Fungus is a colloquial term for a group of animal and human diseases caused by micromycetes.
I will talk about the types of fungus, the causes of diseases, and their symptoms. You will learn what mycoses and under what circumstances you can become infected from a pet. Familiarize yourself with diagnostic methods and treatment methods for fungal diseases. Find out what antifungal drugs and vaccines exist and how much they cost.
If after all this information you still have questions, ask in the comments.
Prices and information are current as of March 2021 and are constantly updated.
Types of mycoses and their locations
Fungal diseases cause damage to the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs. Even non-specialists know about lichen, which affects dogs. The scientific name is dermaphytosis. In addition to lichen, the following mycoses can occur in dogs:
- Aspergillosis;
- Blastomycosis;
- Candidiasis;
- Malassezia.
Dermatomycosis
The causative agents are micromycetes Microsporum and Trichophyton. They can live on the surface of the dog for years and are activated when the immune system weakens under the influence of other diseases, stress, improper living conditions and feeding. Favorable conditions for the development of micromycetes are warmth and dampness. Therefore, dogs with unkempt, matted fur that has become matted are at risk.
The pathological process begins with the appearance of patches of baldness that occur on the face, torso, and paws. The skin peels, itches, the dog scratches itself. The injured surface is contaminated with secondary microflora, and dermatitis develops. Scales form, fall off, are carried by the winds, and pose a danger to susceptible animals and humans.
The fungus on the skin leads to its roughening, the ichor sweats out, crusts form, and pyoderma develops.
The first signs of lichen
With improper treatment or its absence, the lesions merge and spread throughout the body.
Watch the video:
Aspergillus
The disease is caused by widespread mold fungi. Dogs with weakened immune systems, tumors in the nasal cavity, or injuries associated with foreign bodies are susceptible. There is a local form that occurs mainly in young dogs of short-faced breeds and generalized aspergillosis in German shepherds.
With a local variety of mycosis, mold fungi parasitize in the nasal cavity, as well as in the sinuses of the upper jaw. Rhinitis develops, which does not respond to antibiotic therapy.
In the generalized form, the brain and spinal cord are affected, which causes nervous phenomena and paralysis. If mold has penetrated the kidneys, blood is found in the urine.
Rhinitis develops with aspergillosis
Blastomycosis
The disease is caused by a fungus that lives in rotting leaves. Dogs inhale the mycelium, which enters the lungs where it transforms into yeast form. The pathogen penetrates the blood and causes pneumonia, arthritis, osteomyelitis, and eye damage. The disease is difficult to treat and most often ends in death. In case of contact with damaged skin, dermatitis occurs, which proceeds easily and ends with complete recovery. Gardeners become infected while working with soil. Symptoms of the disease resemble flu or pneumonia.
Dogs become infected with blastomycosis through contact with fallen leaves.
Candidiasis
Candida fungi begin to actively reproduce as a result of dysbiosis caused by stress, prolonged use of antibiotics or corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs. Fungi multiply because their natural competitors, bacteria, die. The second name for the disease is thrush, because a fungal biomass appears on the mucous membranes, resembling milk in appearance. When the skin is affected, it is possible to distinguish Candidiasis from other types of fungal diseases only with the help of laboratory diagnostics.
Candidiasis affects the following organs and tissues:
- leather;
- mouth;
- vagina;
- conjunctiva.
Candidiasis in a dog
Malassezia
Yeast fungi of the genus Malassezia are permanent inhabitants of dog skin and protect it from staphylococci. When natural competitors die or weaken, micromycetes actively develop and cause dermatitis. There are the following causes of malasseziasis:
- Side effects of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics.
- Improper coat care. Malassezias love moisture and warmth. Therefore, it feels good under tangles or dense caked wool. Frequent bathing with degreasing shampoos destroys compounds that protect hair and skin from exposure to adverse environmental factors and pathogens of infectious diseases. Yeast loves clean, moist skin and fur.
- Unbalanced diet: a lack or excess of vitamins, microelements and amino acids leads to metabolic disorders and a weakened immune system.
- Heat and humidity indoors. The dog does not have sweat glands. Therefore, ideal conditions for the growth of fungi are created under the coat.
- Concomitant skin diseases. The dog licks the sore spots. Moisturizing the wool improves the conditions for fungal growth.
The folds of the skin, lips, the inner surface of the auricle, claws, and the spaces between the fingers are affected.
