Content
1. What contributes to the development of staphylococcus in dogs 2. Symptoms of staphylococcus in dogs 3. Complications of the disease 4. Correct diagnosis to detect infection 5. Features of treatment 6. Is canine staphylococcus transmitted to humans 7. Preventive measures 8. Is there a vaccination against infection 9. Video about the disease
Staphylococcus in dogs is quite common. Even despite careful care, constant hygiene procedures, proper, balanced nutrition, regular scheduled vaccinations and vitamin supplements, no one is immune from the problem.
Large breeds of dogs need long walks, which have a beneficial effect on their health. But it is walks that often become the causes of infection with a disease that affects the blood. Staphylococcus spreads quickly in natural environmental conditions, and at the same time is an incredibly tenacious organism.
Bacteria are constantly present in the body of healthy animals, but are in a dormant state. With normal immunity, the disease practically cannot develop. However, with the onset of heat, the risk of infection increases many times. This is due to the increased activity of dogs. Walks become longer, and contact between pets and each other increases. Any damage to the skin allows harmful organisms to enter, causing unbearable itching. The disease should not be ignored - the infection poses a serious danger, spreading rapidly in the animal’s body, causing complications and causing pathologies in all vital organs and systems. Owners need to promptly seek help from specialists. Timely comprehensive therapeutic treatment helps reduce the risk of developing a dangerous complication and premature death of the dog.
Diagnostics
The leading method for diagnosing staphylococcal infection in dogs is a visual examination, taking an anamnesis and taking into account clinical symptoms. To a lesser extent, they rely on laboratory test data.
Samples for bacteriological culture should be taken from the loop (in females) or prepuce (in males) . The sterility of the manipulation is important: the tube is quickly opened, the material is taken, trying not to touch the covers with your hands, and closed with a swab.
Swabs from wounds on the skin of dogs or from the ear canals do not give accurate results, as they contain foreign microorganisms.
A blood test to determine staphylococcus in dogs is also useless. The infection can be successfully detected only in 8-10% of cases.
Additionally, an examination is prescribed for possible allergic reactions and systemic pathologies. This is necessary to determine the root cause of staphylococcus in dogs and eliminate it.
What contributes to the development of staphylococcus in dogs?
Infection mainly occurs through contact of a healthy animal with an infected one. Pseudointermedius affects dogs with weakened immune systems.
The disease can occur in two forms.
- When the source of the disease is the pathogenic organisms of staphylococcus - a primary infection.
- If the infection develops against the background of other diseases, it is a secondary infection. This form of the disease is the most dangerous, causes serious disturbances in the body, and is severe.
Infection often occurs if the pet has parasites. The high-risk group includes puppies, old pets, those who are often ill, and weakened.
Predisposing factors to bacterial infection are:
- high amount of carbohydrates in the body;
- allergy;
- diabetes;
- instability to this type of pathogen (especially with weakened immunity);
- infectious diseases of the liver, kidneys;
- with an unbalanced diet, deficiency of micro, macroelements, vitamins;
- when infected with ticks, fleas.
Important information! Pseudointermedius often provokes other diseases in animals.
Causes and pathogens of the disease
Staphylococcus is a genus of bacteria widespread in the world. The reasons for the spread of this disease include the high resistance of these bacteria to drugs, the ability of staphylococci to synthesize a diverse number of toxins, each of which can act separately. All this makes it difficult to use various means of protection and prevention. Also, various scientific studies include environmental deterioration, unbalanced feeding of pets, and most importantly, the uncontrolled use of antibiotics by animal owners as the reasons for the spread of staphylococcus.
As for specific pathogens, the following types of staphylococcus are found in dogs:
- saprophytic staphylococcus (Staphylococcus saprophyticus);
- epidermal staphylococcus (Staphylococcus epidermidis);
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus);
- hemolytic staphylococcus (Staphylococcus haemolyticus);
- But most often in dogs, coagulase-positive staphylococcus (Staphylococcus intermedius) is found.
Previously, it was believed that all of the above types of staphylococcus could cause the disease, but thanks to the achievements of modern science, in particular phylogenetic analysis, it was found that in most cases, clinical manifestations are caused by Staphylococcusps eudintermedius, which is a subspecies of Staphylococcus intermedius.
Old literature indicates that the disease can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, but at the moment it is believed that the confusion was due to the fact that the pathogens are morphologically similar and old laboratory diagnostic methods did not allow them to be distinguished from each other.
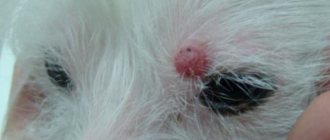
Fact: Staphylococcus aureus does not occur in dogs! (in the photo there is a pet with otitis media - one of the possible manifestations of the disease)
Hemolytic staphylococcus in dogs deserves special mention. Hemolytic staphylococcus is a bacterium that causes infectious and inflammatory reactions in the human body. The name hemolytic microorganism received because of its ability to hemolyze, that is, to destroy. Hemolytic staphylococcus is a conditionally pathogenic bacterium for humans; it is capable of causing various purulent processes. Sometimes in the results of bacteriological culture the owner comes across such an expression as “hemolytic coagulase staphylococcus aureus positive in the dog.” But it only means the presence in the culture of a microorganism that is part of the dog’s normal microflora, that is, it cannot cause infection, and there is no need to worry about such a result.
Symptoms of staphylococcus in dogs
It is difficult to recognize the disease with the naked eye. Symptoms of the disease vary. The main signs of infection to look out for are:
- formation on the skin and suppuration in the form of tubercles;
- the presence of round-shaped spots with crusts (in appearance they are similar to “ringworm”).
