Features of allergies in dogs and its classification
An allergy is an abnormally increased reaction of the body to some foreign substance that has entered it by any means. Under normal circumstances, everything foreign and harmful is simply removed from the body, but in allergy sufferers a certain inflammatory reaction occurs with the release of histamine into the blood. It is this substance that makes itself felt by redness, rashes and itching anywhere on the body.
Very often, this pathology has a genetic predisposition, and the strength of its manifestation depends on the amount of allergen that enters the body.
Features of the flow:
- more severe symptoms (especially in the manifestation of itching) than in other warm-blooded animals and humans;
- large list of allergens;
- increased manifestations over the years;
- The condition primarily affects the skin of dogs.
The most unpleasant complication of allergic reactions are scratches and wounds that appear due to strong uncontrolled scratching. Open wound surfaces serve as entry points for pathogenic bacteria, so the process is often complicated by purulent inflammation in the areas of scratching.
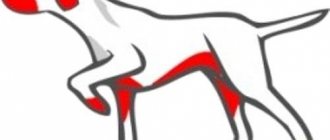
The parts of the body that are most often affected by allergies in dogs can be seen in the photo:
The classification of allergic reactions in dogs combines the types of allergens and the ways they enter the body.
Types of allergies:
- food allergies in dogs;
- medicinal;
- chemical (for animal care products or household chemicals);
- infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal or helminthic);
- insect (reactions to insect bites and cutaneous blood-sucking insects, i.e. allergy to fleas in dogs);
- autoimmune reactions (the rarest form).
Allergic reactions manifest themselves in two ways:
- cumulative (some time after contact with the allergen - up to several weeks);
- instantaneous (almost immediately after interaction).
Antihistamine drops
If the dog cannot take tablets in one form or another, they can be successfully replaced with drops. There are many advantages to using such drugs.
- Can be easily mixed with water or just quickly poured into the animal's mouth.
- They begin to act faster, which means their work is more effective.
The dosage of substances in drops is higher than in tablets, so it is important not to overdo it in an effort to cure your pet.
Zodak
The active substance of cetirizine hydrochloride. Excipients: acetic acid, purified water, propylene glycol, sodium acetate trihydrate. Belongs to the group of competitive histamine antagonists. Blocks receptors.
Prevents the development of a reaction. Improves tolerance of allergy symptoms.
It is prescribed at a dose of 0.25 mg per 1 kg of animal weight. More detailed recommendations will be made by the attending veterinarian. The drug is used over a 7-day course.
Read Treatment of enteritis in dogs at home
Zyrtec
The active substance is cetirizine dihydrochloride. Excipients: lactose monohydrate, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate.
White oblong tablets, before use it is better to dissolve in water or distribute in food. Facilitates the course of an allergic reaction. Has an antipruritic effect. Used for urticaria, fever, year-round or seasonal allergies.
Dosage is approximately 10 mg per day. If Zyrtec is used in the form of drops, then 5 drops once a day. Used for 7 days.
Allergies in dogs: general and specific symptoms
The body of any animal is densely covered with hair, so signs of increased reactivity of the body do not immediately become visible. It is useful to carry out an unobtrusive examination of the skin, muzzle and ears at the moment of direct contact with the dog. It should be noted that the shorter and lighter the coat, the more pronounced and noticeable the symptoms.
The following list of symptoms may indicate that your pet has an allergy.
Locations of allergies
signs of itching (constantly scratching ears, scratching the body, gnawing or actively licking paws, rubbing against the floor or furniture);
- clear nasal discharge and lacrimation;
- peeling and redness on the pads of the paws and in the space between the toes;
- there is a rash, redness, local swelling, scratching;
- dandruff and increased dry skin;
- hair loss, bald spots without visible signs of inflammation;
- signs of inflammation in the ears;
- increased sweating in the chest and armpits (allergic effusion);
- diarrhea or frequent bowel movements without changes in stool status.
Important: dogs do not sweat in the sense in which people are accustomed to understanding the meaning of this physiological phenomenon. The sweat glands in these animals, which control thermoregulation, are located only on the pads of the paws and in the mouth area. Increased humidity in the armpits and in any other part of the body is always a sign of health problems and, most often, a symptom of an allergic reaction!
