Bursitis in dogs is a common disease that occurs as a result of injury or infectious diseases. This disease brings a lot of inconvenience to the animal and its owner. Requires immediate contact with a specialist and rapid treatment. If you see that something is wrong with your dog’s paws, you need to contact a veterinarian for help.
What is bursitis in dogs
The synovial bursa, which is intended to protect the joint from various mechanical damage, becomes inflamed - this is bursitis in a dog. This pathology is very dangerous because it reduces the animal’s mobility, creates a powerful blow to the nervous system, and depletes the pet’s body. Doctors still cannot come to an opinion about what causes this disease. The most obvious reasons are:
- infectious diseases;
- various joint injuries;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- partially allergic reactions;
- excessive physical activity.
Prognosis for an animal with carpal hygroma on a dog’s paw
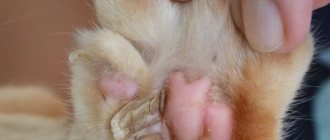
In most cases, hygroma of a dog's wrist on the paw is a swelling that is not dangerous to the life and health of the pet. The prognosis for this pathology is favorable.
We recommend reading about mammary tumors in dogs. From the article you will learn about the causes of the appearance of a neoplasm, types of breast tumors, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of pathology.
And here is more information about benign and malignant formations on the neck in dogs.
False bursa, according to veterinary experts, occurs in large breeds, as well as with constant injury to the elbow joint. The uncomplicated form of the disease is a cosmetic defect and does not cause concern to the pet. The complicated form requires aspiration of the contents, drainage and the use of antibiotics. With adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Symptoms of tumor appearance
If we talk about acute bursitis, its main symptoms are: swelling in the bend of the joint, this swelling is hotter to the touch than the rest of the animal’s body;
- severe pain when moving, the dog may whine and lean more
- on healthy paws, squeezing the sick one;
- severe pain is felt at night;
- lameness, sometimes the animal tries to move less;
- Sometimes a purulent formation may form in the swelling. The cone becomes very dark.
By quickly identifying bursitis in a dog, you can prevent the disease from becoming chronic, thereby relieving pain symptoms and removing swelling in the joints. False (or chronic) bursitis is a form of disease in which a lump or swelling appears on the dog’s joints, but does not cause him any pain and does not make it difficult for him to move.
Who is affected by bursitis?
Bursitis is a common disease in large breed dogs. Small Chihuahuas, Yorkshire Terriers, and Pekingese usually do not suffer from this disease, since the structure of their joints is slightly different.
Large dogs, especially service dogs that spend a lot of time doing physical activity, are more likely to suffer from bursitis. At the age of 6-7 years, such dogs may be slightly lame on one or two hind legs. Since the disease progresses quite quickly, the dog’s limbs may fail within a couple of weeks. In such cases, treatment and hospitalization do not help. Therefore, veterinarians so strictly recommend monitoring the animal’s activity.
Symptoms of the disease
There are a number of symptoms that should serve as a clear signal to the pet owner that they urgently need to take the dog to the vet.
The disease usually develops quite quickly, so in this case it is unacceptable to waste time.
- The first thing that becomes noticeable in a sick animal is pathology of the contours of the elbow joint . As is already known, the walls of the bag swell, and because of this, exudate accumulates in the cavity. As a result, a kind of bump forms on the dog’s paw.
- The pet will be very reluctant to use its diseased limb, perhaps even limping , as pain in the joint area begins to manifest itself.
- In chronic forms of elbow joint disease, connective tissue growths and bridges that look like ridges and ridges may form on the paw. and bursolites are formed in it that consist of dense parts of fibrin and epithelioid cells.
- With severe inflammatory processes, a fistula may form over the joint. Purulent discharge may come out of it into the external environment.
- The acute form of bursitis differs from the others in that it manifests itself as sudden, excruciating pain for the dog. The pain intensifies during movement and at night. You may notice that the pet does not sleep, but sits in the same position for a long time. After several such acute attacks, bursitis becomes chronic . Now the pain will be a little weaker, but very long lasting.
Did you know? Dogs have not two, but three pairs of eyelids. In addition to the usual upper and lower ones, they also have a nictitating membrane that protects and moisturizes the eye.
Treatment of elbow bursitis in dogs
If bursitis is suspected, treatment should be carried out immediately. To do this, you need a full examination of the animal by a veterinarian and collection of the necessary tests. After which the degree and form of the disease is determined and appropriate treatment is prescribed. Treatment is usually quite conservative, and surgery is extremely rare. At the initial stage, the animal should be given maximum rest and immobility, any physical activity and long walks should be stopped for the duration of treatment.
