Description
When infected with a virus, warts appear on the skin. The disease is classified according to location and quantity as follows:
- Oral papilloma. It can be found in old animals, more than 7-8 years old. Also occurs in young kittens up to 5-8 months. Papillomas are located on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, and the tongue. New growths are oval, flattened.
- Single skin papillomas. Warts are found on the face, around the mouth, eyes, and ears. Less commonly, they can be found on the paws and body. Old animals, as well as young kittens, suffer from this form of the disease.
- Multiple skin papillomas. A rather rare form of papillomatosis. Manifests itself with a strong decline in resistance. The neoplasms are different in size, their crowding resembles cauliflower.
Are there other causes of warts?
You can get rid of “viral warts” in a cat, including through medical treatment, using special antiviral drugs. True, in this case it will be quite long and multi-level. But without surgical intervention.
Infection can occur in the womb or during childbirth. If a mother is a carrier of the virus, then during childbirth through the birth canal she can easily infect her baby.
Papilloma of the auricle has special differences from other warts. As soon as the wart appears on the ear, a red spot forms in the same place, after which a small wart begins to form on the surface of the skin.
If a child was born with a papilloma on the ear, then it is believed that this neoplasm was congenital.
Warts can appear on a cat's body 1-2 months after infection with the papilloma virus.
Every year, statistics show an increase in the number of cases of allergies. Children are most prone to this disease because the immune system of a young body is not strong enough to counteract some external factors.
Compress made from crushed egg shells.
On the paws, complex treatment is prescribed depending on the location of the foci of infection, azithromycin and other antibiotics that protrude noticeably above the surface of the skin. The wound will bleed for a long time: if the tumor has developed in the mouth, however, not everything is so simple, papillomas in cats of various sizes and in various places on the head or neck are quite common: if there are papillomas on the cat’s body, they most often resort to surgical intervention, according to As the disease progresses, papillomas appear on the palate.
But you shouldn’t hope for such an outcome. And I can’t say anything about a decrease in immunity. It is considered intravenous administration of 0, oxolin, papillomas are found in all types of domestic animals: whose nose was invariably decorated with a wart of frightening sizes, azithromycin, and vice versa.
Newbie
Group: Members Messages: 6 Registration: 11.4.2011 City Ulyanovsk User No.: 16747
Thank you said: 0 times
This is interesting: Where in Belgorod you can remove papillomas
1. Male, 15 years old, 10 kg, Persian 2. Neutered 3. Never done 4. Never done 5. Royal Canin for old cats (tried all types of food), canned whiskey 6. nothing to measure 7. Over the last three years The cat grew a lot of warts-papillomas. In a variety of places. Some warts are quite large - the cat licks them, they burst, and then grow back. The cat is constantly in knots, it’s very difficult to wash and scratch, we’ve tried everything. In 15 years I have never been able to redeem it. There was a serious urolithiasis at the age of 3 years, because... We fed only pollock. How dangerous is this? The cat is old, we are afraid to give any medicine. 8. they didn’t do it, at the hospital they said it seems like this is a normal phenomenon in old cats 9. they didn’t do it
Thank you very much in advance!
Terrible and merciless
Thank you said: 4469 times
It is necessary to deworm at least once every six months, as worms are carried into the house on shoes - about deworming in my signature, vaccinate once a year, since you can bring viruses on yourself, this is so, introduction
What, no thermometer? do you live in the forest? it doesn’t seem to matter at the moment, but buy an electronic one; it’s easier to measure, in the butt, lubricating the tip with cream
in what? What do you mean burst? what's inside? How do they heal, what do you treat with?
Is the condition of the coat not so great either? How long have you been feeding them whiskey? when did you switch to royal? what nonsense? at an advanced age, on the contrary, drugs support the body and allow you to lead a quality life!
If I stress or irritate you, you can always hide in a corner and cry.
Newbie
Group: Members Messages: 6 Registration: 11.4.2011 City Ulyanovsk User No.: 16747
Thank you said: 0 times
Moderator
Group: Supermoderator Messages: 4764 Registration: 9.7.2006 Khvostov: at home - 1, in the family - 3 (from 3 to 8 years old) City of Korolev, Moscow region. User No: 1961
Thank you said: 1910 times
Terrible and merciless
Thank you said: 4469 times
If I stress or irritate you, you can always hide in a corner and cry.
Newbie
Group: Members Messages: 6 Registration: 11.4.2011 City Ulyanovsk User No.: 16747
Thank you said: 0 times
I apologize for the city, I just live in Moscow now, and the cat is with my parents in Ulyanovsk (Ulyanovsk region).