Specific signs of different types of allergies:
Food |
|
Flea dermatitis |
|
Contact dermatitis |
|
Atopic dermatitis |
|
Infectious | standard symptoms of increased reactivity accompany a primary disease of a fungal, viral or bacterial nature. |
Medicinal |
|
Allergic otitis media |
|
Autoimmune |
|
Photos of types of allergies
| Autoimmune cutaneous vasculitis | Allergic otitis media | Interdigital dermatitis | Drug allergy |
| Food allergies | Quincke's edema with anaphylaxis | Erythema multiforme | lupus erythematosus |
| Flea dermatitis | Hives | Atopic dermatitis | Bullous pemphigoid |
Anaphylactic shock in a dog: symptoms, first aid
Regardless of what causes anaphylaxis, it always occurs the same way. It can be local and systemic, and the first form can transform into the second. Most often it occurs due to bites or injection of drugs.
Local manifestation:
- urticaria (local redness, rash, itching);
- angioedema (under the skin and in deep tissue layers).
Systemic signs:
- vomiting and increased agitation, which is replaced by depression;
- respiratory depression;
- cardiovascular failure and possible loss of consciousness.
Important: if there is a risk or actual occurrence of anaphylactic shock, you should immediately take the animal to a veterinary hospital. You have no more than 1 hour to provide first aid to the animal, otherwise it will die!
Actions of the veterinarian:
- Immediate intramuscular administration of suprastin or diphenhydramine - 0.2 ml/kg.
- Intravenous cordiamine 0.02-0.6 ml/kg or subcutaneous sulfocamphocaine 0.2 ml/kg (supports heart function).
- Subcutaneously any of the steroids: hydrocortisone, dexamethasone or dexon - 0.5-1 mg/kg depending on the size of the dog.
- Intravenous “cocktail” of glucose and ascorbic acid in one syringe (m ml + 0.2 ml/kg).
- Intramuscularly 1 amp. immunofana.
Next, after stopping the attack within 24 hours:
- Calcium chloride from 1 to 5 tbsp. - drink during the day.
- Instead of water, it is better to drink a decoction of the string.
- Relieve itching with hydrocortisone spray 2-3 times a day (4 amps of hydrocortisone, 80 ml of alcohol, 50 ml of glycerin, 350 ml of water - put in a hand spray bottle).
Pills
Diazolin
The histamine receptor blocker has an antiallergic effect. Reduces swelling of the mucous membranes. The therapeutic effect appears 30 minutes after use.
It is used for the prevention and treatment of rhinitis, urticaria, angioedema, skin itching, eczema, conjunctivitis and so on.
For small breed dogs, 50 mg is prescribed 2 times a day. For large breed dogs, 50 mg up to 3 times a day. Available in tablet form.
The course lasts up to 7 calendar days. It has good effectiveness, so it is often used in veterinary practice.
Claritin
Main active ingredient: Loratadine. Excipients:
- propylene glycol;
- glycerol;
- lemon acid.
Presented in the form of a clear syrup. The active substance Loratadine is a compound with an antihistamine effect.
Acts as a selective blocker for histamine receptors. Long-term antiallergic effect. Does not affect the central nervous system. Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
It is used for seasonal or year-round allergic exacerbations, rhinitis and conjunctivitis. With enlargement of the nasal mucosa, burning and lacrimation. Used internally, regardless of the time of meal. Prescribed depending on the body weight of the animal.
If your body weight is less than 8 kg, 5 mg per day is prescribed. More than 8 kg - 10 mg per day. The course lasts up to 5 days as prescribed by the doctor.
Cetirizine
Active ingredient: chlorophenyl. The addition is acetic acid.
It is prescribed for pronounced allergic reactions, psoriasis, swelling of the mucous membrane, frequent sneezing, and so on. It is used in a dosage of 5 to 60 mg, depending on the weight and age of the animal.
It is eliminated from the body in approximately 10 hours. It can be used as a prophylaxis in small dosages to alleviate the symptoms of year-round rhinitis.
Read How to treat tick-borne anaplasmosis in a dog: shocking consequences of the disease
Use the products for 5 days as prescribed by your doctor.
Suprastin
Active substance: chloropyramine hydrochloride.
Excipients: stearic acid and gelatin. This is an analogue of a classic antihistamine. It blocks histamine receptors and has a corresponding effect.