Malasseziasis is characterized by the following pathological symptoms:
- the skin smells like a dog;
- the fungus develops on the paws, and the claws turn brown and become brittle;
- brownish discharge is found in the ear canals;
- the skin thickens, looks moist, oily, and acquires a reddish tint;
- pathological foci spread throughout the body.
Malassezia dermatitis
Dogs of the following breeds are predisposed:
- Basset Hounds;
- Boxers
- British Setters;
- Cocker Spaniels;
- German Shepherds;
- Poodles;
- Dachshunds;
- Shih Tzu.
Malassezia is not transmitted from a sick dog to relatives or humans.
Signs of fungus
The infection has a number of characteristic symptoms, by which it can be easily recognized at an early stage.
Seasonality
The fungus loves moisture and warmth. It develops in autumn or spring. In regions with a humid climate, dogs are infected with the fungus all year round.
Initial stage of infection
At first, the dog licks its paws more often than usual. Later she begins to bite them and becomes restless.
When walking, the pet limps or stretches one of its legs, this looks like a limb injury.
Symptoms
Upon careful examination, the owner may observe the following changes:
peeling on the paw pads;- the appearance of small wounds and abrasions;
- delamination and breaking of claws;
- redness and swelling of the skin between the fingers;
- bald spots.
The skin on the paw pads becomes ulcerated and peels.
Causes and routes of infection
Mycoses occur in dogs with weakened immunity. Fungal pathogens are ubiquitous. Malassezia, Microsporum or Trichophyton fungi can live on the surfaces of dogs for years, remain in a symbiotic relationship with them and do no harm. But when the body’s defenses are weakened, micromycetes are activated, multiply, and cause damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Malassezia is not transmitted to other dogs or humans.
The fungi Microsporum and Trichophyton can infect dogs, humans and other animals with weakened immune systems by contact. The causative agents of Aspergillosis, Blastomycosis and Candidiasis are not transmitted from one individual to another. However, I do not advise taking care of a sick pet lightly, since the causative agent of the disease opens the door to infections that are dangerous to humans and animals. Possible damage to the eyes or skin that has lost its integrity.
Prevention
You should try your best to prevent your pet from getting diseases, especially fungal ones. It is recommended to take a number of preventive measures:
- do not allow contact with homeless four-legged animals;
- remove rodents from the house;
- All pets should be examined and treated in a timely manner;
- do not start illnesses that have begun;
- if a paw is cut, immediately stop the flow of blood, disinfect it, and bandage it;
- after walking, especially in damp weather, rinse your limbs well and wipe dry;
- balanced diet;
- sufficient physical activity;
- daily home inspection;
- compliance with the rules of sanitary and hygienic care;
- taking vitamins that strengthen the immune system;
- scheduling scheduled vaccinations;
- timely adoption of measures against ticks and fleas.
Similar articles:
- Cushing's disease in dogs
- Periodontal disease in dogs
- Flatulence in dogs
- Distemper in dogs
- Diarrhea in a dog
- Rheumatism in dogs
Diagnostics
I do not advise engaging in treatment without a diagnosis in a clinic. The preliminary cause of the disease is determined by a veterinarian based on clinical symptoms and the collected medical history. When exposed to a Wood's lamp, fluorescence in the green range indicates fungal damage.
A sample of pathological material is taken for bacteriological culture and cytological examination. If the airways are affected, rhinoscopy is performed. If a pathological process in bone tissue is suspected, fluoroscopy is prescribed.
Exclude eczema, pityriasis rosea, and otodectosis.
Diagnosis of fungal dermatitis
Contacting a veterinary clinic is the best solution for the owner of a pet susceptible to fungal infection. Before prescribing a course of treatment, the veterinarian examines the animal, establishes the clinical picture of the disease and carries out diagnostic measures. To rule out other diseases, such as brucellosis in dogs.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the specialist performs the following actions:
- collects anamnesis, interviews the dog owner about the current condition of the animal;
- conducts a clinical examination of the pet;
- scrapes from the affected area of the skin;
- carries out mycological and bacteriological cultures from foci of inflammation;
- takes blood, urine and stool tests.
If, after diagnosis, Malassezia in dogs is confirmed, the veterinarian will prescribe a course of treatment. At the initial stage of the disease, treatment can be carried out at home by the owner himself. In case of an advanced stage and prevention of relapse of the disease, the course of treatment is carried out under the supervision of veterinarians in a veterinary clinic.
