Ascites in dogs is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. Another name for the disease is dropsy of the abdomen. The accumulated fluid is called transudate.
In the abdominal cavity in the normal state there is a small amount of fluid, which ensures normal sliding of the abdominal layers and prevents the internal organs from sticking together. But in some pathologies, too much of this fluid accumulates and it ceases to be absorbed by the peritoneum.
The most important thing to understand is that ascites is not a disease. This is a consequence and a symptom that something is wrong in the body. There can be many reasons why transudate accumulates in the abdominal cavity. There is no point in simply pumping out excess liquid until we understand where it came from. In this article we will try to figure it all out.
Causes and types of ascites
Types of ascites differ in the cause and nature of the fluid.
Ascites almost always develops as a result of increased blood flow in the internal organs. There may be many reasons for this:
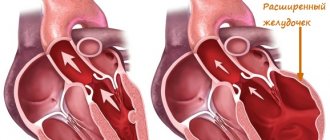
- Most often this occurs due to a malfunction of the heart. For example, with heart failure or heart defects.
- Another common cause is various liver tumors, both primary and metastases from other organs.
- Other liver pathologies are cirrhosis or fibrosis.
- Vascular disorders (which also occur in the liver), such as portal vein embolism or portocaval shunt formation.
- Increased pressure in the vena cava (the risk of developing ascites appears when the pressure in the caudal vena cava increases to 15 - 20 cm of water column, while the norm is 2 - 7 cm).
- For kidney failure or other kidney problems.
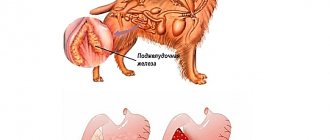
- Ascites can occur with pancreatitis. This usually occurs as a result of severe trauma that ruptures the pancreas.
- Protein starvation, namely hypoalbunemia.
- The basis of ascites transudate is lymph - edematous fluid not associated with inflammatory processes. However, other fluids can be mixed with it: blood from internal bleeding (occurs from injuries) and exudate - this is a purulent-inflammatory fluid. It can accumulate in the abdominal cavity due to gastrointestinal pathologies (for example, intestinal obstruction).
Symptoms and dangers
Dogs have a very difficult time with ascites. The amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity can be from 1 to 10 liters.
In this case, compression of the internal organs and strong pressure on the peritoneum occurs. In some cases, ascites can even lead to death, so it is very important to contact a veterinarian in time.
It is not difficult to suspect this disease - the clinical picture is very clear:
- a very “bloated” belly. It is important that the abdominal enlargement is symmetrical. In small dogs this can be noticed already in the first day, in large dogs it is more difficult;
- with an unnaturally huge belly, the dog loses weight, its ribs literally begin to show through;
- arch in the back;
- noticeable shortness of breath, initially with active movements, then even when walking. The symptoms listed above are specifically for dropsy of the abdomen. This condition is accompanied by signs of the underlying disease;
- with liver pathologies, the mucous membranes become icteric;
- With kidney disease, increased water consumption and frequent urination are possible.
Indications for use
Indication for this procedure is the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. May be accompanied by severe abdominal pain, fever, and clinical signs of shock.
Laparocentesis is a very sensitive method in the diagnosis of peritonitis, tumor formation in the abdominal cavity, pancreatitis, congestive heart failure, and intra-abdominal bleeding.
Abdominal puncture is performed under ultrasound guidance or blindly. So, if there is more than ml/kg of free fluid, the doctor performs laparocentesis without ultrasound control. With a smaller volume, a false negative result is possible, since fluid accumulates around the abdominal organs or in the omentum. It is also possible for fluid to accumulate inside peculiar pockets.
A false positive result can be obtained by puncturing the liver or spleen.
During the procedure, the doctor monitors the formation of blood clots in the lumen of the needle, since rapid blood clotting indicates damage to the abdominal organs during puncture.
Diagnostics
Despite obvious clinical signs, you first need to establish for sure that the dog has abdominal hydrops.
Signs similar to ascites are characterized by:
- full bladder;
- pregnancy;
- ovarian cysts in females;
- prostate cysts in males;
- pathological changes in the uterus;
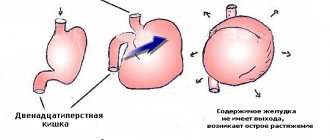
- acute dilatation of the stomach.
If, based on a full examination, if necessary, using additional methods, ascites is established, this is not the end.
Diagnosis is just beginning - it is very important to establish the true disease that caused dropsy.
