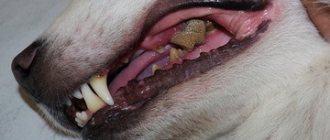
Gingivitis in dogs is a dental disease characterized by inflammation of the gums. If left untreated, the animal risks losing teeth or dying from sepsis. To avoid complications, it is important to detect alarming symptoms as early as possible and contact a veterinary clinic.
Symptoms of gingivitis development
In the first days there is weakness and refusal to eat. Thirst and appetite persist. The dog approaches the feeder, but cannot eat due to the pain that occurs when chewing. A painful attack is accompanied by whining or squealing. Due to poor nutrition, weight decreases.
The disease develops gradually. Periodic improvement in well-being followed by relapse is possible. The more symptoms of inflamed gums a dog has, the worse his condition. Symptoms of gingivitis in dogs include:
- dense plaque on the teeth and mucous membranes of a yellow-red or gray-brown color;
- swelling and redness of soft tissues;
- bleeding when chewing and loose teeth;
- profuse drooling;
- small ulcers in the mouth;
- discharge of pus when pressing on the swollen areas;
- blue discoloration of the soft areas between the teeth.
The most striking sign of pathology is an unpleasant and pungent smell of rot from the oral cavity. Its appearance is typical for a particularly severe form. When an abscess occurs, that is, purulent inflammation of tissues, the general temperature rises. In such cases, treatment for gum disease in dogs should begin immediately.
Tumors in the oral cavity
Such neoplasms, as a rule, do not cause any concern in the early stages; the dog feels well, is mobile and active. The main symptom: hot and white tongue, mobility of one or more teeth. If the gums are of normal color and all teeth are healthy, this is a reason to suspect a malignant neoplasm.
It is often confused with stomatitis, because the neoplasm visually resembles a lesion with inflammation. Therefore, for a correct diagnosis, it is better to conduct a histological examination.
As a rule, the prognosis is unfavorable. The life expectancy of dogs with malignant tumors is reduced to a year. It is almost impossible to cure an animal. You can prolong life and temporarily alleviate your pet’s condition with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.
Benign tumors are more common in dogs with a flat skull, while malignant tumors are equally common in all breeds. Benign neoplasms make it difficult to drink and eat. The animal refuses to eat and does not take a stick when playing. The owner observes chewing food on one side of the jaw, the animal quickly gets tired, rubs its muzzle against objects, and rubs its muzzle with its paws.
Therapy for benign tumors is aimed at excision of the tumor. During surgery, the tumor is excised along with nearby healthy tissue to prevent recurrence of the disease. If the tumor is benign, then the outcome of the treatment is favorable and the dog continues to live for many years, delighting its owner. It will also be interesting about pemphigus.
Remember that if your pet has a white tongue, you should definitely take her to the veterinarian to diagnose the disease. After all, the cause of plaque or discoloration of this organ can even be cancer or serious pathologies of internal organs.
Source
What factors and diseases cause gingivitis?
Dental diseases most often occur in older animals. With age, the quality of teeth deteriorates and immunity decreases. It is impossible to prevent this factor. Fortunately, other causes are related to diet, oral care and other pathologies. All of them are treatable and preventable.
Helminthiasis
Inflammation of the gums in dogs is caused by vitamin deficiency, that is, a lack of vitamins. When parasites infect the body, they destroy some of the incoming nutrients. There is an acute shortage of ascorbic acid.
This reason is rarely diagnosed, since the dog’s body independently synthesizes vitamin C. The situation changes with a severe form of helminthic infestation, when the body is too weak. The routes of entry of ascorbic acid are blocked not only from the outside, but also from the inside. Helminthiasis is most severe in puppies.
Tartar
If the mucous membranes are inflamed due to tartar, then there is a high probability of periodontitis. The fossilized plaque gradually grows into the gum pocket, peeling off the soft tissue. The wider the pocket, the worse it holds the tooth root. The animal requires urgent treatment aimed at preserving its teeth. A veterinarian-dentist will tell you how to treat gingivitis in dogs of this form - in the worst case, surgical intervention will be required.
Poor nutrition
The condition of the oral cavity is affected not only by the amount of vitamins, but also by the type of feeding. A dog's gums bleed due to food that is too rough or, conversely, too soft. In the first case, solid food particles injure soft tissues, leaving small cuts. In the second case, either tartar forms or the mucous membranes loosen. To avoid consequences, it is important to combine both types of nutrition.