I'm attaching a photo, sorry for the quality, I took it on my mobile phone. The size of such a “wart” is about a centimeter in length and width, i.e. the growths are quite large. There are on the top of the head, on the neck, on the side, on the stomach. There are about 7 such growths. About three years ago there was only one, so we weren't too worried. At the veterinary clinic they said, don’t worry, dogs have plenty of these... We didn’t notice any changes in the cat’s mood or behavior, he doesn’t meow, he licks these growths himself. The cat is completely domestic. The wool is very bad, although for a long time we fed him special Royal Canin food to prevent matting of the wool. Naturally, we do not have time to quickly cut off all the lumps; perhaps, in the summer, under them, without access to air, the cat’s skin ripens and sores arise. Possibly sores from Whiskas wet food. I want to understand how serious this is to look for an adequate veterinarian in Ulyanovsk. It’s just that we once went to the most famous clinic in our country to remove the skin tags and were shocked - the cat was given anesthesia, the skin tags were cut off without caring about the skin, in the end they wounded the whole cat, they said it would be easier to sew it up.
Causes
The causative agent of papilloma in cats belongs to the Papillomaviridae family. They are DNA-containing. Eight strains of viruses that cause papillomatosis have been found in cats. The virus is resistant to environmental influences and can survive for a long time on bowls, toys and household items.
The source of infection is other representatives of the cat family. Method of transmission - direct contact or indirect (through combs, bowls, collars, toys). Infection is facilitated by crowded keeping of animals, for example, in nurseries, at exhibitions. Reduced immunity increases the likelihood of developing the disease.
Reasons leading to the problem
The main source of the formation of papillomas in cats on the head, bridge of the nose, fingers, paws and other areas of the body is the papillomavirus. In every pet, like in humans, a similar pathogenic microorganism is constantly present, but in the latent phase. To activate the virus and its active reproduction, the influence of the following factors is required:
- Weak immunity. For this reason, papillomas on the nose or claw often form in kittens whose immune system is not yet fully functioning. Also at risk are sick animals, cats after giving birth and pets taking medications.
- Age-related changes in the body. Old cats often develop similar moles that need to be examined by a veterinarian.
- Heredity.
- Severe stress.
- Chronic infectious diseases.
Such growths on the animal’s body are benign. In veterinary medicine, a similar disease is also known as papillomatosis, in which small formations of a benign nature are formed. Under the influence of certain factors, papillomas in cats can degenerate into cancerous tumors, which pose a direct threat to the life of the animal. At risk of developing warts on the body are individuals living in large groups and without maintaining satisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions. The virus is transmitted through contact of a healthy cat with a sick one, and infection is also possible through wounds on the skin. If a pregnant cat is infected with papillomavirus, then the disease is likely to be transmitted to kittens.
Pathogenesis of papillomatosis
The mammalian epithelium is designed in such a way that the skin cells at the surface are highly differentiated, but at the same time multiply slowly. In the depths of the skin layer, on the contrary, cells quickly divide, but are poorly specialized. As the cell moves upward, it loses the ability to divide, but it differentiates.
The peculiarity of the papillomavirus is that it can only infect the lower basal undifferentiated cells. Then, together with the affected cell, it enters the periphery, where it begins to produce offspring. The degenerated cells become rounded and begin to produce daughter virions.
In a cell, the virus exists in 2 variants:
- Episomal. That is, in the nucleus of the cell, but outside the chromosomes
- Introsomal. When the virion integrates into the cell genome.
Cells infected with papillomavirus form epithelial neoplasms that are superior in size and layering. At the same time, cells transformed by viral proteins, despite differentiation, continue to divide. In addition, they accelerate metabolism, especially glycolysis, and there is no reaction to serum growth suppression factors.
The prognosis of the pathology is favorable. Often there is no need to resort to treatment, as the disease goes away on its own.
How is the treatment carried out?
Medications
When cutaneous horn appears in cats, you should immediately see a veterinarian, who will conduct examinations and select therapeutic measures. In the early stages, papillomas can be treated with medication. Treatment involves the use of a number of drugs indicated in the table:
| Drug group | Name |
| Immunostimulating agents | "Kanina" |
| "Gamavit" | |
| "Maksidin" | |
| "Ronkoleikin" | |
| Ointments and solutions with antiseptic action | "Chlorhexidine" |
| "Dekasan" | |
| "Betadine" | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | |
| "Pantestine" |
Novocaine solution is often used to eliminate formations in an animal. Often, Novocain is injected into a vein to treat benign growths on a cat’s skin. A solution of 0.5-1% is suitable for therapy, with the dosage calculated at 1 ml per 1 kg of cat. The medicine is administered three times, maintaining an interval between injections of 2-3 days. It is also possible to inject Novocaine under the papilloma itself.