It has an antiemetic effect, as well as antispasmodic activity. It is administered orally.
It is used in the dosage specified by the doctor. Adults are prescribed from 75 milligrams per day. Young individuals are prescribed up to 50 mg per day.
The course of admission is no longer than 5 days.
Tavegil
Active substance: clemastine fumarate. Has antipruritic and antiallergic effects.
Used at 2 mg per day. Presented as a solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration.
Storage should be in a protected place. It has an antihistamine effect, reduces inflammation, spasms, pain, and itching.
The course of taking the drug is up to 7 days.
Desloratadine
Active ingredient: desloratadine.
Additional: chlorine and dihydrobenzopyridine.
Presented as a white powder that is slightly soluble in water. Blocks peripheral histamine receptors. Suppresses a whole cascade of cytological reactions.
The drug is used in a dosage of 0.5 to 20 mg, depending on the weight and age of the animal.
On average, when taking the minimum dosage, the drug can be used for up to 2 calendar weeks. If during this time there is no improvement in allergic reactions, an urgent visit to a doctor is required.
Levocetirizine
The active ingredients are levocetirizine, phenyl, methyl and acetic acid.
The formula has a geological antiallergic effect. Levocetirizine is a competitive antagonist for histamine. It blocks its receptors and affects the stage of the allergic reaction, which is considered to be histamine-dependent.
It can prevent the development of allergic reactions and also facilitate their course. It is recommended to use the drug for 5 days.
To take the tablets, it is recommended to dissolve them in water and give the animal in small quantities. So, about 50 mg tablets should be dissolved in 2 ml of water. This dosage is suitable for medium-sized animals. Only a veterinarian will determine the exact dosage, based on the symptoms and performance of the animal.
Diagnostics
Before the diagnosis of allergy is confirmed, the veterinarian will rule out those diseases that have similar clinical manifestations. Differential diagnosis includes skin scrapings, stool analysis for helminths, trichoscopy, bacterial cultures and blood tests, etc.
Because Since the symptoms of all conditions are basically similar, the main diagnostic principle of veterinary dermatology is to exclude potential allergens one by one. The very first reasons that people pay attention to are skin parasites (fleas) and food.
To determine food reactivity, diagnostic nutrition is administered for 1.5-2 months and a protein map is drawn up. During this period, the dog's body's reactions to various food proteins are tested. All reaction results are recorded in a protein map. Products containing proteins that are reactive to the body will need to be excluded for the rest of the animal’s life. There is no other way to find out what food a dog is allergic to! Human tests are absolutely not suitable in this case.
To determine the reaction to fleas and their saliva, use a wet white paper test, visual inspection, and a trial diagnostic treatment. When testing with wet paper, red spots from “black” dandruff combed from the dog’s skin and fur will spread out on the sheet - these are traces of flea activity.
Allergies to other substances in the environment can be determined if owners are attentive to their pets. An attentive owner notices the slightest changes in the health of the pet and the reasons that caused these changes, which are then brought to the attention of the veterinarian. Also, when assuming allergies to plants and their pollen, seasonality is taken into account, and not just external signs of the disease.
Allergy treatment
If a dog has an allergy, only a veterinarian knows how to treat it. Only a specialist must remove the body from a reactive state, because only he can distinguish non-standard reactions from some other infectious and non-communicable diseases that have a similar clinical picture.
Treatment of allergies in dogs is always complex and depends on the type of reaction and its symptomatic manifestations. But regardless of the nuances of the development of the condition, two main points of treatment are present in any case:
- Stopping exposure of the body to allergens.
- Antihistamine therapy - general and local.
Sick or recovering animals are fed with special hypoallergenic food for dogs with allergies, specially designed for such cases. You can also create your diet according to your food diary, excluding all reactive food names.
The same procedure also applies to medications - only those drugs that do not cause allergies can be administered. Drugs that have provoked a non-standard reaction at least once are usually recorded in the animal’s personal medical record or in the veterinary passport.
Features of medical care for different types of allergies:
- Food - determination of the type and elimination of food allergen through a diagnostic diet.
- Insect - removal of all cutaneous blood-sucking insects from the surface of the animal and from its environment.
- Drug - immediate antiallergic or, if necessary, antishock therapy (usually local treatment is not required).