How to treat fungal diseases
The treatment strategy is developed in the following areas:
- Provide comfortable living conditions. Isolate your pet and provide it with a comfortable, warm rookery.
- Transfer the patient to veterinary feeding for dogs with skin diseases. Eliminate treats with human treats, as well as table scraps.
- Provide your veterinarian with medication prescriptions. The initial stage is external antimycotics with a wound healing effect. If treatment does not bring the expected result, use oral or parenteral medications.
I have selected popular antifungal drugs for dogs. A list of medications, their description and cost are provided in the next section of the article.
When should you go to a veterinary clinic?
In order for a dog to become a loyal friend for many years, it is important to carefully monitor the health of your pet, including its coat and skin. The first signs of the development of fungal diseases are:
- Formation of receding hairline . The development of a fungal infection in a dog most often begins with the formation of a bald spot on the dog’s fur. Depending on the pet’s immunity, living conditions and hereditary predisposition, the rate at which the fungus spreads throughout the body may vary. In some dogs, the fungus affects the skin within one week, in others - within 1-3 months. Bald patches most often appear first on the paws and head, and then spread to the nose, behind the ear and neck area. When a dog becomes bald, the skin of a dog acquires a reddish or grayish tint, and sometimes flaking pieces of skin can be seen;
- Severe itching . Constant scratching of the skin between the toes, behind the ears, near the nose, in the lower area of the paws and other areas may indicate the onset of fungal development. Particular attention should be paid to the dog if it scratches the fungal lesion until it bleeds. In this case, it is necessary to treat the scratched area with any antiseptic and show it to the veterinarian. Frequent scratching of certain areas of the skin usually leads to the skin cracking and becoming scarlet, rough and dense. In advanced cases, the pet experiences severe pain to such an extent that it cannot even stand on paws suffering from the fungus;
- Deterioration in the appearance of the coat . If a dog is affected by the malassezia fungus, the hair coat may gradually change in the early stages of the disease. Depending on the stage of the disease, the fur may fall off, become tangled and dull. Many dog owners mistakenly believe that such changes in the appearance of the coat are the result of a change in food, a sudden change in weather, or a change in hygiene products. In fact, none of these factors can have such a strong negative effect.
You should visit a veterinarian as soon as possible if your dog:
- itching and pain appeared;
- the skin turns red or peels;
- swelling or puffiness has formed in certain areas of the skin;
- a bald spot has appeared;
- local temperature increased.
It is important to remember that fungal dermatitis and atopic dermatitis in dogs, the symptoms of which develop very quickly, negatively affect the canine’s immune system.
Self-treatment is considered unacceptable, because fungi can actively spread throughout the animal’s body and lead to negative consequences.
At best, pustules may form, and at worst, putrefactive skin processes and intoxication.
Antifungal medications for dogs
To treat fungal infections in dogs, be prepared to use the following types of medications:
- external preparations: ointments, gels, creams, solutions, ear drops, shampoos;
- internal antifungal drugs, presented in capsules or tablets;
- veterinary feed;
- therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines.
The veterinarian only prescribes medications; it is up to you to use them in most situations. Therefore, stock up on gloves and hand sanitizers after contact with a sick dog.
Among the external drugs most often used are the following:
Ointment Yam BK
A complex mixture of zinc oxide, elemental sulfur, salicylic acid and tar. Packaged in jars or tubes weighing from 10 g to 1 kg. Effective in the initial phase of fungal infections. Recommended as a folk remedy for the treatment of lichen in humans. Rub Yam ointment over crusts and fur 2 times a day for up to 10 days in a row.
The cost of a 20 g jar is 70 rubles.
Lecaderm
An ointment that combines the antifungal component Clotrimazole with the antibiotic Gentamicin and the corticosteroid antiphlogistant Bentamethasone. Medical analogue - Triderm. First apply any cream that softens the crusts to the affected surface. Remove the scabs, apply a thin layer of ointment. Treat twice a day until improvement occurs. After this, the frequency of treatments can be reduced to one every 2-7 days. The course of treatment is 7-14 days.
The cost of a 15 g tube is 480 rubles.
Nystatin
Medical ointment adapted for the treatment of dermatomycosis and candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes. Apply the ointment several times a day to a surface cleared of crusts for candidiasis and dermatophytosis. Don't let it lick it off. The therapeutic effect is enhanced by simultaneous use of tableted Nystatin. The course of treatment is at least 7 days, even if improvement occurred earlier.