The doctor should attach a special bandage or elbow pad to the affected joint. In the first days of treatment, you need to apply cold lotions with an anesthetic or disinfectant. After 2-3 days, cold lotions are replaced by warm compresses. All treatment can be carried out at home.
If the form of the disease has become more complex, the dog’s bursitis must be treated in a hospital, with constant examination by a doctor. For treatment, lamp irradiation, ointments with an antibacterial effect, as well as ointments based on potent antibiotics are used. If the doctor detects the presence of pus, it is pumped out using a special syringe. After that, an injection of hydrocortisone is given into the synovial bursa of the joint, which disinfects and heals.
Treatment and diagnosis
Only a veterinarian can make an accurate diagnosis. The disease is diagnosed through a clinical examination of the dog.
For this purpose, fluid is taken from the joint capsule, after which a bacterial study is carried out and the presence of infectious infections is determined.
Once the presence of bursitis in a dog is accurately diagnosed, its treatment can be carried out conservatively and surgically.
Conservative
- First of all, the animal should be provided with complete rest and soft bedding. If the dog's face is very painful, joint immobility is provided. To do this, the paw is fixed with a pressure bandage or special elbow pads for dogs are used. A cold compress should be applied under the bandage.
- The next day, experts recommend warming the joint with a Sollux lamp, complementing the procedure with warm wrapping.
- If the veterinarian reveals the presence of infectious organisms during the examination, the pet is prescribed antibiotics. In addition, drug therapy includes the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the latter are not effective, hormonal drugs will be included in the treatment process.
Unfortunately, conservative treatment of bursitis may not always be effective. Especially in cases where the disease is in an advanced form. In such circumstances, surgery may be necessary.
Operational
Removing bursitis surgically is a rather dangerous operation. In this case, there are cases when a new one has formed in place of the removed bursitis.
A dog’s elbow is a place that takes a very long time to heal, so surgery is fraught with a number of complications. That is why many veterinarians resort to this method of treatment only in extreme cases.
You will be interested to know how long dogs live.
The surgeon injects a 5% alcohol solution of iodine or a 10% solution of silver nitrate into the bursa cavity, massages the surface and puts a bandage on top of the animal. The solutions, being inside, destroy the inner layers of the bursa, as if “burning” it out. As a result of such manipulations, the formation of exudate stops.
After 3–5 days, the surgeon opens the bursa, removing its contents, including necrotic tissue. The cavity is washed with antiseptics and treated like a purulent wound.
Treatment of elbow bursitis
The elbow joint requires the same treatment as the hind leg joints. Special compresses and ultraviolet light will help eliminate the appearance of purulent formations and also quickly eliminate pain. If surgery is necessary, it is performed immediately. But many experts warn about possible complications after surgery. Namely:
- formation of fistulas at the suture site, which require additional intervention, as well as correction with a bandage or plaster. Such fistulas are most often
- found in old dogs when the recovery process drags on for up to 3-4 months;
- the anesthesia that is used can cause disruption of the circulatory system, especially in the areas where the bursa is removed. This complication can lead to prolonged use of bandages and protective pads;
- During the operation, an infection may occur, which will cause a severe inflammatory process. This often happens and requires further treatment with strong antibiotics to avoid purulent formations.
Surgery very often causes new diseases and complications. Since the operation will help remove bursitis, but it cannot always eliminate the inflamed areas of the skin, which, when the suture heals, again form bursitis. Elbow bursitis is often confused with dysplasia. The symptoms and external criteria are very similar. Therefore, you need to consult only experienced specialists and not use alternative treatment for such a complex disease.
Forecast
Typically, treatment brings good results within 2-3 weeks, and in the postoperative period from 3 to 6 weeks. Depending on the extent of the disease, symptoms such as pain and severe swelling disappear within a few days, after which the joint needs to heal completely.
To do this, the dog must always be in a special corset. Additionally, ointments or immunostimulants are rubbed in. During the postoperative period, the dog remains in the hospital for several days, where hydrocortisone injections are given for 7 days. If the operation does not bring the desired results, it is repeated.
Conservative and surgical treatment methods
Surgical intervention is resorted to in exceptional cases. Most hygromas can be cured with conservative therapy, the basis of which is the elimination of the etiological factor. To prevent re-injury, dogs are given soft bedding and strong physical activity (work, training) is avoided.
