Causes of the disease
There are many factors leading to volvulus. Here are the most common ones:
- congenital abnormal development of the mesentery;
- individual body features, weight and age;
- unbalanced diet;
- feeding on cheap, low-quality feed;
- systematic overeating or undereating (feeding once a day);
- swallowing air while eating, which leads to flatulence;
- walking and physical activity immediately after eating;
- dangerous abdominal injuries;
- chronic pathologies of the stomach and intestines that have not been treated;
- hormonal imbalances;
- genetic predisposition.
Temperament and the degree of resistance to stress are also associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: cheerful and active dogs practically do not suffer from volvulus, while restless animals have to be operated on frequently.
Causes
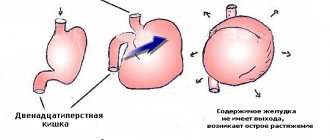
The dog's stomach is an elastic sac connected to the esophagus and intestines on two opposite sides. Food masses, entering it through the esophagus, push air back out. With the help of gastric juice, which dissolves food, the digestion process begins. The stomach, when full, stretches and reaches the lower wall of the abdomen. This ability is responsible for its possible twisting around the esophagus or spleen.
The main causes of this condition have not yet been studied; there are only a number of factors that cause the disease:
- Dimensions, weight and age of the animal. With a large body weight, the internal ligaments stretch and become less elastic. They cannot hold a full stomach in the correct position, which is why torsion occurs.
- Unbalanced diet. Due to cheap feed and a large amount of cereals in the animal’s diet, digestion is disrupted and gastrointestinal problems arise. High-quality food is replaced by a large number of unhealthy foods, which stimulates an increase in appetite and an increase in the amount of food eaten at one meal. The stomach stretches excessively, its walls become thinner and flabby. Such animals run the risk of developing intestinal volvulus.
- Irregular or rare feeding of the animal. Owners who try to feed their pet enough at one time provoke the occurrence of gastrointestinal disorders in it, leading to volvulus.
- Eating food quickly, leading to the swallowing of excess air and dilatation of the stomach.
- Physical activity of the dog on a walk immediately after eating. The stomach, filled with food that has not yet had time to digest, can stretch and twist with the rapid movements of the animal.
- Hereditary factor. Animals whose parents suffered from a similar disease have a very high risk of this disease.
Most often, large breed dogs suffer from this disease: bullmastiffs, Dobermans, shepherds, Great Danes, Labradors. It is treated exclusively surgically after identifying the disease in order to differentiate between dilation and volvulus of the stomach, which have the same clinical picture.
Which breeds are more susceptible
Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in representatives of large breeds with deep chests. These breeds include St. Bernards, Dobermans, Great Danes, Irish Setters, Labradors, Shepherds (German, East European, Central Asian), Bullmastiffs, etc. This is explained by the fact that heavy weight causes ligament weakness and sprains. When stretched, they cannot hold a full stomach in its normal position.
In dogs weighing more than 40 kilograms, the risk of volvulus is enormous.
Main symptoms
It is very easy to determine intestinal volvulus in your pet, since the pathology has a pronounced clinical picture regardless of which part of the gastrointestinal tract is affected. The disease is acute and progresses rapidly. The dog experiences severe wave-like pain of a spasmodic nature. She experiences constipation and uncontrollable vomiting with foam, during which the muscles of the upper peritoneum tense. The most striking symptom of volvulus is the tone of the muscles of the hind limbs. It’s hard for the dog to stand, so he tries to lie down and stretch out his paws. Upon palpation, you can feel a swollen intestine and a tight, swollen abdomen.
The temperature rises to 41 degrees. New symptoms appear: bluish skin, salivation, difficulty breathing.
Having noticed these signs, you cannot hesitate, otherwise the dog may die from acute sepsis. There is no more than 8 hours to save the animal, but we can only talk about a good prognosis if professional help was provided in the first 1-1.5 hours after the attack.
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
Due to the rapid development of pathology, the veterinarian does not have time for diagnosis. The basis for surgical intervention are symptoms of intoxication and rapid heartbeat.
To rule out other diseases, the doctor inserts a gastric tube into the dog, the size of which depends on the animal’s body weight. A probe freely entering the stomach and the release of gases means expansion of the stomach (bloating), but if the passage of the instrument into the organ is impossible, we are talking about intestinal volvulus.
If probing is impossible for some reason, the abdominal cavity is examined using x-rays. This will determine the extent of the damage.
Caring for your pet after surgery
After the end of the operation and recovery from anesthesia, the animal is left in the clinic for 4-5 days. There he is provided with:
- Treating the seam with antiseptic agents.
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Taking gastroprotectors and antiemetics.
- Parenteral feeding after volvulus surgery in dogs.