First of all, it is worth analyzing the ascites fluid. A puncture is made and a small amount of fluid is collected for analysis.
Attention! There is no need to immediately pump out a large amount of transudate! This will not lead to recovery and, moreover, may worsen the pet’s condition!
Based on this study, in most cases it is already possible to make a diagnosis or build a plan for further diagnosis.
Standard diagnostic plan:
- An x-ray of the abdominal cavity is required to assess the condition of the internal organs.
- If necessary, an abdominal ultrasound is prescribed for a more accurate picture.
- A common cause of congestive ascites is cardiac disorders (heart pathologies) - we conduct a cardiac examination, including: ultrasound of the heart, ECG and chest X-ray.
- It is also necessary to conduct a clinical and biochemical blood test. Particular attention is paid to liver enzymes, urea, bilirubin levels (bile pigment) and protein levels (they look at albumin rather than total protein).
- If abnormalities in the liver are established, then portography may be a significant diagnostic method (this is an X-ray examination of the portal vein after the injection of a contrast agent into it). Thus, damage to the portal blood flow is established, which leads to changes in the liver.
Treatment
At home, you will not be able to provide even first aid to your pet. As soon as you notice the first symptoms of ascites, take your dog to the veterinary clinic as soon as possible.
To begin with, the doctor assesses the general condition of the animal and, if necessary, pumps out a small amount of fluid, enough to alleviate the dog’s condition.
You cannot pump out all the liquid at once, as this may worsen the condition.
The treatment itself is aimed at eliminating the cause of ascites, otherwise there will be no point in pumping out the transudate from the abdominal cavity, since after a while it will accumulate again until the main problem is solved.
There is no single treatment regimen for ascites. It all depends on the cause - the actual disease that caused the ascites, the condition of the dog and many associated factors.
Sometimes you can get by with drug treatment, in other cases, urgent surgical intervention is required.
If the cause of abdominal dropsy is a malignant tumor of the liver, then sometimes the animal cannot be saved.
Causes of abdominal ascites in dogs
Abdominal ascites in dogs never appears out of nowhere, since it is not an independent disease. Dropsy of the abdomen is a complication of any serious illness. Therefore, treatment will directly depend on the correct identification of the underlying disease. Most often, the “culprits” of ascites are:
- Neoplasms of the abdominal cavity;
- Peritonitis;
- Low levels of blood proteins (hypoalbuminemia);
- Heart and respiratory ailments;
- Liver and kidney diseases;
- Obesity/wasting;
- Parasite infestations;
- Peritoneal injuries.
Dog care
After and during treatment, your pet needs special care.
It is necessary to adjust the diet; depending on the underlying disease, the dog may need a special diet.
If it is already known that the dog is prone to ascites, you need to control the amount of fluid consumed and limit the intake of salt into the body.
Carefully and clearly follow all the recommendations of the treating veterinarian if you want your pet to be healthy.
Dropsy in a dog. What to do? Treatment of ascites
Now let's try to understand this issue in detail. If dropsy is diagnosed in dogs, treatment is usually carried out comprehensively. Sometimes they also resort to symptomatic therapy.
Fluid condensation is formed as a result of various inflammations in the body. It is necessary to find out the root cause and cure it, and then the dropsy will disappear on its own.
If the animal’s condition is serious, then an emergency operation is needed - laparocentesis. During this procedure, unnecessary fluid is removed from the abdomen. But this operation does not help for a long time. After all, over time, the liquid will accumulate again, its periodic removal leads to a significant loss of protein, and the pet’s condition worsens significantly.
To compensate for the deficiency of the element, the dog is injected with the drug “Albumin” or the excreted liquid is simply purified, after which it is reintroduced into the body.
After purifying the liquid, 500 IU of heparin is poured into 50 ml. Then the resulting solution is administered intravenously for 48-72 hours. Sometimes toxic substances and mycobacteria are found in the liquid. Therefore, it is necessary to administer antibiotic drugs. With this treatment option, the dog’s condition improves significantly, and sometimes recovery occurs.
Prevention
The development of abdominal hydrops in a dog cannot be predicted. Often the cause may be a congenital abnormality of the circulatory system. However, you can improve your pet’s quality of life to reduce the risk of developing any pathologies.
- You need to be careful when choosing a puppy. Already at this stage there are many pitfalls. If you take a dog from a kennel, you need to be sure of the pedigree of the dog’s parents and that the breeder takes a responsible approach to his business. This is the only way to reduce the risk of congenital anomalies.
- Timely vaccinations and treatments against external and internal parasites will protect your dog from many diseases.
