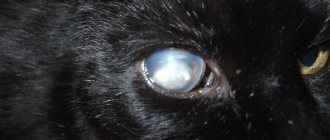
The kitten has one pupil that is narrow and one that is wide.
It is generally accepted that cats' main senses are smell and hearing, but healthy eyes are an equally important factor for cat health. It happens that owners notice extremely dilated pupils in their pet, but when the light is turned on, no reaction occurs.
Glaucoma
A disease characterized by increased intraocular pressure and an increase in the size of the eyeball. This occurs due to the pressure of fluid on the optic nerves, as a result of which these nerves are damaged, which provokes possible blindness. Basically, the pathology is of secondary origin, primary exposure is a rare case.
The pupil in cats is located in the center of the iris and allows light to pass through the eye into the retina. The pupil constricts or dilates according to the amount of light entering the eye, with both pupils typically dilating in dim light and constricting in bright light. Anisocoria is a condition in which a cat's pupils are different sizes, or in other words, one pupil is larger than the other. In some cases, the abnormal pupil may be the one that is smaller; in other cases, the larger pupil may be abnormal.
Is anisoscoria curable in cats?
The prognosis for complete recovery also depends on the cause of anisoscoria. In some cases, the cat may require long-term drug therapy to eliminate the underlying disease. If the underlying disease has caused vision loss, it is extremely unlikely that the blindness will be reversible.
It is generally accepted that cats' main senses are smell and hearing, but healthy eyes are an equally important factor for cat health. It happens that owners notice extremely dilated pupils in their pet, but when the light is turned on, no reaction occurs.
Glaucoma
A disease characterized by increased intraocular pressure and an increase in the size of the eyeball. This occurs due to the pressure of fluid on the optic nerves, as a result of which these nerves are damaged, which provokes possible blindness. Basically, the pathology is of secondary origin, primary exposure is a rare case.
The pupil in cats is located in the center of the iris and allows light to pass through the eye into the retina. The pupil constricts or dilates according to the amount of light entering the eye, with both pupils typically dilating in dim light and constricting in bright light. Anisocoria is a condition in which a cat's pupils are different sizes, or in other words, one pupil is larger than the other. In some cases, the abnormal pupil may be the one that is smaller; in other cases, the larger pupil may be abnormal.
Reasons for different pupils
Heterochromia is different eye colors. At the same time, the iris is not the same. Heterochromia can be complete or partial. In the second case, only part of the eye is painted a different color.
If a cat falls, the resulting blow to the head can cause a mild concussion. Even minor damage to blood vessels can cause dilation of the pupils. Most often, after a minor injury, the eyes return to normal within a couple of hours. If this does not happen after 24 hours, the animal must be taken to the veterinarian.
- Uneven pupils in a pet may appear due to a malfunction of the nervous system. The cat needs to be given a cozy, quiet corner and, if necessary, given medications prescribed by a veterinarian. The reason may also lie in old age, eye inflammation or the appearance of tumors. Different pupils may appear due to untreated cancer. Metastases quickly spread throughout organs, including the brain. As a result, the effect of different constriction of the pupils occurs. This effect can be caused by a stroke.
If a cat has one pupil that is narrow and the other wide, this phenomenon sometimes occurs due to stress. Most often, the unusual effect goes away on its own as soon as the animal calms down.
Anisocoria
One of the most common cat problems is anisocoria. These are different pupil sizes. One of them turns out to be underdeveloped. With anisocoria in cats, only one pupil is dilated. He is completely unresponsive to light. Causes of the disease:
- cancer; glaucoma; disruption of the nervous system; inflammatory processes in the body; anterior uveitis; pupillary constriction syndrome; deformation of the optic nerve (especially the optic nerve); malfunctions of the cerebellum; muscle abnormalities; eye injury.
Anisocoria not only indicates painful processes in the body, but also indicates fatal pathologies.
Sometimes a cat's pupils become different sizes due to illness. This pathological condition is called anisocoria. It is a manifestation of diseases of varying severity, requiring long-term treatment and rapid correct diagnosis.
The cause may be problems in the animal’s nervous system:
- head injury, concussion; disturbances in the functioning of the optic fiber; problems in the cerebellum; optic nerve disorders; problems in the functioning of the cranial nerves responsible for eye mobility; malfunction of the optic nerve.