To treat uncomplicated bursitis, it is enough to change the content - soft bedding should restore the function of the joint.
Aseptic hygroma usually does not require treatment. The owner should change the approach to keeping the dog - provide the dog with a comfortable and soft bed. In some cases, a bandage is also applied to the affected joint. Recovery and disappearance of symptoms is observed within 2-3 weeks.
The first step in therapy is to eliminate the etiological factor to avoid further injury. During the rehabilitation period, it is better to isolate the dog in a room with soft bedding or place beds in the pet’s favorite resting places. The bedding is left even after recovery, as relapses are possible.
Commercial elbow pads are now available to immobilize the elbow joint and protect it from external forces. Such devices are easily fixed on the animal, adapting to individual characteristics. Most dogs can easily tolerate joint pads.
To reduce exudation in the first days of the pathological process, it is recommended to apply ice, make alcohol lotions and tight bandages.
In the future, they switch to warming procedures to speed up recovery processes. The dogs are given a massage of the surrounding tissues, warming bandages and heating pads are applied. They rub in irritating substances and make applications of ozokerite and clay.
Aspiration of exudate from the synovial bursa most often turns out to be ineffective - after pumping out, the bursa gradually fills up again. This can be useful in purulent forms. In this case, after aspiration of the pus, it is necessary to rinse the cavity with an antiseptic solution.
Surgery is usually resorted to only after unsuccessful therapeutic treatment. A drainage is installed for prompt drainage of exudate, and antimicrobial therapy is prescribed. Fixing and protective bandages are applied to the limbs. Treatment is carried out until scar tissue forms, which prevents the re-formation of bursitis. But often such treatment leads to impaired motor activity.
If purulent bursitis is accompanied by the formation of a fistula, then it is necessary to remove the pathological contents. The cavity is examined for the presence of pockets filled with pus. The wound is washed with hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate or other antiseptic solution. Antibiotics and sulfonamides are placed in the cavity, and they are also used in systemic form.
Otherwise, they make surgical access to the pathological cavity and proceed in the same way. To prevent the edges of the wound from closing, drainage is installed for the free outflow of exudate. At the same time, general measures are taken to treat aseptic bursitis in order to reduce the inflammatory and exudative reaction. Treatment is carried out until the purulent process is completely eliminated. After which the wound is sutured, and the animal’s condition is constantly monitored to avoid relapses and complications.
Preventive measures
To avoid such an unpleasant disease as bursitis, you need to follow some rules that will protect your pet. Among them:
- good living conditions (the dog should not sleep in a cold place or in a draft);
- the place to sleep should be soft and warm (it is undesirable for the dog to sleep on cold tiles or linoleum), avoid dampness in the room where the animal is located;
- for large breeds, the diet must contain chondroitin,
- glucosamine and other supplements that affect good joint function; dry food or food must be balanced and appropriate for the weight and characteristics of the animal. Food should contain plenty of grains and protein products. Do not use fatty foods and bones in your diet;
- physical activity as the dog ages. Even large breeds should not get carried away with activities that involve overcoming high barriers. Combine active games and long walks. In the cold and damp seasons, avoid walking in the rain, and also ensure that the dog does not become hypothermic.
Bursitis in dogs is a disease that requires immediate treatment and sometimes surgery. And although the consequences after treatment are not always positive, with proper care the dog will feel comfortable for a long time. To avoid disease, you need to follow the recommendations of a specialist and properly care for the animal. But if you notice symptoms of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. Remember that home treatment can only make the problem worse.
Currently reading:
- Thyroid dysfunction in dogs (hypothyroidism)
- The whole truth about the treatment of joint dysplasia in dogs
- Games to choose for training a dog
- What to do if your dog sprains a paw or sprained ankle
Useful video
Watch this video about treating elbow hygroma with PRP:
Similar articles
- A tumor on the neck in dogs: why it appeared under the skin...
Quite often, especially in summer, a tumor can be detected on the neck of dogs, also under the jaw, skin. The reasons why it appeared may be different, and the lump can be benign or malignant. Treatment depends on… Read more - Ligament rupture in a dog (knee, cruciate, na...)
Ligament rupture in dogs can occur both under the influence of external and internal hereditary factors. The symptoms are very similar to a sprain. Read more
- Mammary tumor in a dog: types...