The cost of a 30 g tube is 75 rubles.
Imaverol
Antimycotic solution Ethylconazole. Transparent brown liquid is poured into dark glass bottles of 100 cm3. The course of treatment consists of four treatments.
If your dog has a significant area of its body affected, this is exactly the drug that will help defeat the disease.
Imaverol does not irritate mucous membranes and is not toxic if it enters the stomach. The contents of the bottle are intended for dilution in 5 liters of warm water. For a large dog, it is convenient to split the contents of the bottle into 4 treatments. Trim your pet, remove the scabs, rub against the grain. A small dog can be bathed. The course of treatment consists of four treatments with an interval of 3 days. The contents of the bottle must be used up within three months after opening.
Cost 100 ml - 1246 rub.
Fungin forte
It is a 30 ml spray containing the antimycotic Clotrimazole. Before applying the aerosol, free the pathological surface from the scab, trim the hair and apply the medicine twice a day for 15 days.
Lactating and pregnant females should not be treated.
The cost of a 30 ml bottle is 420 rubles.
Surolan
If fungus is found in the ears, the best remedy is Surolan ear drops. The drug is produced in bottles of 15 or 30 ml. The active ingredients are the antifungal agent Miconazole, the anti-inflammatory drug Prednisolone, and the antimicrobial drug Polymyxin.
Clean the ear canal from crusts and exudate, apply 3-5 drops twice a day. After recovery, continue treatment for a couple more days. The maximum duration of treatment is 15 days. Instill Surolan in both ears to prevent inflammation in the second organ. Once the container is opened, use up the contents within 90 days.
The cost of a 30 ml bottle is 1246 rubles.
Nizoral shampoo
A medical antifungal agent intended for bathing a pet when a significant part of the body is affected. The active ingredient is the antimycotic Ketoconazole. Place your dog in the bath, rub the shampoo into the affected areas and leave for 5 minutes. Come up with some kind of game so that the pet does not jump out. Rinse the shampoo with warm water, dry with a towel, and do not let it out of the bathroom until it dries. Duration of treatment is 5 days in a row.
The cost of a 60 ml bottle is 679 rubles.
Oral medications have side effects, so they are prescribed when external remedies do not help. The following drugs are in demand:
Griseofulvin
A medical product adapted for the treatment of dogs. Available in 125 mg tablets. Do not use the antifungal medication yourself to avoid diarrhea and vomiting. The dosage is selected by the veterinarian individually. The dog's condition must be monitored every ten days using blood tests. If biochemical parameters deviate from the norm, Griseofulvin is discontinued.
The cost of 20 tablets is 258 rubles.
Itrazole
The active ingredient is Itraconazole. The duration of treatment is determined by the veterinarian. One tablet is intended for a dog weighing 10 kg. The first seven-day period is given the full dose. Subsequently, the frequency of administration is reduced to 1 time every 2-7 days. The drug has a hepatotoxic effect. If you notice. if your pet has constipation and vomiting, allergic skin rashes or swelling, stop taking it and tell your doctor.
The cost of a package of 42 capsules is 1420 rubles.
Drug treatment of fungal diseases will not lead to recovery without proper nutrition. It is problematic to create a diet from natural products, so you should consult a veterinarian to choose one of the following medicinal foods:
- Hills d/d (RUR 1,761/2 kg);
- Purina DRM (RUR 2,383/3 kg);
- Royal Canin Skin Support (RUR 1,675/2 kg).
The following fungal vaccines have been developed to prevent diseases:
- Vakderm (95 r./dose);
- Polivak-TM (60 r./dose);
- Microderm (380 r/4 doses).
Antifungal drugs produced in Russia, in addition to having a preventive effect, have a therapeutic effect. However, antifungal vaccines for dogs have not found widespread use outside the Russian Federation due to frequent complications. If a pet is vaccinated during the incubation period, it will definitely get sick, and in a severe form. While without vaccination, clinical symptoms may not appear or the disease will be mild.
However, if no treatment methods help, the veterinarian performs a provocative administration of a biological product. Dermatitis worsens, but after repeated vaccination, hair begins to grow back and skin defects heal. I do not advise taking independent actions, since exacerbations of other chronic diseases are possible.