Disturbances in the functioning of the cat's visual system:
- constricted pupil syndrome; inflammation of part of the eye (anterior uveitis); cancer of the organ of vision; various muscle abnormalities; increased eye pressure (glaucoma); retinal atrophy; lens luxation; problems with blood supply to the eye; posterior uveitis; the use of drugs that change the function of the pupil of the animal.
- a brain tumor; poisoning; stroke; infection; heart disease; kidney or stomach diseases; severe pain caused by injury or any disease.
Serious illnesses are usually accompanied by other symptoms. If you notice that your cat's pupils are dilated or one of them is larger than the other, it is important to carefully monitor your pet. Any owner will notice changes in the animal's behavior or any other alarming signs.
When one pupil is narrow and the other is wide, you need to check the reaction of each of them to light separately. If one of them does not respond to changes in lighting, it is necessary to urgently examine the animal for the presence of diseases. Many of them develop with virtually no symptoms and ultimately lead to blindness of the animal. That is why it is extremely important to contact a specialist in a timely manner and provide the animal with qualified assistance.
Cats are very patient with pain, so the owner may not even realize that something is bothering the pet. Due to constant pain, the cat's pupils will be dilated, but in most cases they will be the same size. This happens with injuries and dislocations, but then the animal will limp, be limited in its movements and not allow it to touch the sore spot.
Pain sometimes occurs due to various inflammations and problems in the functioning of organs. Then there may be no other visible signs. Such cases are the most dangerous, since the owner may not pay attention to changes in the cat’s eyes for a long time, and the disease will progress.
Anisocoria is usually a symptom of another disease and is caused by many reasons:
- Damage to the cornea of the eye Disease or injury to the brain or nerves passing through the affected eye Glaucoma - a disease in which increased pressure builds up inside the eye (the affected pupil will be dilated) Uveitis, or inflammation of the inside of the eye (the affected pupil will usually be narrowed) Diseases of the retina Scar formation between the iris and the lens of the eye, a condition that can develop after uveitis Atrophy of the diaphragm, or a decrease in the amount of tissue in the iris, i.e., degenerative changes associated with aging Congenital defect of the iris, the tissue in which the iris does not develop properly Cancer in affected eye Seizure syndrome that may be associated with leukemia in cats.
If anisocoria occurs suddenly, you should take it seriously and contact your veterinarian as soon as possible. This will reduce the chance of your cat's vision becoming impaired.
Causes of anisoscoria in cats.
Anisoscoria is a symptom of other diseases
, its reasons may be:
- Injuries and damage to the cornea, such as ulcers;
- Diseases and injuries of the brain or nerves leading to the affected eye;
- Glaucoma. A disease in which increased intraocular pressure persists - the pupil of the affected eye becomes dilated;
- Uveitis, or inflammation of the inside of the eye—the pupil of the affected eye is usually smaller;
- Retinal diseases;
- Formation of scar tissue between the iris and lens (called posterior synechia), a disorder that can develop after uveitis;
- Iris atrophy (or reduction in the amount of iris tissue) is a degenerative change usually associated with aging;
- Congenital iris defects, in which the iris tissue does not form correctly;
- Cancer affecting the eye;
- Spastic pupil syndrome is a disorder that may be associated with feline leukemia virus infection;
The sudden onset of anisoscoria is an emergency and veterinary attention should be sought immediately to prevent permanent vision changes.
Cats have different pupil sizes. Why do cats have different pupils?
Cat owners should be attentive to their pets: if you see anything incomprehensible in their behavior or physical condition, you should go to a specialist. If the owner sees different pupils in a cat, this may mean the consequences of a blow to the head or cerebral vascular disease in the animal.
When a veterinarian notices different pupils in a cat during a routine examination, he first asks the owner about the animal’s behavior and physical condition. Pets can get into fights with those who live nearby and get some kind of injury from them; a cat can simply hit its head when falling and get a slight concussion. Due to minor injuries, sometimes there is an uneven constriction or dilation of the cat's pupils, which usually returns to normal after a couple of hours.
