What kind of organ are the paraanal glands?
The occurrence of complications is often associated with a lack of appropriate knowledge. After all, detecting a diseased organ without knowing about its existence is an almost impossible task. To fill in the gaps, it is enough to clarify only 2 points: find out the location and features of the functioning of the paraanal glands.
Location
The mysterious organ is hidden right behind the anus - not far from its transition to the rectum. It consists of two symmetrical “bags” filled with odorous secretion. Due to their location, these seals cannot be seen, but can be felt.
Operation
The secretion secreted by the paraanal glands in dogs has an individual smell. It is this that animals “read” when getting to know each other, when they sniff the back of the body of a new acquaintance.
In the absence of pathologies, the secretion produced periodically comes out. This occurs when defecation, leaving territorial marks or strong emotional arousal.
When natural outflow is disrupted, fluid accumulates inside. Blockage of the excretory ducts is accompanied by inflammation of the organ. This can lead to a number of complications, including tissue rupture. To save the animal, cleansing is done manually.
Anal glands in dogs: inflammation
Treatment of inflammation of the paraanal glands is carried out only by a specialist. If signs of such a pathology appear for the first time, it is worth contacting a veterinary clinic for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate therapy. If an animal has an abscess in its organs, then attempts to cleanse the glands on its own can lead to the death of the pet.
After examination, the specialist may prescribe treatment according to the following scheme:
- Epidural sacral anesthesia. Required for pain relief in cases where the dog experiences severe discomfort during cleaning or examination.
- Organ cleansing.
- Rinsing the anal glands with special antiseptics.
- Surgical excision of cancerous tumors.
- Removal of paraanal glands in dogs with an abscess.
Possible causes of inflammation
For pets, the exocrine function has long ceased to be necessary. They do not fight for the female and rarely mark territory. The once important organ gradually becomes rudimentary and is less and less cleansed naturally.
Other causes of inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs include:
- low activity and excess weight, which impair intestinal motility;
- frequent digestive problems including diarrhea and constipation;
- weak immunity;
- improper feeding of bones, excess protein, insufficient or excessive amount of fiber in the diet;
- frequent mating and pregnancy;
- infection with bacteria, viruses or helminths;
- anal area injuries;
- infrequent walks, forcing you to restrain the urge to defecate;
- neglect of hygiene;
- congenital disorders in the development and position of the organ.
Establishing the cause of inflammation is an important part of further therapy. Eliminating it increases the chances of preventing relapses.
Causes of problems
If such animal behavior is accompanied by intestinal disorders, then the main causes of the disease will be:
- blockage of the anal glands;
- helminths;
- enterocolitis;
- proctitis
A common cause of the disease is blockage. A dog's glands are small sacs containing a brown secretion that has an unpleasant odor. Located on both sides of the anus. During defecation, part of this secretion comes out.
Discharge from the pouches lubricates stool and facilitates bowel movements. The unpleasant smell is designed to scare off enemies, attract individuals of the opposite sex and helps mark territory.
When emptying, feces press on the walls of the perianal sacs, and the brown substance naturally exits through the outlets. With diarrhea, constipation, and other intestinal disorders, they may not be cleansed as they should.
Symptoms by stage of development
Depending on the symptoms that appear during inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs, the pathological process is divided into 4 stages. As the serial number increases, the likelihood of complications aggravating further treatment increases.
First stage
The initial stage is accompanied by severe itching and a gradual reduction in the amount of secretion produced. It remains transparent or acquires a yellowish tint. To eliminate itching, the dog constantly licks himself or cuts circles on his butt.
This symptomatology is similar to helminthiasis. Do not rush to give an anthelmintic before diagnosis. Not only will this not help, but it will also weaken your immune system.
Second stage
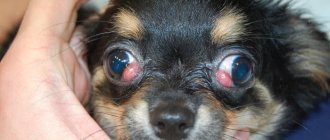
The development of inflammation is accompanied by thickening of the secretory fluid and a reduction in its volume. Due to frequent scratching, the hair in the affected area begins to fall out. The inner surface of the thighs is covered with tiny bubbles with transparent or cloudy contents. The hind limbs are constrained by spasms that impair coordination.
Third stage
Secretory fluid is practically not secreted. It resembles a thick cream and becomes darker. Due to the growth of bacteria attracted by stagnation, inflammation spreads to adjacent tissues. The spasms get worse. Instead of single muscle contractions, cramps appear.
Fourth stage
The escaping liquid resembles grainy cottage cheese and turns black. If the ducts are completely blocked, paralysis of the hind limbs and the development of an abscess are possible. The patient experiences severe pain not only during bowel movements, but also at rest. A sharp increase in temperature to 40 °C indicates blood poisoning, which can be fatal. The animal requires urgent hospitalization.