Treatment of fungus in dogs
For mycoses, animals are prescribed drug therapy, which is selected depending on the type of pathogen, the general condition of the dog, and the presence of contraindications to the use of certain drugs. This treatment is based on the use of local agents that restore the skin and eliminate itching, as well as general medications to fight infection. The most effective remedy is a fungal vaccine for dogs, which allows you to cope with the infection quickly. Let's consider methods of combating the most common types of mycosis.
Ear
This pathology is usually not contagious and does not require the use of potent drugs. Typically, when diagnosed with “fungus in a dog’s ears,” treatment is limited to the use of the following medications:
- Ear drops. Oritsin, Bars, Amitrosine are used for such purposes.
- Shampoos: Nizoral, Imaveron, which have an antifungal effect. Allows you to exclude damage to neighboring areas of the skin.
- General funds. Used when the animal's immunity is reduced. Giseofulfin and Fluconazole are considered the most effective in this regard. They can be prescribed to the dog either in the form of injections or in the form of tablets.
If systemic medications are recommended for an animal with otomycosis, the doctor can also prescribe immunostimulants, immunomodulators, and hepatoprotectors. The latter are used to support the liver, which can be adversely affected by antibiotics.
The duration of treatment and dosage regimen are determined for each sick individual individually. Unauthorized changes in medical recommendations at the request of the dog owner are unacceptable, as this can lead to a deterioration in the pet’s health.
On my paws
In these cases, therapy comes down to taking the above systemic drugs in the form of tablets, injections, and local remedies:
- Antifungal ointments, including Dermatol, Miconazole, Akriderm.
- Sprays They are used to treat fungus on the skin after bathing your pet.
- Tar shampoos.
- Folk remedies, for example, oregano oil. They can be used for short-term relief of symptoms if the dog owner is not able to see a doctor right away. They are not considered as main drugs.
Treatment with such products at home should be carried out several times a day. Also, in case of skin lesions, a person needs to boil the dog’s bedding, treat his accessories (collar, leash), toys with an antiseptic. If the place has had contact with an allergen, it is necessary to isolate the pet from it. You can limit your dog's walking until he has fully recovered. This issue must be resolved with a veterinarian, taking into account the general condition of the pet, the location of the fungal infection, and the level of immunity.
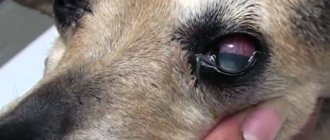
Ophthalmic
For such forms of mycosis, complex treatment is recommended, including:
- Taking antifungal eye drops. Depending on the veterinarian's recommendations, they are instilled up to 3 times a day. Both eyes are treated, even if symptoms of infection are recorded in only one.
- The use of ointments applied to the mucous membrane of the eyelid.
- Vaccination of the animal, injections of antibiotics. They are prescribed if the fungal infection in the eyes is secondary and develops against the background of another acute or chronic disease.
When treating mycosis, it is recommended to wear a special collar for the animal. This way, he will not be able to injure the skin around the eyes and mucous membranes and introduce infection to the affected area after treating it with drops or other drugs. The same applies if the disease appears on the animal’s lip or nose.
Video: what to do if your dog has fungus in the ears, paws or eyes?
Answers on questions
I have analyzed the most frequently asked questions from dog breeders on the topic of this article and will try to answer them.
What types of fungus can a person get infected from a pet?
Causative agents of Trichophytosis and Microsporia.
How to protect yourself from infection when caring for a sick dog?
When applying external medications, as well as giving tablets, you should wear disposable gloves, which are destroyed after use. Hands and open areas of the body are washed with soap and washed.
What dog breeds are predisposed to fungal diseases?
First of all, animals exposed to unfavorable environmental conditions: service and hunting animals. Decorative dogs, often short-faced ones, are also not protected from infection. They live in comfortable conditions, but can become infected while walking through contact with wild relatives or objects that have come into contact with a sick dog. These are the costs of directed selection, in which desirable traits arise due to weakening of the immune system.
Has a vaccine been developed against Malasseziasis?
Russian veterinary pharmaceuticals produce vaccines only against Microsporia and Trichophytosis.
Treatment
An integrated approach is a prerequisite for the speedy normalization of microflora in the animal’s body and the destruction of dangerous pathogens. The best results are obtained by combining the use of tablets and suspensions internally with external treatment of the affected areas.
