Injuries and eye wounds in cats
Cats can get eye damage as a result of a fight or a fall from a height. Wounds can be penetrating, superficial or deep. When the eye is injured, the eyelid becomes inflamed - this is a natural reaction of the body.
Swelling and bleeding may occur. If you think that your cat’s eye is watery and swollen due to a foreign body getting into it, take a magnifying glass, a flashlight and carefully examine the organ. It is quite possible to remove the object yourself using tweezers. Inocaine drops or Lidocaine spray are used as a local anesthetic.
However, if you doubt that you can carry out the procedure while maintaining calm and composure, it is better not to take risks and entrust this matter to a specialist. Otherwise, you can further injure the animal's eye.
Entropion (etropion)
This is a congenital or acquired pathology in which the skin fold of the eyelid, most often the lower one, turns inward due to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus. As a result of inversion, the eyelashes and fur come into contact with the cornea of the eye.
At first, the kitten experiences slight discomfort, and the presence of the disease can only be guessed by profuse lacrimation and slight redness.
Then inflammation and swelling appear, due to which the eyelid changes its appearance, photophobia, cloudy mucous discharge from the eyes, the tissues of the eyelids become hot and swell, and the eyes do not open. In the future, volvulus contributes to the development of chronic conjunctivitis and keratitis. Advanced cases lead to corneal ulcers.
Prolonged mechanical irritation of the eye can lead to serious complications, including blindness or loss of the eye, so treatment (surgical) must be timely. After anesthesia, your pet needs to be provided with quality care.
Main causes of tumor
There are many factors that can provoke the appearance of a tumor. Before starting treatment for your pet, it is important to determine what caused such a symptom. Experts identify the following main causes of eye pathologies:
- Injury. A common factor that contributes to the formation of swelling is trauma. If a cat hits its head hard, it may develop traumatic swelling. Fights between a pet and another cat can also become the root cause of eye damage. Wounds of the eyelid can be superficial, deep or through. In this case, the swelling of the eyelid is accompanied by redness of the eyes or slight bleeding. If the wound is shallow, it will heal on its own and the swelling will subside. If there is deep damage to the eyelid, it is necessary to put a bandage on the pet’s eye and take it to the veterinarian.
- Foreign object. A foreign body entering the eye can also cause a tumor. Sand, thorns or some plant can get into the middle. In this case, the eye becomes hot to the touch and exudate oozes from it. Trying to remove the item yourself is not recommended. It's best to take your four-legged friend to the vet.
- Avitaminosis. With vitamin deficiency or metabolic disorders, cats sometimes experience inflammation of the eyelids. For simple inflammation (swelling appears and the edges of the eyelids become red), it is important to use an antibiotic ointment. Oxycort and prednisolone will help your pet recover quickly. Phlegmous inflammation manifests itself in the form of swelling of the eyelid and is accompanied by a purulent abscess. If a cat has such a tumor under the eye, it is recommended to immediately visit a veterinarian and open the abscess. The specialist may prescribe a course of injections, as well as further washing of the eyelid with chamomile or a 3% solution of boric acid.
- Conjunctivitis and keratitis. Inflammation of the eye in the form of conjunctivitis and keratitis is another reason for the formation of a tumor. In the first case, swelling appears around the eye, and redness is also noticed. With conjunctivitis, most often there is increased lacrimation and accumulation of mucous secretions in the corner of the eye. To treat the disease, eye drops are used (0.25% solution of novocaine or chloramphenicol, as well as sofradex or 1% solution of kanamycin).
- Oncology. The previously listed types of eye diseases respond well to treatment. If you quickly determine the cause of the swelling of the eye and undergo a course of procedures, your pet will soon recover. In some cases, a tumor under a cat's eye may indicate the presence of cancer. The pet loses vision and develops swelling under the eyes. Only a veterinarian must treat a malignant tumor.