Additional symptoms
Inflammation of the anal glands in dogs can also have additional symptoms. Among them it is worth highlighting:
- constant movements with the tail pressed tightly to the anus;
- the dog’s reluctance to sit still for at least five minutes;
- fresh pus and blood in the feces;
- frequent constipation;
- weeping open wounds in the anal area.
At-risk groups
The risk group includes pregnant and lactating females, as well as some representatives of small breeds: dachshunds, pugs, Pekingese, Spitz, Shih Tzu. If you follow the recommended caloric intake of food and regularly walk your pet, not forgetting about outdoor games, make sure that he is not naturally prone to excess weight. In this case, any deviation from the listed actions is fraught with the sudden development of pathology.
Who is at risk
Inflammation of the paraanal glands in dogs is very common. However, the factors that can provoke such a disease have not yet been precisely established. The risk group includes animals that have been noted to have:
- frequent diarrhea;
- obesity;
- weak tone of the muscles of the anus and rectum;
- chronic soft stools;
- unbalanced diet;
- cancerous tumors located in the glands or in tissues near them;
- undistributed or excessive secretion production.
Diagnosis of the disease
An examination in a veterinary clinic is carried out to exclude similar pathologies, identify the cause and stage of the inflammatory process. You shouldn’t delay making an appointment until your condition worsens. Lethargy, lack of appetite and unbearable itching are quite serious symptoms that require a mandatory examination of the four-legged patient.
The list of mandatory diagnostic tests includes a blood test, skin scraping and assessment of secretions. If there is pus, blood or a foul odor, a bacterial culture test is also taken, which determines the type of bacteria and their sensitivity to antibiotics. Other diagnostic methods are prescribed on an individual basis.
Cleaning the anal gland at home
It is possible to clean the paraanal glands from secretions at home. Wearing rubber gloves and lubricating your finger with Vaseline, you need to insert it into the anus. With light movements you need to press on the seals at the very exit, alternately from both sides. The procedure is applicable if the dog behaves calmly during the process and does not experience pain.
The mechanical cleaning method is not suitable for small breeds of dogs, because... threatens damage and rupture of the anus.
It is also possible to clear the glands of fluid by applying pressure to the outer surface of the irritated area. By lightly squeezing the outside of the rectal wall, secretions can be released.
Dogs that are genetically predisposed to developing the disease need to be cleaned more often, without waiting for inflammation and rupture of the abscess.
In case of severe inflammation, however, it is better to contact a veterinarian, who will carry out the procedure as painlessly as possible for the pet, without damaging any organs. After cleaning at the veterinary clinic, the doctor may suggest surgical removal of the glands. Excision is best done if the disease is advanced and threatens an early relapse. The veterinarian may administer local anesthesia and sedatives to the dog if it becomes very agitated.
How to properly clean a dog's anal glands
Treatment methods
In most cases, the blockage is removed by mechanical cleaning. Rinse and surgery are prescribed when the process is advanced, and drugs are used to eliminate inflammation and kill bacteria.
Drug therapy
For inflammation of the paraanal glands in a dog, rectal suppositories (Methyluracil, Proctosedyl, ichthyol suppositories) are used for treatment. They not only have an anti-inflammatory effect, but also increase tissue regeneration. A contraindication for use is a violation of the integrity of the organ.
To relieve pain, a novocaine blockade is prescribed, and the bacterial infection is eliminated with a course of antibiotic therapy. Due to possible side effects, all dosages and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor.
Washing
Patients with stages 3 and 4 of the inflammatory process undergo washing of the “bags”, clearing them of accumulated pus. During the procedure, local anesthesia is used. After opening the abscess, the surgeon removes its contents and rinses the ducts with an antibacterial solution. The resulting wound heals quickly if you avoid licking it with a veterinary cone.
Mechanical cleaning
In the first stages, the blockage is removed by mechanical cleaning. It is carried out in 2 ways:
- Outer
. The “bags” are wrapped around the outside with your fingers and squeezed towards each other. After the fluid has drained, the anus is treated with Vaseline.
- Interior
. With a finger inserted into the anus, you need to feel the inflamed organ and try to squeeze out the secretion from it through gentle massage movements.
The second method is carried out strictly in a veterinary clinic, since in the absence of skills it can lead to injury to the anus. The external method is easier and less dangerous, so it can be used at home.
Surgical intervention - removal
In case of advanced inflammatory process, congenital pathologies or frequent relapses, anal sacculectomy is recommended, that is, removal of the “sacs”. The operation does not affect the quality of bowel movements, since it does not affect the anus and rectum. Within a day, the pet returns to normal activity.
During rehabilitation, it is important to increase the frequency of walking. Frequently holding back the urge leads to constipation, which can lead to sutures coming apart. Wound healing is also facilitated by following a special diet.
The main functions of the paraanal glands
The paraanal glands are an organ that is located on both sides of the anus, corresponding to the position of the clock hands at 4 and 8, under the tail. The glands belong to the external secretion, but if they are not enlarged due to inflammation, then it will not be possible to examine them.