A mammary gland tumor can form in a dog due to hormonal imbalances, as a hereditary disease. It can be malignant and... Read more
- Polyp in a dog: main appearances in the nose, trachea...
A polyp occurs in dogs as a consequence of a long-term inflammatory process. A polyp may be found in the nose, trachea, rectum, bladder and even... Read more
- Malignant tumor in a dog: options - on the eyelid...
Unfortunately, dogs are increasingly being diagnosed with a malignant tumor. It can be on the eyelid, face, paraanal glands and internal organs, bones... Read more
What is bursitis and why is it dangerous?
The bursa or bursa is a sac made up of connective tissue. It facilitates the movement of tendons and the work of muscles. Inflammation of this bursa is called bursitis. In dogs, the membrane of the elbow joint most often becomes inflamed, and less often the knee joint.
The main complications of bursitis (usually the purulent form) are:
- purulent arthritis;
- phlegmonous purulent bursitis.
The acute form of the disease becomes chronic if treatment is not started in a timely manner. In severe cases, it is necessary to completely remove the joint capsule.
Which categories of dogs are especially predisposed to developing the disease?
Dogs of large and giant breeds are predisposed to bursitis: mastiffs (Dogue de Bordeaux, Dogo Argentino), shepherds (East European shepherd), bullmastiffs, etc. More often, this disease affects pets who sleep on a hard surface and carelessly (sharply and loudly) lay down on the floor.
Reference. False bursitis can develop in large puppies during the period of active growth. This phenomenon is not considered a pathology. The resulting tumor is painless, its role is to protect the joint from excessive stress. Such bursitis goes away on its own as it grows.
Treatment
Treatment methods for bursitis depend on how far the disease has progressed and what specific form is observed in the animal. If bursitis can be identified in the initial stages, then, most likely, it can be cured without surgical intervention, limiting itself to conservative methods.
Treatment of bursitis in the early stages
Conservative methods of treating bursitis include the following procedures:
- the veterinarian applies a pressure bandage to the animal’s paw, which allows you to fix the limb and not cause additional pain to the dog;
- The animal is prescribed cold compresses: they will constrict the blood vessels and thus reduce blood flow to the inflamed area. After a few days, cold compresses are replaced by hot ones (which are not allowed to be used for purulent bursitis);
A cold compress consists of several layers of fabric and allows you to evenly treat the affected part of the body
- Some experts also advise using infrared lamps in treatment using a Sollux lamp. It is prescribed as an alternative or addition to hot compresses and has a similar effect;
- in case of a chronic course, special irritating ointments are prescribed, as well as iodine iontophoresis, which is carried out in a clinic and involves connecting a small current;
The use of currents allows you to relieve inflammation and restore the diseased limb
- after opening the fistula (if any), the dog must undergo a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which will not allow pathogenic bacteria to penetrate the open wound.
You can read more about how to make a hot compress for a dog below.
Making a compress for a dog
Surgical intervention
As you might guess, surgical intervention is prescribed for advanced stages of bursitis, when conservative therapy is powerless. The procedure involves cleansing the bursa and includes the following steps:
- the surgeon opens the bag and removes from it the remains of pus, exudate and dead flesh;
- the skin at the site of inflammation is sutured in such a way that the empty bag does not interfere with the dog’s movement;
- if the joint has been significantly destroyed, some clinics replace it with an implant made of plastic or titanium. Unfortunately, this procedure is quite expensive and is rarely practiced in Russia.
Symptoms
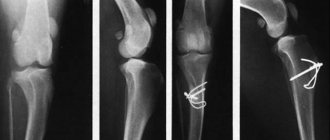
In the initial stage, inflammation of the bursa may go unnoticed, as there is a slight swelling in the area of the elbow or hock joint. In acute cases of bursitis in a dog, the resulting lump increases significantly in volume (see photo).
In appearance it resembles a benign tumor ─ hygroma. Upon palpation, the mobility of the neoplasm, which is elastic to the touch, is revealed. Associated symptoms in the acute course of the disease:
- painful sensation during movement;
- lethargic state of the pet, poor appetite;
- moderate limitation of mobility accompanied by lameness;
- hyperemia and increased body temperature in the affected area.
In the chronic course of the disease, there is no pain in remission; joint stiffness may be observed due to localized proliferation of fibrous tissue.
In the case of purulent bursitis, dark-colored phlegmon is formed, which, when opened, is complicated by fistulas that are difficult to regenerate. The purulent form can be complicated by the development of sepsis or arthritis in dogs.