By carefully observing his pet, the owner can see that the cat's different pupils are gradually becoming the same. If this does not happen a day after the blow, you should take the animal to a specialist and conduct an examination. You need to understand that you will probably need to visit your feline ophthalmologist. Specialists of this profile can be found in large cities, but in the provinces this is unlikely to happen, so you need to trust a veterinarian you know, who can also give good advice.
Sometimes, the cause of the disease can be identified through a routine examination and blood test, especially if the cat has different pupils due to a disruption in the functioning of the nervous system. In such cases, it will be enough to give the pet medications prescribed by the doctor for some time, and the cat should have a calm corner in which it is not threatened with any nervous shocks. If there are other animals living in the apartment that haunt the sick person, it is advisable to move her into a separate room. If necessary, the veterinarian will prescribe eye drops, which will need to be instilled at a certain time; cats do not like such procedures, so an assistant will be needed.
In cases where a cat's pupils suddenly become different, the veterinarian may suspect that the animal was hit on the head or there was a fight with an opponent; after two or three hours, when the stress passes, the eyes should become the same.
Animals kept for commercial purposes, for the production and subsequent sale of offspring, are periodically examined by a veterinarian. If he finds pupils of different sizes in a cat, it is advisable to seek the help of a feline ophthalmologist to find out the cause of this phenomenon. After a certain age, pets may develop various diseases, including eye diseases; an inflammatory process inside the eye or a tumor is quite possible.
An experienced veterinarian, through a blood test and visual examination, may well discover that the animal is undergoing an inflammatory process; sometimes appropriate medications relieve inflammation and the pupils become normal. In some cases, drops are prescribed that can narrow a dilated pupil or dilate a narrowed one. If there is no improvement, a more thorough examination is necessary.
There are known cases where pupils of different sizes in a cat were observed due to cancer; untreated cancer gives metastases to various organs, including the brain, which is why a similar effect occurs. The underlying ailment should be treated, and the size of the pupils will return to normal, if this is possible. Pets, like people, can develop a stroke, which also has a negative impact on the eyes. Making an accurate diagnosis is possible only after a thorough examination; a general veterinarian is simply not able to do this without special equipment. Therefore, if treatment does not bring relief, you should look for a clinic that has all the equipment to check the health of a sick cat, and specialists who can make the correct diagnosis.
Sometimes different pupil sizes in a cat occur due to minor injuries or stress; in such cases, the phenomenon goes away after a few hours and does not leave negative consequences; it is enough to provide the animal with a calm environment.
When changes in the pupils do not occur instantly, but gradually, a serious illness should be suspected, it could be a brain tumor, retinal detachment or another ailment; only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis after a thorough examination.
When dilated pupils in a cat are a sign of normality
The following causes of dilated cat pupils are classified as physiological:
- Estrus: the cat is excited, and in this state the adrenal glands release adrenaline into the blood, which causes the pupils to dilate. When the sexual hunt ends, the pupils return to normal.
- Game: when making jumps and performing complex turns, the pet is excited, it needs to strengthen its visual perception.
- The cat is dissatisfied with something: it hisses, arches its back, and bulges its eyes. This condition passes very quickly.
- Hunting: To track down prey, good vision is necessary, which is achieved by increasing the lumen of the visual lens.
- Night or low light - to see better, you need to open your pupils wide.
- Stressful state when a new pet appears in the house , or fear, the sound of a vacuum cleaner turned on, or an encounter with an aggressive dog. When the animal calms down, the pupil narrows.
- Rehabilitation after surgery. The residual effect of anesthesia on the eyes persists for a long time.
- Old age: visual acuity also decreases in humans, but cats do not wear glasses, but solve the problem by expanding the lumen of the lenses.
Be sure to read:
Correspondence between the ages of cats and humans: methods of determination, stages of development by human standards
A cat has one pupil that is narrow and one that is wide.
Different pupils in a cat are usually a sign of a disease, cerebral vessels or a head injury. In this case, you need to pay attention to the physical condition of the animal and its behavior.
Heterochromia is different eye colors. At the same time, the iris is not the same. Heterochromia can be complete or partial. In the second case, only part of the eye is painted a different color.
If a cat falls, the resulting blow to the head can cause a mild concussion. Even minor damage to blood vessels can cause dilation of the pupils. Most often, after a minor injury, the eyes return to normal within a couple of hours. If this does not happen after 24 hours, the animal must be taken to the veterinarian.
