change in the structure of the coat: the hairs become brittle and easily break off at the base.
Ringworm in cats can appear after contact with vectors of infection, which are rodents and other animals. It is also possible to become infected through contact with things that have spores on them. The disease may not appear immediately due to the long incubation period. It is characterized by different areas of skin baldness depending on the type of lichen. The skin in areas of baldness becomes red and inflamed.
Ear fungus
Ear fungus is considered one of the most famous infections, which, if not properly treated, can become chronic. The causes of the disease may be:
- Allergic reactions;
- various infectious diseases;
- unbalanced diet;
- congenital and hereditary pathologies;
- injuries and contact with the ear canals.
Symptoms of ear fungus include the following:
- An unpleasant pungent odor and a dark coating on the affected areas;
- constant scratching of the affected area;
- leakage of serous fluid from the ears;
- redness, swelling and pain in the ears;
- irritated or apathetic behavior of the animal.
Claw fungus
The main cause of infection with claw fungus is a paw injury coupled with a weakened animal’s immune system.
Symptoms of the disease may include licking and biting of the paw due to itching in the infected area, discoloration of the claw and redness of the area around it, as well as pain when moving. Often the fungus is not limited to one or a few claws; in advanced forms of the disease, the infection can affect the entire paw.
Fungal eye diseases
Cats often have fungal eye diseases, which are divided into infections that affect the mucous membranes of the eyelids and the eyeball itself. The main cause of the disease is damage to the eye organ and the entry of a foreign body with fungal spores.
The main symptoms of an eye infection include redness and swelling of the eyelids, and excessive lacrimation. In advanced cases, eyelashes may fall out, the area around the eyes will become bald, and purulent discharge may occur.
Main types of fungal infections
All fungal diseases in cats are divided into 2 large groups.
- Parasitic on mucous membranes and skin.
- Systemic – affecting systems and organs. Fungal damage to the central nervous system may even occur. They are extremely rare in cats. More often they affect the body of dogs and can take their lives.
In this condition, the skin of a sick cat turns red, areas of baldness and scratching appear on it. Treatment of the disease should begin immediately after its detection.
Diagnostics
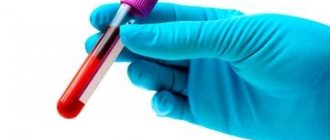
The diagnosis can be determined by the pronounced symptoms of the disease, but for a clearer determination it is recommended to show the animal to a veterinarian. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to take a scraping of the biomaterial for further seeding on nutrient media and subsequent microscopy. In addition, it is possible to determine a fungal infection by illuminating the infected area with a specialized ultraviolet lamp, which illuminates colonies of microorganisms in emerald color.
In addition to the basic research methods, a blood test, examination of smears from the mucous membranes, and microscopy of wool in an alkaline solution to identify fungal spores can be performed.
Diagnostics and therapy
Treatment of fungus in cats is a very complex and rather lengthy process. If you notice characteristic signs of the disease in your pet, you need to show your pet to a veterinarian. The veterinarian will take a medical history, perform a physical examination, and also prescribe a number of laboratory tests to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the causative agent.
Identifying the cause of the pathological process is also important, as it allows you to accurately adjust the course of treatment.
The owner’s task is to strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations, which makes it possible to successfully fight the pathology without causing serious complications.
Damage to the skin by fungal pathogenic microorganisms is diagnosed using a special Wood's lamp. This lamp makes it possible to establish microsporia. Next, scraping is carried out from the affected areas with further cultivation of the pathogenic microorganism on nutrient media. This allows you to determine the type of pathogen and select adequate treatment. A general blood test, biochemical blood test, and microscopy of selected wool samples are also carried out.
Of no small importance in making a diagnosis is a skin biopsy, smears from the mucous membranes and prints from the affected areas. Manifestations of pathology and determination of treatment tactics are closely intertwined. Depending on the type of pathogenic microorganism, the degree of damage and the general well-being of the cat, a qualified veterinarian carries out therapeutic measures.
Self-medication in this case is contraindicated, as it can cause dangerous complications. To treat fungus in cats, special shampoos are used, as well as ointments and powders applied to the affected areas. It is recommended to administer antihistamines if the animal experiences severe itching.
Scratching can be prevented by using a special immobilizing collar, placed on the sick animal in the form of a funnel. This device also helps prevent medications from being licked off. At first, the cat may show dissatisfaction with the special collar, but over time it gets used to it.
For systemic pathologies caused by fungal infection, antifungal agents are used in the form of injections and tablets. Treatment of concomitant bacterial infection is carried out using antibiotics, selected strictly individually, taking into account the characteristics of the animal’s body. If therapy does not produce positive results, the specialist changes the treatment regimen. Fungal pathologies take a long time and are difficult to treat, so the owner needs to be patient.
Treatment of fungus at home
Treatment of fungus in cats depends on the type of infection, the size of the affected area, and the general condition of the animal’s body.
General treatment methods include:
- the use of antifungal shampoos;
- applying topical antifungal agents to infected areas;
- taking antihistamines if there is itching;
- use of a specialized collar to limit scratching;
- oral or injection antifungal medications.
When treating fungus in cats at home, it is necessary to ensure that the animal does not lick recently lubricated areas or scratch them with its paws.