Autoimmune disorders
Sometimes the mucous membranes swell in completely healthy pets. If you are confident in the quality of your pet’s diet and regular oral hygiene, check it for autoimmune disorders. With this diagnosis, the body perceives native cells as foreign bodies and destroys them. It is impossible to predict this pathology, but it is quite possible to keep it under control.
Changing baby teeth
Red gums in a dog aged 3 to 7 months are associated with the change of baby teeth. This process is unpleasant and takes a lot of effort. Due to decreased immunity, vulnerability to infections increases. During this period, it is not recommended to vaccinate or increase physical activity.
Allergies
When interacting with an allergen, the production of histamine, the substance responsible for the allergic reaction, increases. It is transmitted into the blood, increasing the permeability of blood vessels. Not only native substances penetrate into the formed pores, but also foreign ones. Without taking antihistamines, secondary infections are added to allergies.
Diseases of the internal systems of the body
In the chronic form of the pathology, deep functional impairments are often found. In this case, the pathology is secondary and is treated only after the primary disorder has been eliminated. Gingivitis can be caused by pathological processes in internal organs: kidneys, liver, digestive tract, even in the respiratory tract.
Causes of pale gums
The pallor that may appear on a dog's gums can typically be caused by anemia, which results in insufficient red blood cells, and can have a variety of origins as described above. In addition, discolored gums in dogs will appear in conditions that lead the animal to a state of shock, which implies a serious risk to its life. If we notice that our dog's gums are pale, we should contact a veterinarian to determine the cause and treat it.
Pale gums in dogs due to anemia
We have seen that anemia is the main cause of pale gums in dogs. This anemia can be caused by various circumstances, which we have grouped into the following:
- Blood loss : behind the pallor of the mucous membranes there may be internal or external bleeding. Sometimes this loss is small, but chronically extends over time. For example, these are hemorrhages, which can cause gastrointestinal ulcers, as well as internal and external parasites, especially in weakened puppies or animals. Tumors can also cause bleeding. In these cases, we see pale gums and tooth decay in these dogs.
- Hemolytic anemia : Occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than normal. This destruction can be caused by immune-mediated problems, in which the body attacks its own cells, but it can also be congenital or caused by infections such as Babesia or Leptospirosis. When a blood cell ruptures, it is divided into its components, bile and hemoglobin. In the most severe cases, it can turn the urine brown and mucous membranes yellow. Sometimes this anemia is due to a reaction to certain medications or, in newborn puppies, neonatal isoerythrolysis.
- Insufficient red blood cell production : Red blood cell production may be altered in chronic conditions such as kidney or liver disease. Similarly, loss of iron due to chronic bleeding from gastrointestinal ulcers or severe infestations of hematophagous parasites is another cause. Some medications and tumors can also affect this production.
Pale gums in dogs due to shock
There are situations of serious risk to the dog’s life, in which it falls into a state of shock. One of the signs that occurs in these dogs is pale and cold gums. Some of the pathologies with a risk of shock are hard abdomen, gastric volvulus/dilatation, or peritonitis. In all cases, immediate veterinary attention will be required as otherwise the dog may die.
As you've already seen, changing gum color in dogs is always an indication that something is wrong. Therefore, it is very important to quickly contact a specialist for the first examination, especially if the gums are pale.
Author of the article : Maria Besteiros.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis in dogs is classified according to the severity of symptoms, location of occurrence and form of manifestation. Depending on these factors, 6 types of pathology are distinguished.
Acute and chronic
The acute form is characterized by vivid symptoms and rapid deterioration of well-being, while the chronic form is characterized by a smoothed clinical picture, periodic improvements and relapses. The chronic form is more dangerous because it is difficult to diagnose early.
Localized and generalized
In the localized form, the inflammation manifests itself as a point, and in the generalized form the process covers all soft tissues. In the latter case, the treatment still affects the entire oral cavity.
Catarrhal (serous) and hypertrophic
The catarrhal form occurs due to the influence of external factors (trauma, bacteria and viruses, allergens), the hypertrophic form - due to the influence of internal factors (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system, hormonal disorders, blood diseases).
In the hypertrophic form, inflammation is localized on the canines, incisors and molars. Depending on the symptoms, it can be edematous or fibrous. In the second case, in addition to redness and swelling, ulcerations appear on the mucous membrane. The fibrous form is often found in older dogs, large breeds and collies.