- Uneven pupils in a pet may appear due to a malfunction of the nervous system. The cat needs to be given a cozy, quiet corner and, if necessary, given medications prescribed by a veterinarian. The reason may also lie in old age, eye inflammation or the appearance of tumors. Different pupils may appear due to untreated cancer. Metastases quickly spread throughout organs, including the brain. As a result, the effect of different constriction of the pupils occurs. This effect can be caused by a stroke.
If a cat has one pupil that is narrow and the other wide, this phenomenon sometimes occurs due to stress. Most often, the unusual effect goes away on its own as soon as the animal calms down.
One of the most common cat problems is anisocoria. These are different pupil sizes. One of them turns out to be underdeveloped. With anisocoria in cats, only one pupil is dilated. He is completely unresponsive to light. Causes of the disease:
- cancer; glaucoma; disruption of the nervous system; inflammatory processes in the body; anterior uveitis; pupillary constriction syndrome; deformation of the optic nerve (especially the optic nerve); malfunctions of the cerebellum; muscle abnormalities; eye injury.
Anisocoria not only indicates painful processes in the body, but also indicates fatal pathologies.
Poisoning, injuries
The reason why a cat's pupils are of different sizes may also be due to the animal taking certain medications that affect visual functions. Some plants sometimes cause this same reaction. In this case, a healthy eye may not respond to mild intoxication, but a sick eye may do the opposite, since it is more sensitive.
If the cat staggers when walking, there is a lack of coordination and vomiting, this indicates poisoning. Changes in the eyes are caused by toxins. They can enter the animal's body along with food or from poisonous plants that the cat has chewed.
When scarring or clouding of varying intensity begins to appear in the eyes after an injury, not enough light is getting into the animal's eyes. The reflex reaction of the body is the dilation of the pupil, it becomes larger. This way they capture more light. In this case, the bright reaction is less pronounced than in the normal state.
Different eyes do not always indicate illness. Cats' pupils change as soon as they smell or see a dog. She is perceived as a clear threat. However, the main cause is illness.
If for a long time the owners notice that the cat has different pupils, they often suspect health problems. Depending on the symptoms, the cause may not only be an eye disease. A change in the cat's behavior and the obvious consequences of a blow as a result can lead to irreversible consequences if the size of the pupil is not monitored in time.
What is anisocoria?
It is generally accepted that cats' main senses are smell and hearing, but healthy eyes are an equally important factor for cat health. It happens that owners notice extremely dilated pupils in their pet, but when the light is turned on, no reaction occurs.
Glaucoma
A disease characterized by increased intraocular pressure and an increase in the size of the eyeball. This occurs due to the pressure of fluid on the optic nerves, as a result of which these nerves are damaged, which provokes possible blindness. Basically, the pathology is of secondary origin, primary exposure is a rare case.
The pupil in cats is located in the center of the iris and allows light to pass through the eye into the retina. The pupil constricts or dilates according to the amount of light entering the eye, with both pupils typically dilating in dim light and constricting in bright light. Anisocoria is a condition in which a cat's pupils are different sizes, or in other words, one pupil is larger than the other. In some cases, the abnormal pupil may be the one that is smaller; in other cases, the larger pupil may be abnormal.
Causes of varying magnitude
Anisocoria in cats is a disease when one pupil is larger than the other. Depending on the lighting, the pupil contracts in bright light or dilates to be able to see in the dark. The pupils become wider if a stressful situation arises, because emotions cause aggression in the predator’s body. Once the danger has passed and the cat has calmed down, they will become smaller. If the owner notices a difference in size, then it is necessary to monitor the situation for some time, as this may be a signal for the development of the disease. Anisocoria can occur due to injury, infection, neurological problems, or the presence of tumors. The causes are multiple and can be symptoms of complications of chronic diseases.
Veterinarians identify the following pathologies in the functioning of the optical system of the eyes:
- injury to the cornea, that is, the upper layer; ingrown eyelashes, infections or cancer; increased pressure inside the eye if the pupil is dilated; inflammation of the pupil if it begins to narrow; Horner's syndrome.
There have been cases when, due to oncology and the development of a malignant tumor process, dilation of one pupil was observed in cats.
Different pupils can be a manifestation of liver disease in an animal.