Before starting therapy, be sure to shave all areas affected by the fungus. Often, the veterinarian advises to cut or shave the pet short over a large area, taking into account the degree of infection and the location of the source of the fungal infection.
During treatment, you need to be careful when treating the skin, fur, ears, and mucous membranes; be sure to isolate the dog in a separate enclosure if there are other pets at home. You should not leave a sick animal alone for a long time, so as not to cause psychological trauma.
Which bones are allowed for dogs and which ones are not allowed and why? Read useful information.
Why does a dog ride on its butt, what does it mean and is there any cause for concern? The answer is in this article.
Follow the link and read the instructions for using the antiparasitic drug Ivermek for small breed dogs.
Effective names and groups of drugs:
- antimycotic ointments and gels. Before applying the composition, be sure to remove hair from the problem area. The drug is selected taking into account the nature of the fungal infection and the age of the pet. If the affected area is large, thick formulations should not be used: the dog may become intoxicated. Effective ointments: Clotrimazole and Mycozolon;
- shampoos with components that destroy fungus. The compositions are suitable for the treatment and prevention of mycoses. It is useful to bathe a dog with a therapeutic and prophylactic agent after a walk in the forest, or being in a pond or lake. Effective compositions: Ketoconazole, Imaverol, Nizoral;
- vaccines and tablets with antimycotic action. The drugs Microderm, Fluconazole, Griseofulvin, Polivac are used not only during the period of prevention, but also during the treatment of fungal skin lesions in dogs. Some hunting breeds often develop allergies to vaccines, so caution must be exercised;
- sprays with antimycotic action. An effective type of treatment even for dogs with thick and long hair. The drug is sprayed according to the instructions onto problem areas and adjacent areas. It is important to ensure that your pet does not lick the fungicide. For protection, use a medical collar or muzzle. The drugs Fungil and Zoomikol have earned positive reviews from veterinarians and owners.
Birch tar is a proven folk remedy for fungus in dogs. Despite the pungent odor and unpleasant appearance, the natural product dries and heals wounds and scratches well, reduces itching and irritation. If there are no allergic reactions, you can buy your pet tar soap or wear a diluted solution based on natural resin.
Features of treatment
For the treatment of mycoses, regardless of the pathogen, the same drugs are most often used. Treatment includes local and systemic treatments to remove the most pathological manifestations and prevent their re-formation. Features of local therapy:
- removing hair from and around the affected area, sometimes the dog is completely trimmed;
- The dog should be washed with shampoo or a special product 2-3 times a week;
- creams, lotions, liniments are applied to the affected areas of the skin;
- Chlorhexidine solution and miconazole are effective against fungi;
- treatments are carried out for another 2 weeks from the moment of receiving negative laboratory results;
- for subcutaneous mycoses, excision of the affected areas is performed.
The use of systemic treatment must be determined on a case-by-case basis. For minor skin lesions, the use of strong drugs may give a negative result. Their use should be resorted to if a generalized form is noted, or local treatments have not led to recovery.
The drugs of choice are griseofulvin, ketoconazole, and itraconazole. The drugs are administered daily, the course of treatment continues until recovery, negative laboratory results are obtained and another 2 weeks. If the dog experiences indigestion or other pathological reactions to the drug, then stop using it immediately.
The main thing in the treatment of Malassezia is to eliminate the causes that lead to changes in the barrier function of the skin.
Subcutaneous fungal infections in dogs often occur in severe forms, requiring radical treatment measures. Conservative therapy with the use of antifungal drugs is often ineffective; it is used as a deterrent. Ketoconazole and potassium iodide are used as conservative measures. Extensive excision of the affected tissue is performed, often requiring amputation of the limb.
Drugs for the treatment of systemic pathologies in dogs:
- amphotericin B - administered intravenously with saline or water for injection;
- fluconazole;
- griseofulvin;
- thiabendazole;
- Potassium iodide.
General compensatory therapy is mandatory. Physiological solutions, calcium preparations, and glucose are prescribed intravenously. This is necessary to relieve intoxication, so diuretics are used at the same time. Sulfocamphocaine, caffeine, and veroshpiron are also prescribed to maintain the functioning of the heart and lungs.
Often fungal infections are complicated by bacterial flora or they themselves are the result of other diseases. Therefore, in most cases the use of antibiotics is indicated. Interferon and immunoglobulins are also prescribed. The administration of hyperimmune serum against dermatophytosis is useful, which significantly accelerates the recovery and recovery of the animal.