- Infectious - determining the type of infection accompanied by an immune malfunction and eliminating it (without eliminating the cause of the allergy, antihistamine therapy will be ineffective).
- Atopic dermatitis is not completely curable, so symptomatic antihistamine therapy and local antipruritic effects will accompany the dog throughout its life.
- Autoimmune reaction - administration of massive doses of glucocorticoids to relieve exacerbation of the disease, followed by transfer to minimal maintenance doses; therapy that suppresses immune activity so that the body stops “attacking” its own cells and organs;
- symptomatic therapy, depending on which organ or system is “attacked” by the immune system.
- Allergic otitis - against the background of antihistamine therapy, general anti-inflammatory treatment of otitis is carried out.
Preparations for injections
Hormonal allergy medications can be administered either intravenously or intramuscularly. These products are available in the form of solutions in ampoules, suspensions or lyophilized powders in bottles. For dogs can be used:
- Hydrocortisone.
A 2.5% suspension of hydrocortisone acetate is produced by Ukrainian. The package contains 10 ampoules of 2 ml, price - from 300 rubles. - Suprastin.
One of the rather expensive representatives of steroid drugs, a product of the Hungarian pharmaceutical company Egis. Available in 1 ml ampoules, each containing 20 mg of chloropyramine hydrochloride. Price of 1 ampoule - from 130 to 170 rubles. - Prednisolone.
The most popular corticosteroid for systemic use, it has powerful antiallergic and immunosuppressive effects. It is usually administered intravenously. Ampoule solutions of prednisolone sodium phosphate are produced by many domestic and foreign pharmaceutical companies (Russia), Biopharm (Ukraine), Gedeon Richter (Hungary), Ipka Laboratories (India) and others. A package of Prednisolone from Biopharm CJSC costs about 80 rubles. - Diprospan.
An effective means of relieving an acute allergic reaction from American, the active ingredients are betamethasone dipropionate and disodium phosphate. The price of 1 ampoule of Diprospan is 225 rubles. - Metipred.
Injectable preparation based on prednisolone. Available as a lyophilized powder in 250 mg bottles. The cost of 1 bottle is about 500 rubles, (Finland). - Sol-Decortin.
A representative of a new generation of prednisolone-based corticosteroids with a minimized number of side effects. Manufacturer: pharmaceutical corporation Merck KGaA (Germany). - Dexamethasone.
The active substance of the drug dexamethasone sodium has an effect similar to prednisolone. This corticosteroid drug is widely used to provide first aid for severe forms of allergies - edema, anaphylactic shock. Dexamethasone is produced by Russian pharmaceutical companies, Vector, Vostok, Wicher-Pharm, German Bayer, Weimer Pharma, and Polish pharmaceutical companies. A package (5 ampoules of 1 ml each) of the Russian drug costs about 100 rubles.
Attention! The doctor decides whether the dog needs a hormone injection if he has an allergy; he is guided by the results of the examination of the animal, the severity of the disease, the age of the dog and the presence of concomitant diseases. Independent use of hormonal drugs to treat allergies is unacceptable.
Review of Allergy Medicines in Dogs
Due to the peculiarities of the manifestation and course of allergic reactions in dogs, the range of antihistamines allowed for use in them is quite wide. All antihistamines are divided into 3 large groups:
- drugs that reduce the response of H1/2 receptors (what reacts to histamine in the body);
- drugs that bind and remove histamine;
- drugs that prevent the production of histamine.
In dogs, drugs belonging to the first group are most often used, i.e. they reduce the body’s response to histamine circulating in the blood, relax smooth muscles, relieving spasms, reduce swelling by reducing vascular permeability and eliminate other obvious allergic symptoms. The decision on what to give your dog for allergies is made only by a veterinarian!
