Classification of eye melanoma
Depending on the area of location, there is the following classification of melanoma:
- Skin of the eyelid is rare and belongs to the category of cutaneous or subcutaneous disorders. This type of cancer is considered very aggressive. It is almost always formed from pigmenting tissues. At the initial stage of development, the pathology resembles a fungal tumor with a stalk and bright coloring. The surface is bumpy and covered with small cracks. The formation contains papillary tubercles. The pathology quickly metastasizes, affecting the brain, liver, kidneys, and lymph.
- Conjunctiva - is a consequence of nevi. In appearance, the formation resembles a hard tubercle with clear boundaries. It rarely grows deep into tissues and is predominantly located on the surface. Pathology can be single or multiple. It is characterized by slow growth and has a tendency to metastasize early.
- Choroid - can be nodular, planar, diffuse and located in any zone of the organ. A characteristic feature of the formation is its dark brown color. It has a spongy structure and a rough surface.
As the disease progresses, it affects the main part of the retina and causes a sharp decrease in vision. Sometimes a person loses it completely. Most often, education is of a multiple nature. The pathology is not characterized by a very rapid development and is considered non-aggressive. It is not prone to early metastases.
Depending on the stage of development, melanoma is classified according to the following TNM parameters:
- Category B – in this case, the formation is located in the deep structures of the skin. It is insignificant, does not show activity and does not metastasize.
- Category N - shows the localization of the formation in the structure of the organ in combination with its partial germination into adjacent lymph nodes. These are where the first metastases occur.
- Category M - in this case, melanoma leaves the organ and grows into nearby organs and systems. In such a situation, metastases affect the internal organs, circulatory and lymphatic systems.
Diagnosis of cancer
If there is any suspicion of the presence of a disease, the following studies are carried out:
- Blood and urine tests to evaluate organ function.
- X-ray. Helps detect the presence of metastases in the animal’s body.
- Ultrasound. Using this method, the presence of a tumor can be detected.
- Biopsy. This is done in different ways: tumor cells are taken using a special syringe or endoscope, or during surgery material can be taken for examination. This is the most accurate method for diagnosing the disease.
Stages of eye melanoma
Ocular melanoma is divided into certain stages, depending on the depth of germination of malignant cells, the degree of their aggressiveness and the tendency to metastasize.
Based on these parameters, the following stages of the disease are distinguished:
- The first is that the formation has limited dimensions and a latent course. It does not exceed a few millimeters in diameter and is single. The tumor is immobile and does not metastasize. There are almost no manifestations.
- The second is that the tumor develops and gradually enters the deep structures of the retina. At the same time, the integrity of the adjacent lymph nodes is preserved. The likelihood of a multiple nature of the disease is minimal. In this case, chaotic cell division occurs faster. This process becomes uncontrollable.
- Third – the first ulcerations appear. In this case, the adjacent lymph nodes and soft tissues that surround the formation suffer. Pathology goes beyond the original boundaries. In this case, severe symptoms and pain of varying degrees of intensity occur.
- Fourth, at this stage even progressive therapy does not produce results. All efforts are aimed at relieving symptoms and improving a person’s quality of life.
Stages of development of breast tumors
The most common type of cancer found in unsterilized cats.
It is characterized by the appearance of lumps (tumors) inside the animal’s mammary glands, which gradually increase in size and can open in the final stages of the disease.
Sterilization is a method that will almost 100% protect your animal from this type of cancer.
By analogy with humans, breast cancer in cats develops from stage 1 to the most complex fourth stage of development. Veterinarians classify the recognition of these stages (degrees) in accordance with clinical signs. Each of them has its own course:
- The first stage is characterized by small compactions. They are painless and do not bother the animal. The size of the lymph nodes at the first stage is not increased. If the owner is lucky enough to discover such a formation and contact a veterinarian for treatment, his pet has a chance for a full recovery;
- the period of the second stage is the appearance of denser neoplasms, reaching three centimeters in diameter. At this stage, surgery can be done, since the tumor on the cat’s chest is operable. The animal can live another year or a little more;
- at the third stage, the tumor acquires dimensions exceeding three centimeters in diameter. Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs. The cat does not allow the chest to be touched, since this area is affected by the disease, and touching the wound causes pain in the animal;
- stage four cancer is incurable. A neoplasm on a cat’s body is visible to the naked eye. The tumor is significant in size. The parameters of the lymph nodes are greatly exceeded. The cat is emaciated. There are metastases in her body. Surgery at the fourth stage of cancer does not give practically any positive results. In fact, it is useless. To prevent the cat from suffering from pain in the last days of its life, it is given painkillers. Natural death occurs quickly, and especially severe cases require euthanasia of the animal.