The bags perform several functions:
- They secrete a liquid with a peculiar odor that attracts the opposite sex or serves to mark territory.
- Serve as a lubricant during bowel movements.
Blockage of the paraanal glands can lead to inflammation, abscess, and in advanced cases, death.
Anal glands in a dog
Dietary regime
The diet is based on easily digestible foods enriched with fiber. Regular consumption of dietary fiber prevents blockage of the ducts by stimulating peristalsis. Additionally, you can take vitamin and mineral complexes prescribed by your veterinarian.
To prevent constipation and diarrhea, it is recommended to use only fresh food, avoiding reheating food. To avoid overfeeding and excessive stress on the intestines, increase the frequency of feedings by reducing the size of portions. Eliminate all prohibited foods from your diet: canned food, sweets, pickles and other dishes from the human table.
When dry feeding, it is recommended to choose food from a veterinary line. Pay attention to the series recommended for digestive problems. The exact brand and serving size should be checked with your doctor.
Causes of inflammation in dogs
Secretion occurs during defecation, fecal masses press on the sacs and liquid appears in small quantities.
Dogs that hold back feces due to infrequent walks are at risk.
Blockage of the glands and the inability to release secretions can occur for a number of reasons:
- Pet obesity.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Abundance of soft food in the diet.
- Frequent diarrhea.
- Injuries in the anal area.
- Pregnancy.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Mechanical damage to the anus during defecation (abundance of bones in the diet).
- Weakened immunity.
- Infections.
Anal glands in a dog
Do-it-yourself cleaning at home
Self-cleaning is carried out for preventive purposes when the diagnosis is already known. For the safety of your pet, it is important to rule out other diseases and make sure there are no complications.
Frequency
On average, it is enough to clean the ducts every six months. Depending on the individual characteristics of the animal, the interval can be increased or decreased. If blockage occurs monthly or even more often, then the problem is eliminated surgically.
How to perform the procedure
It is better to perform the procedure in the bathroom while washing. If you live in a private house, you can go outside during the warm season. Prepare old, unwanted clothing and latex gloves in advance to protect yourself from odorous secretions. Also make sure you have an assistant ready to restrain the dog.
Armed with Vaseline, napkins and a basin, proceed with the following actions with your partner:
- Place your pet in the bathtub and gently lift his tail towards his back. Place your pelvis directly under your anus. It is enough to simply place a small dog in a basin.
- Gently feel the anal area, looking for two lumps.
- Lubricate the anus with Vaseline and gently squeeze the seals, placing a napkin under the leaking secretion.
- After the accumulated fluid has come out, wash your dog and re-lubricate his anus with Vaseline. Use rectal suppositories for the next 4 days.
If there is no secretion, do not increase the pressing force. This may harm the animal. Complex cases are treated only under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Treatment at home
In the first stages, you can clear the accumulated secretions at home. We place the pet in the bathroom to prevent the contents from getting on the interior items. A medical glove should be worn. To relax the muscles, lift the tail up. Lubricate the anus with Vaseline and gently insert your finger inside. Feel the bags below, left and right. Use your thumb to hold the skin around the sphincter. Squeeze with gentle movements. Carry out the procedure on both sides. After this, apply anti-inflammatory ointment and place suppositories for several days.
This method is used when there are no obvious other inflammatory processes.
Possible complications
Prolonged blockage of the ducts attracts pathogenic microorganisms that cause an inflammatory process. This leads to the development of suppuration and damage to nerve endings. The lethal outcome increases with the development of sepsis.
Abscess
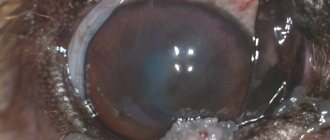
An abscess of the paraanal glands in a dog is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, redness and swelling of the anal area. The formation filled with pus can break through at any time and infect neighboring tissues, forming a fistula.
Fistula
Fistula is a cavity formed after opening an abscess. A small hole appears near the anus. It oozes white, yellow or greenish pus with a pungent odor. It may contain blood impurities.
Intestinal problems
Damage to the intestinal mucosa, caused by the appearance of an abscess or fistula, complicates the act of defecation. Constipation occurs, which can lead to intestinal obstruction. Accumulating feces can lead to intestinal rupture and intoxication of the body.
How does gland dysfunction occur?
All of these factors are the cause of uneven fluid secretion from the anal glands in dogs. As a result, the organs become overfilled and their contents begin to thicken. Blockage of the ducts often occurs. With such disorders, the glands do not stop producing secretions. Viscous dense masses gradually begin to stretch the organs. As a result, inflammation may begin, and then an abscess of the paraanal glands may occur in dogs.
In the future, the development of the pathological process leads to an abnormal concentration of bacteria, which are always present in the accumulated fluid. And this is fraught with serious consequences. This phenomenon affects the rate of accumulation of purulent exudate, as well as the formation of abscesses. In some cases, a chronic disease develops into cancer.