Why did the dog suddenly become lethargic?
It seemed like just yesterday the animal was cheerful, full of energy, willingly taking part in games and other fun. Today the pet lies limply on its bedding, indifferently looking at what is happening around it. His eyes are sunken, he refuses to eat and even his most favorite treats. We begin to understand that something is wrong with the dog. In our new article we will tell you which directions you should start moving in.
What is lethargy in dogs?
As it became clear from the preamble of the article, identifying lethargy in dogs is a fairly simple matter. Such a dog may not respond to the call, ignore the treat, and in general any stimulation stops working. The animal lies and sleeps almost all the time.
Of course, a lot depends on the dog’s temperament: you can only talk about lethargy if you have studied your pet well. What are signs of lethargy for one dog are within normal limits for another. However, let’s say that there have been negative changes in the dog’s behavior. Let's take a closer look at the reasons.
Diet.
Very, very many things depend on proper nutrition, including the dog’s temperament! If an animal is malnourished and does not receive enough vitamins and minerals necessary to maintain optimal physical condition, it will inevitably become lethargic. Start with nutrition, try to adjust your diet a little. If everything goes well, then we pointed out the problem almost immediately!
Animal weight.
Do you have a dog breed with a high activity level? Let's check if her weight is normal. Sometimes excess weight for an active dog causes a domino effect - it immediately collapses and turns to jelly. Again, dietary adjustments will be required to reduce the calorie content of food, as well as increase physical activity!
Diseases and infections.
Your dog may have caught a cold or other respiratory illness while out for a walk. Within two days, the dog’s body begins to prepare for a fight with the infection, and the animal really seems lethargic and lifeless.
Anemia.
Anemia is a blood cell disease in which hemoglobin levels are sharply reduced. The symptoms of anemia are very similar to those described above. Look at the mucous membranes of the animal's eyes and gums - if they are pale, this may be due to anemia.
Breathing problems.
If your dog has not previously had asthma, upper respiratory tract diseases, or allergies, then it may be due to individual exercise intolerance. The dog is not getting enough air to breathe normally. More often than others, such problems occur in dogs of brachycephalic breeds - they are more prone to respiratory diseases, as well as overheating.
Side effects of medications.
Before giving your dog this or that drug, carefully read the accompanying document, which reports possible side effects. Perhaps among them there is lethargy and drowsiness. In this case, consult your veterinarian whether it is worth continuing treatment with this drug or whether you need to choose another medicine.
Immunity disorders.
All the same symptoms appear. It is necessary to show the animal to a veterinarian. To rule out this cause, he will order several tests.
Poisoning.
The effect of various poisons and toxic elements is different for each - symptoms of poisoning can occur either immediately or after a few days. Think about whether your dog could, at least theoretically, be poisoned by something. If the answer is yes, contact your veterinarian immediately!
Carbon monoxide poisoning.
Fortunately, this cause is quite rare, but can lead to fatal consequences. Carbon monoxide poisoning is equally dangerous for dogs and people. Sometimes this happens in garages or parking lots where cars with running engines are parked. Poisoning is also possible in megacities. Perhaps we will devote a separate article to this topic.
Where are dogs' belly buttons?
How to make friends between a cat and a dog? Why does a hedgehog laugh? The entire encyclopedia about animals is on our website.
Source
Methods and means of treatment
If you do not have the opportunity to visit a veterinary clinic immediately after detecting alarming signs, provide first aid. To relieve acute pain, use a decoction of calendula or chamomile, and to slow down the inflammatory process, use a weak solution of soda. Remember that these measures are effective only at the initial stage of the disease.
After visiting a veterinary clinic, the doctor diagnoses the symptoms of gingivitis in the dog and prescribes treatment. When examining the oral cavity, the condition of the teeth, mucous membrane and gum pocket is determined. A four-legged patient gets an X-ray of his mouth. The image clearly shows any damage to hard bone structures.
Additionally, a Schiller-Pisarev sample is taken. This diagnostic method involves using the properties of iodine. When the substance is applied to the affected areas, their color changes to brown. The more intense the resulting shade, the more serious the inflammation.
At the veterinary clinic
Treatment of severe gum inflammation in dogs takes place strictly under the supervision of a veterinarian. A hospital stay will be required for surgical operations. Depending on the situation, the four-legged patient may require excision and suturing of the affected tissue or removal of diseased teeth. When cleaning dental pockets from pus (gingivectomy), general anesthesia is used. To avoid complications after the operation, the animal is kept in the hospital.