Sometimes anisocoria develops due to disorders of the nervous and immune systems, such as:
- Stroke or brain injury. Hepatorenal syndrome. Problems in the urinary system. Hepatic encephalopathy. Develops with liver pathologies. Pre-stroke condition. High blood pressure due to complications in the kidneys.
What are the causes of anisocoria?
Anisocoria is usually a symptom of another disease and is caused by many reasons:
- Damage to the cornea of the eye
- Disease or injury to the brain or nerves passing through the affected eye
- Glaucoma is a disease in which increased pressure forms inside the eye (the affected pupil will be dilated)
- Uveitis, or inflammation of the inside of the eye (the affected pupil is usually narrowed)
- Retinal diseases
- Scarring between the iris and the lens of the eye, a condition that can develop after uveitis
- Atrophy of the diaphragm or reduction in the amount of tissue in the iris, i.e. degenerative changes associated with aging
- A congenital defect of the iris in which the tissue does not develop properly
- Cancer in the affected eye
- A seizure disorder that may be associated with leukemia in cats.
If anisocoria occurs suddenly, you should take it seriously and contact your veterinarian as soon as possible. This will reduce the chance of your cat's vision becoming impaired.
Associated symptoms
Pathologies develop over time and are accompanied by additional symptoms. If a cat has pupils of different sizes, it often reacts to light with only one eye. Intense tearing, redness or clouding of the cornea causes pain and discomfort. She may reflexively squint if there are problems in the functioning of the eyelids. If your cat has poor coordination of movements and is vomiting, poisoning from toxic plants or drugs is possible.
An active lifestyle puts a kitten in danger; you need to pay special attention to its behavior after a fight with other animals or falls from a height. Often a concussion is accompanied by loss of consciousness and, as a consequence, memory loss. Having woken up, the pet does not recognize the owner, hisses, behaves inappropriately, and tries to hide in hard-to-reach places. If the cat came from the street, and upon examination the owner noticed hematomas, bruises, bruises on the head or neck, redness of the mucous membranes or convulsions, it is necessary to urgently contact a veterinarian.
If with such a symptom the animal has become lethargic, then this is worth paying attention to.
Symptoms indicating a stroke deserve increased attention:
- unnatural head tilt; loss of balance; loss of appetite, lethargy, spontaneous bowel movements; paralysis of the paws on one side of the body; vomiting or epileptic seizure.
Diagnosis and treatment
Sometimes a cat's pupils appear different due to minor injuries or stress. In such situations, the problem disappears within 24 hours. Often the pet's condition is not cause for concern. He sleeps peacefully and eats well, there are no problems with the toilet. But if the symptoms do not disappear after a while, the disease should be suspected.
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and find out the root cause why one pupil is narrow and the other wide, after conducting an examination. Veterinarians insist on carrying out the following procedures:
- examination by an ophthalmologist; taking blood and urine tests; x-ray (if injury is suspected); Ultrasound of the eyeball and measurement of intraocular pressure; tomography or MRI diagnostics; bone marrow biopsy.
The disease is quite difficult to treat, so the owner of the animal must be prepared for a long recovery. Rehabilitation of a pet directly depends on the causes of the disease. The doctor may prescribe treatment with antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs. The presence of tumors requires surgery. It is necessary to identify and treat the underlying disease and the size of the pupils in both eyes will no longer cause concern.
Useful materials:
General description of the disease Cutaneous horn on the forehead or face (ICD 10 code - L57.0) -...
Common causes of cloudy eyes in cats The most common causes of cloudy eyes are glaucoma, cataracts or keratitis.…
Main reasonsBefore considering the factors that provoke the appearance of discharge with a sourish odor, it is necessary to immediately note...
Normal temperature in different types of animals Veterinary services Day hospital for animals Veterinary certificates Vaccination…
How is the cause of anisoscoria determined?
Veterinarians begin the diagnosis by conducting a physical examination of the cat, including a detailed examination of the eye structures. Depending on the results, additional, more specific tests may be prescribed:
- Measurement of tear volume and intraocular pressure for each eye;
- Checking the cornea using fluorescent fluid to look for internal injuries or ulcers;
- Laboratory analysis of conjunctival scraping or biopsy;
- Blood tests to detect systemic diseases such as feline leukemia;