Causes of eye melanoma
The exact causes that cause melanoma have not yet been established.
But doctors suggest that the risk of developing the disease increases under the influence of such factors:
- A large number of ultraviolet streams. This category includes both natural sun rays and the radiation that a person receives in a solarium. This reason is considered the main one.
- Light skin, brown hair, gray or blue eyes. People with this type of appearance react worse to external factors. Their tissues have difficulty resisting radiation and quickly transmit it through the skin. As a result, harmful radiation accumulates inside.
- Old sunburn. Even after many years, they can provoke the appearance of a tumor. A destroyed cell lattice can change at the molecular level, which leads to uncontrolled cell division. As a result, they become malignant. These processes provoke the formation of compaction. Over time, it turns into a tumor.
- Genetic predisposition. It has been proven that a tendency to cancer can be inherited even at the stage of fetal formation.
- Age. Natural aging of the body impairs tissue restoration; they become more susceptible to external factors. As a result, there is a risk of the formation of malignant tumors on the surface of the dermis.
Spotting and Understanding Melanoma in Cats and Dogs - Tips for Pets - 2021
With summer and hot weather just around the corner, it's the time of year when people start breaking out their sunscreens to reduce their risk of skin cancer. However, you need to think about your beloved pets because leaving them in the hot sun could mean they develop sun-induced tumors called melanoma. Just because your pet, whether it's a dog, cat, rabbit or other four-legged pet, has a furry coat doesn't mean they aren't susceptible to sun damage, and one of the things you need to watch out for is cancer skin,
Melanoma in cats and dogs does not look the same as in humans, but it is just as dangerous and deadly. Below are a few signs that can help you know if this nasty disease has taken over and help you distinguish whether it is really melanoma or some other condition that looks very similar. With that said, if you notice any strange marks on your pet's skin, you should take them to the vet as soon as you can.
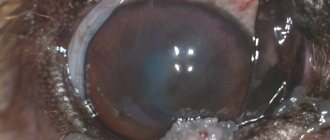
Melanoma of the eye in a cat
Ocular melanoma is more common in older cats. As a rule, it is a malignant tumor that is formed from pigment cells that produce melanin. It is a dark formation that has jagged edges. Sometimes light melanomas occur.
This pathology is characterized by early and rapid metastasis. Most often, the lymph nodes that are localized near the tumor are affected. The only method to combat formation in cats is to remove the eye. Before the operation, you need to perform an x-ray, which will help identify metastases in the lungs. If they are not, surgery will save the animal's life.
How to prevent neoplasms?
All animals over 5 years old must be seen by an ophthalmologist once every six months for a preventive examination. The sooner a tumor is diagnosed and operated on, the greater the chance of saving the animal’s life.
We suggest you read: How to properly put on a cat harness
Even such a slight change in eye color can be a serious tumor with a high risk of metastasis.
Come to us for a consultation WITH ANY even minor pathology, OTHERWISE IT WILL BE LATE!
Diagnosis of eye melanoma
Melanoma can be quite difficult to diagnose. At the initial stage of development, it is disguised as other processes. The optometrist should perform a general examination.
Based on its results, he prescribes additional procedures:
- Ophthalmoscopy is the main method for diagnosing melanoma and other eye pathologies.
- Fluorescein angiography is aimed at examining the ocular vessels. The procedure helps to identify changes in blood vessels, the level of development and structure of the network that feeds the tumor.
- X-ray – allows you to detect damage to the bone elements of the orbit. It can also be used to identify distant metastases in other organs.
- Radioisotope scanning is a diagnostic procedure that involves introducing radioactive isotopes into the bloodstream. The fact is that the metabolism of the tumor is significantly accelerated when compared with healthy tissues. Therefore, isotopes accumulate in it faster. Their high concentration is recorded using a radioisotope scanner.
- Biomicroscopy – eye tissues are studied using a microscope.
- Measuring intraocular pressure - deviation of this indicator in a certain direction can be an indirect symptom of a tumor.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used to assess the extent of spread of the abnormal process to nearby tissues. They also help to find metastases of formation in other organs.
- Histological examination - it can be carried out only after removal of the tumor. Preliminary biopsy of fragments is dangerous. It can cause metastasis.