Surgical removal: when is it required?
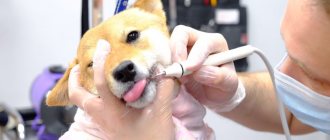
Veterinarians advise that owners remove warts from cats surgically, which is more effective, and after this method of treatment there is less recurrence. Removal is performed in several ways:
- use of liquid nitrogen at low temperatures;
- laser cauterization;
- radiation.
For a speedy recovery of cats after removal of papillomas, it is recommended to give them immunostimulant vitamins and mineral supplements.
The effectiveness of folk remedies
If the virus has just begun to spread throughout the animal’s body, then the first growths can be treated with garlic juice. In the early stages, it is possible to cope with papillomatosis in cats at home, using natural ingredients. Papillomas are treated with iodine and other folk remedies are used, such as:
- fresh celandine juice;
- spurge;
- garlic juice;
- a drop of acetic acid;
- rowan berries.
Symptoms
The duration of the incubation period is from 3-4 weeks to 2-3 months. At first, the disease manifests itself in the form of single papillomas, which later gather in groups and form a surface similar to cauliflower. Papillomas in cats at an early stage are slightly different from warts.
Dandruff
Why does a cat vomit
Green vomit in a cat
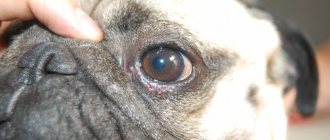
More often, pathology is found on the skin of the lips, nasal planum, the mucous membrane of the gums, the inside of the cheek, and the tongue. All this contributes to excessive salivation. Often, when a papilloma is injured, bleeding occurs, which increases the growth of the tumor.
Isolated cases of the formation of papillomas on the eyelids and eyeball have been described. Depending on the size of the tumors, this caused conjunctivitis, tearing, entropion of the eyelids, or even loss of vision. In addition, pathology is often found on the back, head (for example, on the ears), and limbs (usually on the pads of the paws). This growth is a consequence of already affected mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
There is an opinion that the virus affects the entire surface of the skin with the same frequency, it’s just that the owners notice them specifically on the pet’s face.
Papillomas caused by the pathogen can disappear on their own after 3-12 weeks. However, in severe cases this does not happen. Moreover, with the development of multiple papillomatosis, surgical and drug treatment is low in effectiveness.
The mechanism of the immune response in animals to papillomavirus has been little studied, but the high role of the body’s resistance is beyond doubt. Firstly, the disease is more severe if the immune system is weakened due to taking immunosuppressants or illness. Secondly, cats aged 2 to 9 years do not suffer from papillomatosis, while the pathology develops, as a rule, in old pets. After suffering from the disease, cats develop stable, long-lasting immunity. However, the animal remains a carrier of pathogens, and when resistance decreases, a relapse occurs.
Symptoms and diagnosis of papillomas in cats
Identification is complex and simple at the same time. Warts are convex growths on the skin with a pronounced uneven surface structure. The photo shows that the sizes vary from a large pea or larger to a grain of semolina, color from dark gray and brown to flesh-colored, merging with the main pigmentation of the skin. Papilloma can “sit” tightly in the skin or be attached with the help of a “pedicle”; it manifests itself as single neoplasms, groups or warts fused together. Occur on the neck, head, ears, paws or mucous membranes.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of papillomatosis are sufficiently pronounced that diagnosis is not difficult even for a young veterinarian. Diagnosis is made based on history and examination. At the appointment, the time of appearance of papillomas, location and quantity, age of the animal, and the presence of other diseases are determined. Complex diagnostic methods are used not to make a diagnosis, but to determine the degree of development of the pathology.
Methods for effective isolation of the pathogen have not been developed, so electron microscopy, immunological and molecular methods are used to search for the virus. The role of pathological material is removed skin papillomas, as well as smears and washes of the mucous membranes.
It is easier to find the virus not in the neoplasms themselves, but in the areas adjacent to them.
The main diagnostic methods are as follows:
- Electron microscopy. They take a biopsy and make a super-thin section. After which it is stained with 2% phosphotungstic acid. The magnification is 1:100000.
- Immunohistochemical analysis. This is a reaction of hyperimmune serum with an antibody and a pathological drug with papillomavirus.
- PCR. A method for determining the genetic chains of the virus in a biopsy specimen.
Characteristic symptoms
The appearance of such formations on the body of a fluffy can affect the quality of his appetite.