Tartar is removed using ultrasound. This is an unpleasant procedure, so, like gingivectomy, it is performed under general anesthesia. Treatment of gums in dogs is not complete without physiotherapeutic procedures. Patients are given:
- soft tissue massage;
- electrophoresis - subcutaneous administration of liquid drugs (calcium, heparin, chlorine) through a constant electric current;
- thermocoagulation of gingival papillae - selective removal of damaged areas using high-frequency waves without destroying the epidermis.
All other therapy comes down to taking medications and treating inflamed tissues, so it is carried out at home.
At home
Treatment for gum disease in dogs includes rinsing and debridement. For rinsing, decoctions of chamomile, yarrow, oak bark and sage are suitable. These plants not only disinfect wounds, but also relieve inflammation. Remember that before use you must consult a veterinarian, since herbs are one of the strongest allergens.
How to rinse your dog's mouth:
- Draw warm liquid into a large-volume syringe without a needle. For giant breed dogs, you can use the Janet syringe.
- Tilt the dog's head and open its mouth slightly.
- Pour a stream onto the dog's gums so that the liquid does not enter the throat. It will pour out onto the floor - you can substitute a basin or lay a cloth.
- It is advisable to rinse not only the inflamed areas, but also the entire oral cavity.
When removing plaque, use a regular cotton pad soaked in peroxide or chlorhexidine. The procedure is carried out several times a day. During rehabilitation, it is important to keep your mouth clean. Avoid the accumulation of stuck food pieces. They can be easily removed with a child's toothbrush. Instead of toothpaste, a weak solution of soda will do. Clean daily until complete recovery.
To relieve swelling, use Polyminerol, Maraslavin or copper sulfate. Contrical, Trasylol and Heparin promote faster healing. Sea buckthorn oil is used as a folk remedy, but it is safer to purchase a special healing gel. It adheres more firmly to the surface, which increases the duration of the therapeutic effect. Such drugs include Cholisal. It not only heals, but also dulls attacks of pain. A veterinarian-dentist will tell you exactly how to treat inflammation of the gums in dogs - he will also advise you on the dosage and show you how to carry out therapeutic procedures at home.
In addition to antiseptic treatment, the animal is prescribed antibiotic therapy. The most popular drugs include Baytril, Amoxicillin and Cobactan. The dosage is determined by the doctor. Among folk remedies, infusions of calendula, chamomile or echinacea are suitable. They can be consumed as a drink or used as a rinse.
Ulcerative inflammation of the gums in dogs is treated with herbal infusions. To prepare the infusion, mix oak bark, chamomile, sage and thyme in equal proportions. Pour 1 tbsp. l. herbal mixture with a glass of boiling water and leave until completely cool. Strain the cooled infusion and rinse your pet’s mouth with it 4-5 times a day. Cauterization of erosive lesions is unacceptable. Such exposure will aggravate the condition of the affected tissues.
For helminthiasis, anthelmintic drugs are used. Raising immunity is stimulated by multivitamin complexes. The emphasis is on vitamins B, P, C and PP.
The duration of therapy is determined by the stage of the disease. In the initial stages, healing occurs quickly and without complications.
Dog menu during treatment and rehabilitation
Treatment of gums in dogs requires a mandatory diet. The animal is transferred to high-protein super-premium or holistic-class soft food. They do not injure the mucous membrane and contain all the vitamins necessary for recovery. After each feeding, the oral cavity must be rinsed with chlorhexidine solution. This will prevent stuck pieces of food from rotting.
If it is impossible to purchase specialized feed, you will have to temporarily switch to natural feeding. In this case, the menu is reduced to pureed vegetables and meat. Such food will have to be cooked until the pain disappears. As soon as the patient’s condition improves, switch to boiled rabbit, veal or chicken. Three times a week, treat your dog with low-fat cottage cheese, kefir or natural yogurt. They will replenish calcium reserves and strengthen bone tissue. To restore vitamin A, serve boiled sea fish, cleaned of bones, once a week.
The usual diet is returned no earlier than 3 months from the start of therapy. If your dog is used to eating dry food, do not rush to return it to the diet for another 2 months after recovery. Remember that the transition to your previous diet should be smooth. Otherwise, there is a high probability of intestinal problems.