Causes, symptoms and diagnosis
Doctors have never been able to completely determine what exactly causes melanoma. Malignant cells form in melancytes and lead to DNA mutation. They multiply very quickly, turning healthy cells that should die over time into mutated ones.
To detect a disease in an animal in time, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- swelling of the eyelid and surrounding tissues;
- corneal clouding;
- red conjunctiva;
- tears and other secretions;
- the appearance of ulcers on the eyelid, bleeding;
- decreased visual acuity;
- the appearance of dark spots on the surface of the eye.
If the disease is not detected in time, it can develop into secondary glaucoma, uveitis, and intraocular hemorrhages.
Since this is a serious disease, careful diagnosis is required, which is carried out only in specialized clinics with the necessary equipment. To make a diagnosis, the following is performed:
- visual assessment;
- biomicroscopy;
- palpation of tissue around the tumor;
- checking intraocular pressure;
- collection of urine and blood for analysis;
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- MRI and RCT;
- biopsy.
Only after the doctor receives all the results can he prescribe medical procedures for the animal.
Treatment of eye melanoma
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the location and size of the melanoma. It's also worth considering your overall health and personal preferences.
A small tumor may not require treatment. If it does not grow, the doctor may take a wait-and-see approach and monitor for signs of growth development. If melanoma begins to grow or complications appear, it is necessary to begin therapy.
Surgery used to treat melanoma may involve removing specific structures or the entire eye. If surgery is aimed at removing melanoma, it is performed within healthy tissue. This procedure is carried out to get rid of small formations.
The extent of surgical intervention depends on the size and location of the formation. The procedure to remove a small tumor on the iris is called an iridectomy. An intervention to remove a tumor on the choroid is called a choroidectomy.
Surgery may also be performed to remove the entire eye. It is called enucleation. This procedure is performed to get rid of large tumors. It is also used if the tumor provokes pain.
After the eye is removed, an implant is inserted in the same position. In this case, the muscles that control eye movement are attached to it. This ensures motor activity. Some time after the operation, a prosthesis is inserted instead of the implant.
Radiation therapy can also be used to treat pathology. It is used to fight small or medium-sized tumors. As a rule, brachytherapy is used. To do this, a radiation source is placed in the eyeball and sutures are applied. After 4-5 days it is removed.
Another treatment option is the use of a laser. Sometimes it is combined with radiation therapy. An infrared laser is used for this purpose.
Treatment
You can detect skin cancer in cats yourself, based on many photos of samples of diseased skin areas. The course of treatment depends not only on the stage of cancer, but also on the general condition of the cat or dog. In the initial stages, chemotherapy and radiation are performed. In severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Chemotherapy and radiation procedures have a very strong effect on the entire body of a pet. Most likely, his health will be poor. Don't be alarmed, this is a side effect of serious treatment. There are many drugs and remedies that alleviate the serious condition of the animal. There is no need to hesitate to consult a doctor in this matter. In any case, it should be borne in mind that the animal will need special care and attention.
We suggest you read: What smell cats don’t like so they don’t shit
Skin cancer in the early stages can be treated without surgery. But at any stage, treatment brings a noticeable improvement in the patient’s well-being. To prevent the disease from progressing, you need to carefully monitor your pet’s condition and contact a specialist at the first suspicion. You can consult with several doctors in parallel to choose the most optimal treatment option.
To prevent melanoma and skin cancer, the animal should be protected from direct sunlight during peak solar activity hours. As a rule, this is the period from 10 to 15 hours.
After the disease is diagnosed, one of the types of treatment (the most appropriate in this case) is prescribed.
Treatment methods are often combined. The success of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the animal’s immunity and your attitude towards treating your pet.
Complications of eye melanoma
If measures are not taken promptly, melanoma can cause dangerous complications.
These include the following:
- Increased pressure in the structure of the eye. As melanoma progresses, there is a risk of developing glaucoma. Symptoms include pain and redness of the eyes. There is also a risk of decreased vision clarity.
- Blindness. Large tumors often cause vision loss in the affected eye and can cause dangerous complications. These include retinal detachment, which can also cause blindness. Small tumors can lead to vision loss if localized in critical areas. In such a situation, there is a risk of impaired central or peripheral vision. Common formations can provoke vision loss.
- Spread of tumor outside the eyes. The tumor can metastasize to distant organs. These include the liver, bone tissue, and lungs.