Diphenhydramine (diphenhydramine)It has a pronounced antihistamine sedative and anti-inflammatory effect. It is used for any reactive failures, including medicinal ones. Administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly in the form of a 1% solution twice a day. Dose: 0.6-0.8 mg/kg animal body weight. |
Diprazine (phenergan, pipolphen, allergan)Effective for dermatitis accompanied by itching. Causes drowsiness. Administered intramuscularly in the form of a 2.5% solution or tablets. Dosage: 4.5-5 mg/kg 2-3 times a day. |
Diazolin (mebhydrolin, incidal, omeril)Prescribed for allergies of unknown origin. Used internally in the form of tablets. Partially inhibits the functioning of the central nervous system. Dose calculation: 3-4 mg/kg once or twice a day. |
Suprastin (allergans)It is used for absolutely all forms of allergies. Has a slight sedative effect. Given in the form of a 2% solution. Dosage: 0.1-0.5 ml twice a day. |
Tavegil (angistan, clemastine)The therapeutic effect is similar to diphenhydramine, but with a longer lasting effect. The dosage is the same for both the 0.1% solution and the tablets: 0.015-0.02 mg/kg 1-2 times a day. |
Ketotifen (astafen, zaditen)Often used for anaphylactic shock, histamine bronchospasm and long-term systematic elimination of allergic reactions (due to the cumulative effect). Dosage: 0.02-0.05 mg/kg. Twice a day course for 2-3 months. |
Astemizole (gismanal)It works well for food allergies, urticaria and rhinitis. They ask inside. Do not use during pregnancy. Dose: 0.3-0.35 mg/kg 2-3 times a day. |
CetirizineAn excellent antiallergic drug that does not cause drowsiness. Once or twice a day. Dose: 0.25-0.5 mg/kg animal weight. |
Loratadine (Claritin)Works well for allergic rhinitis and lacrimation in dogs. Not prescribed to pregnant bitches. Approximate dosage: 0.1-0.15 mg/kg once a day. |
BicarfenAn antihistamine with a broad antiserotonin effect: allergic lacrimation and rhinitis, drug allergies and reactions to food, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, hay fever. Regimen: 1-1.5 mg/kg up to two times daily for 1-2 weeks. In case of seasonal outbreaks, you can repeat the course throughout the year. |
Mechanism of action of antiallergic drugs
Antiallergic drugs for dogs have their own specific effects on the body. The mechanism of action of drugs is based on their ability to reverse inhibition based on histamine receptors.
They do not replace histamine, but they do help block receptors that are not occupied by it for whatever reason. Therefore, drugs are used in situations where it is necessary to prevent an allergic reaction.
The mechanism of action of antiallergic drugs may be weakened due to the obstruction of new batches of histamine in a situation where the disease begins to actively develop. However, modern drugs aimed at suppressing the reaction can affect histamine, serotonin, and leukotrienes.
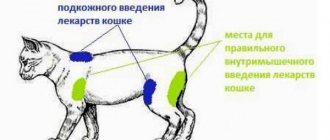
Dog allergy injections
The best way to combat signs of allergies is by injection, which is administered subcutaneously to the dog. Such anti-allergy drugs quickly enter the bloodstream and eliminate the cause of the disease.
True, only a veterinarian has the right to prescribe this method of treatment, based on the following data:
- examination results;
- laboratory research;
- stories from the owners.
The following names are most often used in veterinary practice.
Allervet
Main active ingredient: diphenhydramine. It is the main antiallergic agent. The mechanism of action involves blocking histamine receptors. Histamine is deprived of its application points.
The product can also be used for prophylactic purposes.
The drug reduces the body's response to existing histamine, relieves muscle spasms, reduces the permeability and excitability of capillaries. Designed for small pets or farm animals.
Most often used at the time of manifestation of anaphylaxis, muscular rheumatism, articular rheumatism, as a prevention of vomiting, for diseases of the nervous system, for diseases of the genitourinary tract. The drug is used intramuscularly. Dosage from 0.2 - 0.4 mg per cm3 per 1 kg of weight. Frequency of use up to 4 times a day.
Read Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of piroplasmosis in dogs
The period of taking the drug is up to 5 days, until the symptoms go away.
Hifenadine
The active ingredient is Hifenadine. The drug is presented as a white cross-shaped powder, which has a bitter taste and is odorless. Slightly soluble in alcohol or water. Blocks histamine receptors. Affects the activation of histamine.
Reduces the amount of mediator in muscle tissue. Relieves spasms on smooth muscles in the intestines. Has a hypotensive effect.
Prescribed when:
- rhinitis;
- hives;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- skin itching.
Animals under 3 years old: 5 mg 2 times a day. For older animals up to three times a day. The dose is prescribed by the veterinarian. During treatment, care must be taken, as sometimes the treatment is accompanied by dizziness. The course lasts up to 7 days, after which the use of the drug is reduced to zero.