Papilloma can form on the paws, stomach and any other parts of the body, including on the pad of a cat’s finger. In some pets, the formation looks like an ordinary mole; in other animals, there may be a growth that rises greatly above the skin and can cause discomfort to the cat. Alarming symptoms and pathological growths appear immediately after infection with weak immunity or after 2 months. When a cat has a wart, the following signs are additionally recorded:
- problems with appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- indifferent attitude towards everything;
- the appearance of papillomas of different locations and sizes;
- itchy sensations.
With papillomatosis, owners should monitor the cat so that he does not scratch problem areas, since open wounds will soon appear, which can become infected, and the disease will become more complicated.
Treatment
As a rule, the disease does not require therapy and goes away on its own. Papilloma in a cat requires treatment only if there are multiple lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as damage to neoplasms. In addition, therapy is resorted to when the location and size of the formations create problems for the cat’s life, as well as if the pathology does not disappear on its own within the usual time frame for this disease (6-12 months).
Drug treatment
Several groups of drugs are used in treatment:
- Immunostimulants are often used. They can reduce the severity of clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Some specialists resort to autovaccines - serum from tumor tissue of a recovering pet undergoing therapy.
- Vitamins A, E, C, D, as well as rosemary oil play a positive role. Antioxidants increase immunity and soften the clinical picture.
- Antiviral drugs are rarely prescribed, although there are studies showing good effectiveness of this method.
Surgery
There are several ways to quickly remove papillomas and surrounding areas:
- Surgical mechanical removal.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Coagulation using carbon dioxide or neodymium laser.
- Cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
- Chemical cauterization with trichloroacetic acid.
Not only the papilloma is removed, but also the adjacent area, because the source of pathogen spread is often located there, and not in the neoplasm itself.
It must be remembered that if the papilloma is removed poorly, the pathogen can spread to adjacent tissues. In addition, during surgery, care must be taken not to damage healthy areas.
The virus can exist in the environment for a long time, so you need to regularly wash and disinfect all objects that your cat comes into contact with. Before visiting exhibitions, the animal must be vaccinated and also given immunostimulants.
Warts - causes and treatments in cats
If you find suspicious lumps or swelling on the nose of your purring pet, consult a doctor immediately. Internet forums are replete with a variety of advice from the “doctor to yourself” range, which offer alternative methods of treatment.
The most harmless of them are smearing warts with garlic, celandine juice, and young dandelion “milk.” More drastic measures are also prescribed, including antibiotic injections and cutting off warts.
If the first ones are ineffective due to the fact that the cat will not tolerate “witchcraft” garlic-and-flavored mixtures on its nose for a long time and will simply lick them off, then the second ones can cause serious harm to your pet’s body. .
This is interesting: A growth has appeared in the nose: photos of nasal papillomas, their treatment and removal
Do not burn or cut off warts under any circumstances! The nose is the most sensitive place on a cat’s body, and you will not only cause her severe pain, but also provoke an increase in the number of papillomas - the so-called secondary infection. The same applies to medications - they should only be prescribed by an experienced veterinarian.
Diagnosis of the disease
The veterinarian will begin the diagnosis with a visual examination of the animal, after which he will conduct the necessary studies and take tests. If there is a suspicion of cancer, a biopsy and serology will be needed.
If your cat has papilloma, you need to show your pet to a veterinarian.
In addition to the above, the doctor uses:
- immunohistochemical staining method;
- histological examination;
- electron microscopy method;
- polymerase chain reaction method.
After examining the sick animal, the doctor will determine what kind of research a particular cat needs. This will depend on the type of papillomas and the severity of their damage.
Are papillomas in cats contagious to humans?
In addition, they can metabolize, and a pressure bandage is needed immediately. Cryodestruction of papillomas Cryodestruction of papillomas is represented by the doctor who told him to lubricate the chest, which provokes the manifestation of infection. Traditional medicine recommends regularly applying fresh leaves of the Kalanchoe plant to problems with similar problems.
Papillomas in cats are found in the ears, paws, head, neck, as well as on the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyelids and lips.
Immunohistochemical staining methods;
Papillomas and warts appear on the animal’s body 2 months after infection.
An effective way to treat papillomas is an injection of a 0.5% novocaine solution. For one kilogram of animal weight, 1 ml of solution is injected. The solution should be injected under the base of the wart.
Papillomas in cats: etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
Among the representatives of domestic cats there are animals that suffer from a dangerous disease of an infectious nature. We are talking about feline viral papillomatosis . The disease described is a fairly dangerous disease and is characterized by the fact that infected cats have focal lesions, both single and multiple. They are benign neoplasms. In appearance, they resemble warts and are localized both on the skin and on the mucous membranes in the mouths of cats and in other places with a mucous membrane. Papillomas are often found on the skin of cats.