Melanomas may be difficult to detect
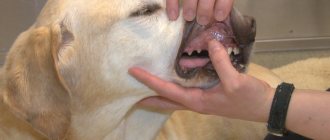
Unlike in humans, where melanoma can be easily felt or felt, melanoma can be difficult to see in dogs, cats, and other pets due to the fur on their bodies. However, the most common melanoma in dogs is oral, and to a lesser extent the same can be said for cats. If your pet doesn't feel comfortable when you open your mouth to examine them, you should leave it with the vet, so it's important that pets have regular health checks. However, if you notice that your pet is suffering from a bad case of halitosis, it could be a sign that there is something very wrong.
If your pet allows you to examine the inside of their mouth and you notice any black and raised areas on their gums that are bleeding, then it could be oral melanoma. You should take your pet to the vet as soon as you can so they can calm your cat down and look at the problem carefully. The veterinarian may want to do a biopsy to make a proper diagnosis and then recommend surgery or radiation therapy. These days, however, there is a vaccine to treat oral melanoma tumors, but you need to remember that it is a treatment, not a cure.
Looking for free pet advice for your pet?. Click here to join the UKs favorite pet community - PetForums.co.uk
Feline melanoma
This is one of the most difficult feline melanomas because it first attacks the iris, which is the colored part of your pet's eye. Melanoma may initially appear as a simple freckle on their eyes, but over time the freckle becomes larger and larger, covering more of the iris as it happens. If you notice a dark spot in your cat's eyes, you should make an appointment and take your pet to see a veterinarian, who would recommend that your cat see a veterinary ophthalmologist to determine whether the melanoma is cancerous or not.
If the results come back because the melanoma is cancerous, the best course of action would be to have your cat's eyes removed, as this is the only way to prevent the tumor from spreading, and although it may be a difficult decision, having the eyes removed means that they will be able to live much longer than if the eye is left in.
Veterinary clinic of Dr. Shubin
Description, biology, behavior
Malignant melanoma of the oral cavity is the most common malignant tumor of the oral cavity of dogs, with a predisposition in older animals (average age 11 years). A possible predisposition to the development of melanoma has been described in the Cocker Spaniel, the German Cattle Dog, and dogs with severe pigmentation of the oral mucosa. It is very rare in cats.
Biology, behavior
Melanoma that develops in areas not exposed to the sun (eg, the oral cavity), compared with melanoma that develops in areas of sun exposure (eg, the skin), is characterized by different biological behavior and a different mechanism of biological transformation. A distinctive feature of malignant melanoma of the oral cavity is: local infiltration, the formation of relapses after surgical excision and a high metastatic potential to regional lymph nodes, lungs and some other organs. Therefore, malignant melanoma of the oral cavity is almost always regarded as a malignant tumor with aggressive behavior.
As mentioned above, malignant melanoma of the oral cavity has a high malignant potential and often metastasizes to regional lymph nodes and lungs. The frequency of metastasis of this tumor in dogs depends on the size of the tumor, location and stage, the average frequency is 80%. Malignant melanoma also has a high immunogenic potential, and today there is active research into molecular and immunomodulatory approaches to its treatment.
Clinical signs
Compared with other oral malignancies, malignant melanoma is more common in low-weight dogs, with a predisposition in the following breeds: Cocker Spaniel, Miniature Poodle, Anatolian Cattle Dog, Gordon Setter, Chow Chow, and Golden Retriever. Also, some predisposition has been noted in males, but it has not been definitively determined. The average age of development of oral malignant melanoma in dogs is 11.4 years. Oral melanoma is reported quite rarely in cats.
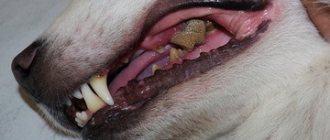
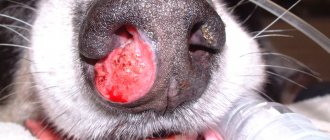
Malignant melanoma of the oral cavity can be located in any part of the mouth; the most typical locations are listed below in descending order: gums, mucous membrane of the cheeks or lips, upper palate, dorsal surface of the tongue. In its classic form, melanoma is black in appearance, however, the amelanotic form of melanoma (up to 1/3 of cases) can be pink or red in appearance. When located on the gum, there is often involvement of the underlying bone and tooth decay. Malignant melanoma of the canine oral cavity grows quite quickly, leading to the formation of a significant volume of masses before treatment begins.
Diagnostics
The final diagnosis of malignant melanoma is determined by pathological examination of a tumor sample. An excisional biopsy should be performed for any suspicion of melanoma; Despite the size of the tumor, you should always remember the severity of the disease, the growth rate and the high potential for the development of metastases (remember the aggressive behavior).