- Blepharitis. Cats sometimes develop swelling under the eye due to inflammation of the eyelids - blepharitis. In addition to swelling of the eyelids, such a pathology is also accompanied by painful sensations. The eyelids become hot and tense when touched. Blinking provokes painful sensations in your pet, which is why most often he lies with his eyes closed.
- Heart and kidney disease. If a cat's eyelids are swollen, then in some cases this indicates a dangerous disease of the internal organs. In this case, the excretory and cardiovascular systems suffer. The general malaise of the cat should alert its owner. A veterinarian must diagnose and treat the disease.
Conjunctivitis in cats
This disease manifests itself in inflammation of the conjunctiva, a thin mucous tissue located between the eyelid and the eyeball. There are many factors contributing to the development of the disease: from colds and the presence of parasites in the body to allergies and exposure to chemicals.
INTERESTING TO KNOW: If a cat shakes its head and scratches its ears
Characteristic signs of the disease are inflamed eyes, discharge from them (initially transparent, then purulent green or yellow). Often, a cat’s eyes cannot open when waking up due to pus sticking together the eyelids. The fur around the eyes sticks together.
Conjunctivitis has several types:
- Allergic. Caused by contact with an allergen. Tears flow from the eyes, which, if left untreated, turn into pus.
- Catarrhal acute. It is characterized by redness, swelling of the eyes, mucous discharge and increased lacrimation.
- Follicular. In addition to the mucous membrane of the eyelid, the lymphatic follicles located on the inside of the eyelid also become inflamed.
- Phlegmous. One of the most severe forms. Pus is not only released outside, but is also located in the subepithelial layer of the entire conjunctiva.
- Purulent. Purulent mucus is released from the eyes, there is a general deterioration in the condition caused by the inflammatory process, and the temperature rises. Vomiting and diarrhea are common.
What to do in such cases and how to treat it at home? Therapy for conjunctivitis consists of regularly washing the eyes with a warm decoction of calendula or strong brewed tea and using chloramphenicol drops or tetracycline ointment. Not one eye should be treated, but both, even if there is no inflammation on the second eye.
It is not recommended to use potassium permanganate or furatsilin, as an error with the dosage can lead to a burn of the conjunctiva. You should also not use plain water for rinsing, as this will disrupt the microflora of the eyes, and chamomile decoction, which promotes baldness of the eyelids.
Cotton fibers increase lacrimation, so it is better to use cotton swabs.
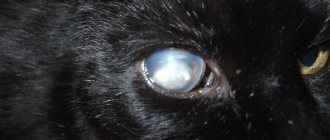
Swollen eyes in a cat photo
It should be remembered that if a cat's eye is swollen and itchy, then there is a high probability of developing an allergic reaction. If pus is present, the process could be complicated by a bacterial infection. If any of these symptoms occur, it is best to take your pet to the vet, as cytology may be needed to make a correct diagnosis.
Keratitis in cats
An inflamed eye in a cat may be a sign of keratitis, which refers to inflammation of the cornea. It is not difficult to recognize: a healthy eye has a shiny and transparent cornea, while a sick eye has a cloudy, rough cornea.
The causes of the disease can be injuries, infections. There are three types of keratitis:
- purulent superficial,
- vascular superficial,
- purulent deep.
With purulent superficial, the epithelial layer of the cornea is affected. The animal develops photophobia, the eyes swell, and the cornea takes on an unhealthy gray tint.
Vascular keratitis of the eyes in cats is characterized by the growth of capillaries into the upper layers of the cornea, which causes clouding of the eye.
The development of purulent deep keratitis is facilitated by microbes that penetrate the corneal stroma. This is the most serious form of the disease. The cornea becomes white-yellow, capillaries grow into the cornea.
INTERESTING TO KNOW: Symptoms and treatment of calcevirus infection in cats and kittens
It is difficult to cure keratitis, and the prognosis is not always favorable. Hormonal, antimicrobial drugs, and antibiotic eye drops are indicated.