- The diet should be complete and balanced.
Dropsy in dogs. Symptoms of the disease
Now let's look at the symptoms of this disease:
- Big belly. In obese dogs this is hardly noticeable. Therefore, no one focuses their attention on this problem.
- Due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, dogs experience difficulty breathing and shortness of breath.
- The mucous membranes have a bluish tint. If fluid accumulations are associated with liver diseases, then the mucous membranes are icteric.
- The fluid presses on the diaphragm and lungs. Therefore, the dog is forced to sit all the time. Dropsy causes swelling. Although they are often a separate disease.
- If edema with ascites is observed, this may indicate hypoalbuminemia or renal failure.
- Fluid may accumulate in the pleura.
- If a dog has increased thirst and goes to the toilet in small portions, then this almost certainly indicates kidney failure.
- The dog develops physical inactivity. She becomes lethargic and indifferent. The animal loses body weight very quickly, it has no appetite, it is drowsy, and has difficulty moving.
- The muscles atrophy, but the dog's weight increases because there is already a lot of fluid.
- With ascites, the animal constantly feels nauseated due to the presence of an underlying disease (pancreatitis, liver failure, etc.). There are also problems with the gastrointestinal tract and an appetite disorder. In addition, you may notice that the dog is in a bad mood, lethargic, and unwilling to do anything. Another symptom is neat, slow, unnatural movements. This manifests itself during a walk, when a previously active animal moves reluctantly, walks slowly, does not frolic, barely moves its legs, and breathes heavily.
- Rapid pulse, dull coat (tangled, crumpled).
Popular questions
How long can a dog live with ascites?
It all depends on the actual disease that caused the ascites and on the volume of fluid that has accumulated in the abdominal cavity. If the initial disease is easily stopped and help is provided to the animal in a timely manner, then ascites will not affect life expectancy in any way.
Are there any chances to cure a dog from ascites?
The question is, is there a chance to cure a dog from the disease that resulted in ascites? If the cause is a tumor, then the chances are not so great; in other cases, the prognosis is more favorable.
Can you get ascites from a dog?
No, this condition is not contagious to humans or other animals.
Why does ascites build up again after a puncture?
This is not surprising, simply pumping out the fluid does not solve the main problem; you need to fight the disease that led to dropsy.
What to feed when sick?
Once diagnosed, your pet may need a special diet depending on which organ is damaged. If the veterinarian has not received any recommendations on feeding, then the main thing is that the diet is complete and balanced, with sufficient protein content.
Use of diuretics
Sometimes diuretics are prescribed to remove fluid. But potassium is removed in the urine, which is released in this way. To maintain it, you need to use special diuretics. But over time, they cause an imbalance in water and electrolyte metabolism. Therefore, do not abuse such drugs.
Good results can be achieved by using protectors for cardio and liver. They help these organs function normally.
The animal's diet should not contain salt, and fluid intake should be minimal.
Briefly about the main thing
- Ascites or abdominal dropsy is not a disease, it is a symptom of an underlying disease. In this condition, excess fluid of a non-inflammatory nature—transudate—accumulates in the abdominal cavity. Its volume can reach up to 10 liters. This causes severe discomfort and pain to the dog, compression of internal organs occurs and strong pressure on the abdominal wall.
- Most often, dropsy develops due to increased blood flow in the internal organs, as a result of a number of diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver, kidneys or pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The main symptom of dropsy is a symmetrical increase in the volume of the abdomen. Other symptoms are lethargy, loss of appetite, weight loss, sagging back, shortness of breath even in a quiet position. Most often, against the background of ascites, we also see signs of the underlying disease.
- Diagnostics is very important, since only making a correct diagnosis will help cure the dog.
- Treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
- You cannot simply pump out all the fluid from the abdominal cavity; this not only will not solve the problem, but can also lead to a deterioration in the animal’s condition.
Clinical signs
In a dog with ascites, you can observe not only a swollen belly. A sick animal cannot breathe freely , and it is difficult for her to inhale due to the intense tension of the inspiratory muscles, but exhalation is not difficult.
With this disease, the animal may experience problems in the gastrointestinal tract in the form of:
- Constant constipation.
- Diarrhea.
If an animal develops dropsy of the brain, it does not remain in a conscious state for a long time; the clinical picture in such a case is expressed in the form of coma or lethargy. When his pet coughs, the owner can hear the gurgling of the liquid in it.
Due to the occurrence of ascites, the pet develops anorexia . During illness, the animal eats practically nothing; against the background of excessive thinness, the huge belly is very noticeable.