If lesions are detected in the early stages, the prognosis is favorable. If you miss time, the infection begins to spread rapidly. Dogs' hair begins to fall out, and large areas of baldness become noticeable. The animal cannot find a place for itself due to the unbearable itching, and cannot fully sleep or rest. Gnawing the skin with teeth and intensive scratching leads to the penetration of pathogenic organisms into the deeper layers of the skin. The result is the appearance of painful boils, often reaching a huge size.
Considering that the disease can be transmitted to humans, and is especially dangerous for older people and children, it is important to consult a doctor as quickly as possible for diagnosis and timely drug treatment.
Staphylococcus aureus is often accompanied by dermatological diseases.
- The ears become infected. Purulent discharge with a characteristic unpleasant odor flows from the ears. The dog is restless. An advanced disease provokes temporary paralysis of the facial nerve.
- Purulent lesions of the skin (pyoderma). It predominantly develops as a form of secondary infection when the pet scratches the skin due to parasite bites. Disease-causing organisms enter wounds.
- Allergic reactions. Characteristic in animals with hypersensitivity to microorganisms causing Staphylococcus intermedius. Characteristic symptoms are purulent papules and skin irritation.
- Infection of the mucous membrane. Untimely treatment provokes the development of pyometra and endometritis.
- Otitis. A disease in which the middle ear becomes inflamed. It often causes erosion in the ears and infects tissues. May be accompanied by inflammation, conjunctivitis, rhinitis.
Staphylococcus aureus has similar symptoms to food poisoning. The type of infection is more common in young pets. This is due to an underdeveloped immune system. When an animal becomes ill, it refuses to eat; profuse diarrhea and frequent vomiting lead to dehydration. If the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner, there is a risk of death.
Important! Dog owners must constantly monitor their pet. Do not contact stray animals. If you suspect staphylococcus, immediately seek professional veterinary care.
Prevention of staphylococcus
Prevention of this disease is aimed at constantly maintaining the strength of the dog’s immunity. Provide your dog with a nutritious, healthy diet. Give her a vitamin complex.
Regularly carefully and for a long time examine the dog’s skin, moving apart all the folds and excluding any possible changes. Minor skin lesions must be treated with antiseptic solutions.
Do not forget and neglect immunization of your pet. And carefully ensure that your dog does not come into contact with questionable animals, as staphylococcus is contagious. The drug ASD has been widely used; it works well against pathogens of infectious diseases; its action is aimed at increasing the resistance of the dog’s body’s defenses and enhancing tissue regeneration processes. It is also used for the growth and development of puppies.
If you follow all these simple rules, the dog will not get sick and will feel great.
Complications of the disease
At the slightest suspicion of intermedius, even with minimal infection of the epidermal lesion, treatment must be started immediately. Wasted time leads to serious consequences.
- In a pregnant dog, the infection is accompanied by complications such as endometritis, vaginitis, and pyometra.
- In male dogs, inflammation of the prepuce begins. The pathological process quickly becomes chronic, which subsequently causes long-term treatment with frequent relapses.
- The spread of pathogenic organisms through the bloodstream is fraught with the appearance of inflamed follicles, carbuncles, and boils in huge quantities. When located in the paw area (between the interdigital folds), the pet’s well-being noticeably worsens.
Features of treatment
An integrated therapeutic approach is important in treatment. The main priority is the destruction of pathogens. For this purpose, a staphylococcal bacteriophage is introduced. Additionally, immunity is raised with the use of immunostimulating drugs (both nonspecific and specific methods are used). The option for activating immune forces is selected taking into account the condition of the animal; in case of pathologies, preference is given to passive immunotherapy with the administration of antistaphylococcal serum. The set of measures necessarily includes taking antibacterial drugs. Since the bacteria that cause staphylococcus are resistant to antibiotics, several drugs are prescribed simultaneously in combination or one after another. In advanced cases, taking antibiotics can last more than a month.
Additionally, symptomatic treatment is carried out.
- Irrigation with special solutions for drying the skin (antibacterial, enzymatic agents).
- Novocaine lotions to relieve itching. Additionally, an antihistamine is given.
- In case of ear inflammation, a mixture containing dermatol with novocaine is blown into the ear canal.
- If it is necessary to restore the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, taking probiotics and prebiotics is indicated.
- Vitamin complexes - to stimulate the immune system.
- Diabetes caused by secondary infections, or allergic reactions, inflammation of the thyroid gland, requires the prescription of appropriate medications.
Is there a vaccination against infection?
To prevent intermedius, the vaccine Staphylococcal Polyvalent Anatoxin (STA) is used.
Vaccinations are given to bitches after giving birth (three and six weeks). Vaccination will reduce the likelihood of infection not only for the dog, but also for the puppies that are born.
Is it possible to completely prevent staphylococcus?
Unfortunately, it's not possible. Any injury to the skin begins the growth of bacteria. However, a set of measures significantly reduces the likelihood of infection.
- It is important to strengthen the animal’s immunity in all ways. To do this, the diet must be complete, with a rich vitamin complex. Long walks will also be beneficial.
- If sick pets live in the house, contact with them is minimized.
- Owners should not skip scheduled vaccinations. Timely vaccination will prevent the disease and increase immunity.
- A careful examination of the skin and coat, with regular hygiene procedures, is no less important. Particular attention is paid to folds.
- Remove parasites in a timely manner using tick and flea repellents.
- At the slightest damage to the mucous membrane or skin, immediately treat with an antiseptic.
- Avoid overheating in hot weather.
- Protect your dog from stressful situations as much as possible - nerves reduce immunity.
With a quick response to the disease and careful care of the dog, staphylococcus will not have a single chance.