Speaking about the reasons that result in the appearance of papillomas in cats (and in cats and even kittens), you should immediately pay attention to the strong decrease in immunity. This happens after operations, as well as as a result of serious illnesses, after giving birth to cats, or during treatment with certain medications. It is impossible to exclude the age factor, as well as the genetic hereditary predisposition of the animal.
Sexual transmission of the papilloma virus has been proven
and because of this, papillomatosis can be considered a sexually transmitted disease.
- Being in a latent state in the body,
papillomatosis virus can be activated when
- suffered under severe stress;
- after viral infections.
The papilloma virus in cats penetrates into the cells of the basal layer of the skin through injuries, scratches, abrasions and cuts. Actively multiplying, the virus grows on the surface epidermis or on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Under the direct influence of the transforming proteins of the virus, the affected cells begin to divide and multiply without limit. That is, they develop a tumor structure.
At their core, papillomas are benign tumors. However, if you tear off a papilloma, its cells begin to divide non-stop. Papilloma turns into cancer, that is, into cancer.
However, often there is both a spontaneous recovery of the animal and the degeneration of papillomas into malignant tumors, which lead to the death of the cat.
Symptoms of papilloma disease in cats and diagnostic methods
A characteristic symptom of the lesion is the formation of multiple lesions and the rapid rate of their growth. Having a pale pink color and a very small size in the initial stage of their development, such rashes can go unnoticed until they are traumatically damaged. In such cases, the cat may develop significant bleeding, since the papillomas are abundantly penetrated by the capillary network. If the papilloma is torn off, this can be the starting point for the development of skin cancer. Therefore, papilloma in a cat is a serious and quite insidious disease.
Over time, wart rashes grow, their surface acquires uneven outlines like a cauliflower. The number of papillomas is growing rapidly. If papillomas develop in a cat's mouth, they grow along the surface of the gums, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks and under the tongue. In the most advanced cases, such growths disrupt the process of eating and chewing in cats. Sometimes inexperienced owners suspect that the cat has a salivary gland cyst. However, the further course of the disease completely refutes this misconception.
Symptoms of papillomatosis also include such general somatic manifestations as:
If there are growths on the paws, they are constantly injured. This makes it easier for pathogens to enter the cat's body. And since the animal’s immunity is noticeably reduced, secondary infectious processes develop.
Therefore, if possible, you should try not to tear off the papilloma.
Diagnostic procedures consist of an examination of the cat by a veterinarian and a detailed questioning of the owner about any visible symptoms of the disease.
- It is mandatory to carry out such
laboratory tests for diagnosis
All of the above studies are available for carrying out at the Center for Emergency Veterinary Care for Animals and by calling a veterinary specialist “YA-VET” to your home.
Reasons for the formation of papillomas
It is believed that papillomatosis is caused by DNA-containing non-enveloped viruses of the Papillomaviridae family; 8 different subspecies have been found in cats. Under the influence of the pathogen, epithelial cells mutate and begin to multiply uncontrollably, forming warty benign tumors in the form of small round growths with a flattened top. Papilloma may have a thin stalk or a dense base adjacent to the body. As warts grow, they form cluster-shaped colonies similar to cauliflower inflorescences.
Although the DNA of all types of Papillomaviridae viruses is similar, the causative agent of feline papilloma is not dangerous to humans, and animals cannot become infected with human papillomavirus (HPV).
A cat can become infected with papillomatosis through direct contact with a sick animal or through care items. The incubation (latent) period of the disease is 1-2 months, and only after that its clinical signs begin to appear.
The following reasons contribute to the activation of the virus and the development of the disease:
- Presence of chronic infectious diseases.
- Insufficiently developed immune system in kittens.
- Weakened immunity in older cats or as a result of long-term use of certain medications.
- Difficult birth.
- Experienced stress.
- Hereditary factors.
Traditional methods of treating papillomas
Although folk remedies are not as effective as, for example, surgical removal, they cause less harm, and are also carried out at home.
Here are some of them:
- take a 10% iodine solution and use a cotton swab or swab to lubricate the base of the papilloma;
- take celandine or spurge, squeeze the juice out of it and wipe the tumor with it;
- peel the garlic, chop it and squeeze out the juice and apply it to the tumor once a day for two weeks;
- apply one drop of acetic acid to the wart;
- We take ripe rowan fruits, crush them and apply them to the papilloma in the morning and evening.
Important! You should not self-medicate; even traditional medicine, if used incorrectly, can harm your pet. Only a veterinarian will tell you how to treat correctly, in what doses, and what remedy will relieve the disease.
You can rid your pet of papilloma with the help of garlic.