How to treat fungus in a cat at home
| Type of disease | Type of medicine | Name |
| skin fungus | tablets, powders | ketoconazole, moxicillin, terbinafine |
| ointments | clotrimazole, yam, tar ointment | |
| shampoos | nizoral, sebozol | |
| injections | microderm, polyvac, dermicocide | |
| ear fungus | drops | aurizon, oricin, posatex |
| pills | ketoconazole, griseofulvin | |
| ointments | Econazole, Sanoderm | |
| claw fungus | pills | terbinafine, fluconazole, lamisil |
| ointments | clotrimazole | |
| bath solution | enilconazole, chlorhexidine, thiabendazole | |
| eye fungus | drops | tsiprolet, chloramphenicol, leopard |
| ointments | tetracycline |
Traditional methods of treating fungus in cats
To treat skin fungus using traditional methods, you can use an ointment made from honey and fish oil. Mix the ingredients to a creamy consistency and lubricate the affected areas 4 times a day. Another option is to use a mixture of olive oil and lemon juice in equal proportions. Soak cotton wool in the heated mixture and wipe the affected areas 4 times a day. Kerosene can be used for a one-time treatment of the skin when treating bald areas of the skin.
Onion juice is used to treat ear fungus using traditional medicine. Half the onion is grated, and the juice from the resulting mass is dripped into the ear infected with the fungus, 5 drops at night for 5 days.
Treatment of claw fungus in a traditional way involves using a solution of apple cider vinegar, hydrogen peroxide in warm water in the following proportions: 600 ml of warm water, 50 ml of peroxide and 50 ml of apple cider vinegar. The cat's paw infected with the fungus is dipped into the resulting solution and held for 30 seconds, then pulled out and allowed to dry.
To treat eye fungus in cats, it is possible to use chamomile infusion. Brew a teaspoon of chamomile with half a glass of boiling water and let it brew, cool to room temperature and drip 2 drops 5 times a day. You can also instill willow decoction. Cut off the ends of branches without leaves. Dry it and break it into several pieces, put it in boiling water, boil and leave to infuse for 20 minutes, then strain and cool. Apply 2 drops 3 times a day.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out only in a veterinary clinic. You should not listen to friends’ advice about what remedy to take to get rid of fungus, since many fungi are dangerous to humans, and the lack of timely and adequate therapy will have an extremely negative impact on the owner.
Only a specialist can determine the necessary treatment for fungus in cats. In order to identify the type of fungus that has affected the cat, the veterinarian takes a skin scraping at the site of the lesion. What kind of infection is occurring is determined very quickly, after which the right medicine is selected.
When a veterinary clinic has a powerful laboratory, they not only determine the type of fungus, but also determine what type of drugs it will be most sensitive to. Thanks to this, it is possible to carry out therapy with the most effective antifungal drugs.
Prevention of fungal diseases in cats
Prevention of fungal infections in cats involves creating optimal conditions for keeping your pet. You should not neglect the rules of hygiene, bathe the cat using preventive antifungal shampoos and timely vaccinate animals against fungal infections. It is also necessary to monitor the balance of the diet and monitor the condition of the animal’s mucous membranes, claws and ears.
Fungal diseases are not uncommon and can be easily transmitted between animals. Most diseases respond well to treatment if you contact a specialist on time. To prevent re-infection, it is necessary to completely disinfect the room in which the infected animal was located. It is recommended to bathe your pet using rubber gloves.
Main types of fungal infections
All fungal diseases in cats are divided into 2 large groups.
- Parasitic on mucous membranes and skin.
- Systemic – affecting systems and organs. Fungal damage to the central nervous system may even occur. They are extremely rare in cats. More often they affect the body of dogs and can take their lives.
In this condition, the skin of a sick cat turns red, areas of baldness and scratching appear on it. Treatment of the disease should begin immediately after its detection.
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Types of fungal infections in cats and their symptoms
Fungi are microscopic organisms that cause the development of many diseases. They can affect the pet's skin and fur, or internal organs. Some fungal diseases are transmitted from cats to humans.
Here are the diseases that occur most often:
- Ringworm. The second name is microsporia. With this disease, clearly defined, scaly, bald patches appear on the cat's skin. An animal suffering from lichen is constantly itching . This disease is easily transmitted to humans, so during treatment it is necessary to wear gloves and wash your hands thoroughly after contact with a sick pet.
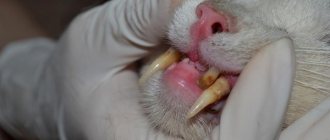
- Candidiasis. This disease is caused by Candida fungi. It develops after a long course of antibiotics. Weeping red ulcers with a white coating appear on the skin (usually on the oral mucosa or genitals) .
- Malassezia. Every cat has this fungus on the skin, but it becomes more active against the background of ear diseases or dermatitis. At the same time, the pet's hair falls out, red and inflamed bald patches appear .
- Cryptococcosis or torulosis. This fungus is found in bird droppings. Cats become infected through airborne transmission. Cryptococci affect the brain, lymph nodes, and skin. Main symptoms: abscesses and fistulas, damage to the nervous system (paralysis, loss of coordination, etc.), nasal discharge.
- Scab or favus. This disease is carried by rodents. The pet develops deep scabs , which are covered with a gray crust on top. The hair on the affected areas falls out and necrosis develops.
- Sporotrichosis. This fungus leads to the appearance of nodules on the skin and internal organs. The skin on the face, paws, and tail is primarily . Nodules may also appear in the area of wounds and abrasions.
All fungal diseases are accompanied by hair loss, peeling or inflammation of the skin.
All fungal diseases are accompanied by hair loss