If the surgical intervention was successful, the pet will be discharged within 5 days after visiting the clinic. He will need to receive further treatment at home. It involves taking gastroprotectors, treating the suture, and taking vitamins. The dog will also need to be provided with complete rest, temporarily isolated from communication with other animals, and follow a diet. Periodically, your pet will need to be taken to the veterinarian. As soon as he is convinced that everything is fine with the animal, the doctor will allow him to return to his previous way of life.
Video: what is volvulus in dogs, its symptoms, signs, treatment
Treatment method and prognosis
Treatment of volvulus - surgery.
The doctor makes an abdominal incision into the abdomen to visually confirm the diagnosis and correct the volvulus. A probe is inserted into the expanded stomach, the remaining food masses are removed from the abdominal cavity, the stomach is washed, after which the organ is sutured to the abdominal wall.
The operation is considered successful if the pathology is completely eliminated and the areas of the intestine that have undergone necrosis are removed.
The duration of the rehabilitation period depends on the complexity of the operation and the condition of the animal. The dog must remain in the clinic for 4-5 days and fed through a catheter. The use of painkillers, antiemetics and antispasmodics, and steroid hormones is indicated.
If the operation is performed in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable.
Treatment of intestinal volvulus (stomach) in dogs
After stomach torsion, the blood supply to the tissues of the organ and its innervation are stopped, which means the cells begin to die, releasing a large amount of toxins into the blood. A general intoxication of the body is created. Owners and veterinarians have only a few hours to promptly accept the animal and provide assistance to it.
The first step after diagnosis is made is to stabilize the animal. An assessment of the general condition is carried out. Vital signs such as the color of visible mucous membranes, heart rate, respiratory rate, capillary refill rate, and blood pressure are measured. Mental status is determined and thermometry is performed. In order to reduce the pressure of the stomach on nearby tissues of the internal organs, several punctures are made with special needles to bleed air.
To adequately correct the volume of circulating blood in the body, intravenous catheters are placed in order to conduct intensive infusion therapy in dosages calculated individually for each dog. The animal must be placed in a hospital for constant monitoring of its condition, oxygenation and correction of vital signs.
Surgery is not the primary treatment option! Only after the animal’s condition has stabilized can it be operated on. In this case, abdominal surgery is performed with access along the white line, during which the stomach is returned to its anatomically correct location. In this case, the stomach is probed through the esophagus and its contents are emptied. Next, the condition of the spleen, pancreas and duodenum must be assessed. Quite often, when the stomach is torsioned, compression of the splenic veins occurs, which also deprives the organ of nutrition and it begins to die.
Khomutinnik Ekaterina Igorevna Chief veterinarian. Candidate of Veterinary Sciences. Specialization: soft tissue surgery, abdominal and thoracic surgery, endosurgery.
If a gastric volvulus occurred more than three hours ago, and changes are observed when examining the spleen, this is grounds for removal of the organ (spleen), the prognosis for recovery of the body in this case will be more favorable. If the spleen is preserved, after this time a very large amount of toxins will enter the blood, which will greatly complicate the recovery process, or even lead to death.
At the end of the operation, gastropexy is performed. This surgical method allows you to prevent recurrent torsions, since the stomach in a certain place is sutured to the inner surface of the abdominal wall, and thus it will not move freely in the abdominal cavity, and therefore cannot twist.
What to do at home
If you suspect a dangerous pathology in your pet, you should under no circumstances panic. You need to act promptly and professionally. You can give an anesthetic injection, calculating the dose based on the dog’s weight. Please note that laxatives and vasoconstrictors should not be given to your dog!
As soon as possible, the pet should be taken to a veterinary clinic, where a doctor will examine it and make a diagnosis.
Upon returning home after discharge from the clinic, the recovering pet should be provided with the most comfortable conditions and good care. The key to recovery is strict adherence to sanitary and hygienic standards, including treating sutures with an antiseptic.
Prevention measures
Like any other disease, volvulus can be prevented by using certain preventive measures. They mainly relate to nutrition, which should be given special attention. The dog should eat strictly twice a day at the same time. The diet is balanced, with a predominance of bone meal, meat, enriched with calcium.
You need to feed your dog after a walk, not before a walk.
If suspicious signs indicating a volvulus appear, you need to inject the dog with an anesthetic and take it to a veterinary clinic as soon as possible.
What is volvulus?
This is a mechanical twisting of internal organs. This pathological condition provokes the development of sepsis and the death of the animal. If the animal does not receive medical assistance within 3-4 hours after its onset, it will die. There are several types of this pathology:
- Twisting of the mesentery, accompanied by compression of the artery. Because of this, the dog's blood flow is disrupted.
- Displacement of the lower intestine. This causes compression of the colon. This pathology provokes the accumulation of toxins in the body.
Other options for displacement of internal organs are possible, however, they are less common. Each of these types, regardless of the cause, can only be eliminated surgically. The owner of the animal needs to remember that if a volvulus is suspected, he should immediately take it to the veterinarian. Any attempts to help your pet on your own will only lead to his painful death.