If melanin is present in tumor samples, pathomorphological diagnosis does not cause difficulties, and even with cytological examination, reliable results can be obtained. About 1/3 of cases of malignant melanoma of the oral cavity are accompanied by the development of a special form - amelanotic (pigmentless, without melanin) melanoma, while making a pathomorphological diagnosis is quite difficult. To facilitate the diagnosis of such cases, immunohistochemical staining with Melan A pigment is used; this type of study has pronounced sensitivity and specificity in making a final diagnosis. It should be remembered that in the case of the amelanotic form of melanoma, making a final diagnosis is not achievable in 100% of cases.
To stage a tumor according to the TNM classification, a dental radiographic examination is performed, which determines the involvement of the underlying bones in the process. Also, the condition of regional lymph nodes is assessed, and if they are enlarged, a biopsy is performed. The lungs are assessed through radiographic examination in 3 projections; The purpose of this type of examination is to identify metastases. Also, a search for joint diseases is carried out, the following diagnostic tests are usually used - general blood test, biochemical panel, ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
In the differential diagnosis of malignant melanoma of the oral cavity, other mouth tumors are taken into account - lymphoma, mastocytoma, histiocytoma, plasmacytoma, carcinoma, sarcoma, osteogenic formations.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment options for malignant melanoma of the canine mouth include: surgical excision; irradiation; chemotherapy, immunotherapy.
The treatment of choice is complete en bloc surgical excision of the tumor, involving 1.5-2 cm of healthy tissue, especially for tumors localized in the rostral part of the oral cavity. In cases where surgical excision of the tumor is not achievable, irradiation is used (if it is large in size or localized in the caudal part of the oral cavity).
For malignant melanoma of the oral cavity, a large resection is often performed; it includes removal of half of the lower and upper jaw, removal of the orbit, and radical removal of the upper jaw. Despite the fact that these operations carry the risk of death of the animal, owner satisfaction with the cosmetic and functional outcome exceeds 85%.
After surgical excision of the tumor, regrowth is observed in 22% of cases of removal of a tumor of the lower jaw, and in 48% of cases of removal of a tumor of the upper jaw. The average survival time with surgical treatment alone is 150–318 days; less than 35% survive more than a year. By comparison, without treatment, the average lifespan for dogs is 65 days.
Another treatment option for canine oral malignant melanoma is radiation (radiation therapy), which has proven effective in locally controlling tumor growth. When carrying out radiation therapy, a complete response is observed in up to 70% of cases of canine melanoma; tumor growth slows down in 83%–100% of cases. Local recurrence occurs in 15%–26% of cases of initial complete response, and the average time for metastasis to form is 139 days. The average lifespan of dogs treated with irradiation is 211–363 days; about 36%–48% of animals survive 1 year; about 21% of dogs survive 2 years.
The results of irradiation in cats for malignant melanoma of the oral cavity (5 animals in total) are described; in 60% of cases there was a response to treatment, the average survival time was 146 days (from 66 to 224).
Surgical excision and radiation provide good local control of tumor growth, but due to its high metastatic potential, the tumor requires further chemotherapy or immunotherapy. It should always be remembered that the main cause of death in dogs with malignant melanoma of the oral cavity is the formation of distant metastases in the animal’s lungs; various chemotherapy protocols are used to slow their development.
General forecasts
The prognosis for dogs with malignant melanoma of the oral cavity is guarded; the main cause of death is the formation of distant metastases in the lungs. The incidence of metastases is about 58% of cases, with an average period of development of 311 days.
The most important prognostic factors for malignant melanoma of the oral cavity are: • Tumor stage according to the TNM classification. • Tumor size. • Achieving local control with the first treatment. • Degree of tumor differentiation (mitotic activity). • Signs of tumor recurrence after previous treatment (if the tumor recurs after surgical excision, the average survival time is much shorter than with primary treatment for melanoma).
Favorable prognostic factors for melanoma of the mouth include the following: • Localization (rostral, on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips, on the tongue). • Small size of primary formation. • No bone lysis.
A little about the localization of malignant melanoma; it also has some prognostic significance. Melanoma of the lips and tongue has the least metastatic potential, and survival time is more dependent on achieving primary control of tumor growth. When melanoma is localized on the upper jaw and hard palate, the average lifespan is much lower.
Valery Shubin, veterinarian, Balakovo