Eye damage by helminths
Contrary to popular belief, helminths are not only intestinal parasites. Many types of worms spread throughout the body through the bloodstream, depositing larvae in all organs, including the eyes.
The cat develops severe inflammation and swelling of the eyes, which does not subside within several days, despite local treatment. If your cheek is swollen, it means that the swelling has spread downwards.
To cope with helminths and determine which type of helminths attacked the cat’s eyes, it is necessary to undergo many tests. The outcome of treatment depends on the growth stage of the larvae. Therapy is medicinal, aimed at expelling parasites from the body, but if the dynamics are negative, surgery is indicated.
Prevention of eye diseases in cats
If you notice that your cat's eyes are swollen, covered with a white or bluish film, watery, or their lens is cloudy, immediately take your pet to a veterinary clinic. Never self-medicate because this can make the situation worse.
It is possible that you will use the wrong drugs or exceed the dosage, thereby harming the animal.
There are a number of preventive measures that can be followed to avoid eye problems:
- Timely vaccination. Vaccinations will help strengthen the immune system, which will protect the cat’s body from dangerous infections. Her risk of developing, for example, keratitis is much lower.
- Examine the animal's eyes after each walk.
- Maintain cleanliness in the room where the animal is kept. Regularly wash the floors there, wipe off the dust so that it cannot get on the mucous membrane and under the eyelid and thereby provoke inflammation.
- Combing the fur so that the hairs do not get into the eyes, rub the cornea and conjunctiva and do not provoke their inflammation.
- Proper balanced nutrition, monitoring the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, since some eye diseases, for example, feline blepharitis, can occur due to dysbiosis.
To keep kittens always healthy, periodically wash their eyes using special products. Your veterinarian will help you choose them based on the individual characteristics of your pet’s body.
The animal's eyes are watery: reasons
Tearing can occur either from natural causes or as a result of illness.
In the first case, tears from the eyes may appear:
- After the furry animal woke up. This is a normal reaction of the body. The cat removes traces of tears itself by washing its face. For kittens, you can wash their eyesight with a swab moistened with boiled water.
- If the cat belongs to a certain breed. The Persian, the British, the Sphinx have tears and a peculiarity of the body. Persians are too fluffy, and doctors often diagnose the Sphynx breed with a disease called “entropion.” In this case, the animal can only be cured by resorting to surgery.
- If hair fibers get on the cornea. This symptom often occurs in long-haired small carnivores. The only thing that will help your cat is regular eye care.
In the second case, the cat may cry due to:
- Mechanical damage, injuries. A pet can damage the eyelid, eye, or cornea in a confrontation with another representative of its breed, during play or a walk. A sharp blade of grass or a twig that scratches the organ of vision can cause serious inflammation.
- Foreign objects. A small speck, a piece of tree bark, or a piece of plastic is enough to cause an inflammatory process to develop in a cat’s eye. Treatment in this case includes procedures for treating with solutions of antibacterial drugs.
- Burn. Curious animals often stick their noses into everything they find at home. Aggressive household chemicals, solvents, and wood varnish can become an object of curiosity, which will lead to a chemical burn. A pet can get a thermal burn if it becomes interested in cooking in the kitchen.
- Allergic reaction. Allergies are the scourge of the modern world; not only people, but also animals are susceptible to manifestations of allergies to various irritants.
- Incorrect eyelash growth. Sometimes a cat has a pathology - the eyelashes grow incorrectly, causing the pet a lot of suffering: the eyelid is inflamed, tears constantly ooze. In this case, the help of a veterinarian is required.
- Helminth infections. One of the signs of the disease is increased production of tears.
- Conjunctivitis. The infection is caused by chlamydia; only a veterinarian can cure the little predator.
- Colds. A cat often cries if it has a cold.
Be sure to read:
A cat sneezes: causes, symptoms, what to do, treatment methods, what should alert you