Common viral diseases of cats
Viruses cause severe, life-threatening diseases in cats. Infection occurs through air, water, feed, bedding and contact with infected animals. The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- Contact with a virus carrier. Visiting cat shows poses a great danger.
- Transmission of viruses through food, water, and air.
- Failure to comply with zoohygienic conditions.
- Stress factors:
- Transportation.
- Bored content.
- Overheating or hypothermia.
- Poor nutrition.
The following diseases are considered the most common and most dangerous among cats:
- Rabies.
- Panleukopenia
- Aueszky's disease.
- Panleukopenia.
- Viral rhinotracheitis.
- Cat flu.
- Calicivirus.
- Coronavirus peritonitis.
- Leukemia.
- Immunodeficiency in cats.
- Herpes.
Virus
Chronic viral infections of cats: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
» Biovetlab.ru » Publications » Chronic viral infections of cats: symptoms, diagnosis, treatmentFishing online store
Chronic viral infections in cats include: viral leukemia, infectious peritonitis and viral immunodeficiency.
These viral diseases are characterized by a long incubation period, which can last from several weeks to several years. Infection occurs in utero or through contact of healthy animals with patients and carriers.
Feline viral immunodeficiency (
FIV)
The causative agent of this disease is an RNA-containing retrovirus of the lentivirus family, which has a tropism for T-lymphocytes. This pathogen is similar to the human immunodeficiency virus, but does not cause infection in humans, just as HIV does not cause disease in cats.
Infection of healthy animals occurs through direct contact with patients or carriers, as well as in utero. Feline immunodeficiency may be accompanied by feline viral leukemia or toxoplasmosis.
Clinical signs
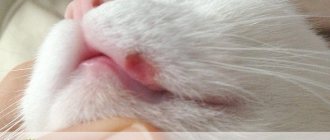
After the virus enters the animal’s body, symptoms of chronic immunodeficiency develop over several months or years: chronic diarrhea, damage to the mucous membranes and skin, weight loss, fever, anemia, and cancer may develop. Against the background of decreased immunity, secondary viral, bacterial or fungal infections of the oral cavity, upper respiratory tract and skin often occur.
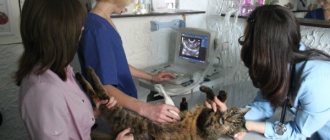
To diagnose this disease, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent express test is performed or the pathogen RNA is detected by PCR. When performing a rapid test, it should be taken into account that it may give a false negative result in the following cases:
- at the beginning of the disease, when the virus is already in the blood, but a sufficient number of antibodies have not yet been developed. In this case, repeat the test after 2-3 months.
- at the last stage of the disease, when the immune system is so depressed that antibodies are no longer formed in sufficient quantities.
Detection of virus RNA by PCR is a fairly accurate method for diagnosing this disease.
Currently, treatment for FIV is based on increasing the animal's immunity and suppressing secondary infections.
Feline viral peritonitis (
FIP)
The causative agent of this disease belongs to the group of coronaviruses. It enters the body of a healthy cat through the fecal-oral route, as well as through prolonged contact of a sick animal with a healthy one. Kittens become infected with the virus from their mother. Kittens and young cats under 2 years of age, as well as older animals, are most sensitive to this virus. Cats with weakened immune systems, malnourished cats, and those with leukemia are most susceptible to the virus. This disease is often observed in catteries where animals are kept in crowded conditions.
The incubation period lasts 2 weeks or more and depends on the pathogenicity of the virus strain, on the amount of it that has entered the body, as well as on the state of the cat’s immune system.
Clinical picture
There are 2 forms of viral peritonitis: dry and wet.
Wet (exudate) form
, in which nonspecific symptoms of feline viral peritonitis in the early stages are expressed in loss of appetite, weight loss, and inactivity of animals.
Then, as the disease progresses, due to increased capillary permeability, fluid effusions into the abdominal or chest cavity. Against this background, difficulty breathing (with accumulation of fluid in the chest cavity) or an increase in the volume of the abdomen (with accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) is noted. In addition, there is an increase in body temperature to 41 ° C, anemia, diarrhea, pericarditis and liver failure develop. The disease often ends in the death of the animal.
In the dry form (non-exudative)
all the same symptoms are observed, except for fluid effusion. Almost all internal organs are affected: liver, kidneys, lungs, eyes. The most characteristic changes are noted in the small intestine - mucosal or fibrinous plaque, wall thickening and the formation of nodules. Paralysis of the limbs may develop.
When diagnosing viral peritonitis, clinical symptoms are taken into account and blood is examined in rapid tests or PCR. If there is an effusion, it is examined by PCR.
Treatment of feline viral peritonitis is symptomatic and consists of fighting secondary (secondary) infection and maintaining the animal’s immunity.
Feline viral immunodeficiency (
FeLV)
This is a fairly common disease in cats caused by retrovirus serotypes A, B and C.
Cats become infected from sick animals through saliva when licking, biting, or through a bowl. Kittens can become infected in utero or through their mother's milk. Most often, cats in nurseries become infected when they are kept in crowded conditions and do not comply with sanitary measures.
Having penetrated the body, the virus multiplies in the tonsils, and from there spreads to the lymphoid organs (spleen, lymph nodes) and bone marrow. In this case, the disease may not manifest itself clinically—it is a latent form. However, with a decrease in immunity, under stress and against the background of other infections, the leukemia virus can be activated and detected in the blood and saliva.
Clinical picture
Sick animals experience decreased appetite, diarrhea or constipation, vomiting, increased body temperature, weight loss, and possibly enlarged lymph nodes. Subsequently, anemia and pallor of the mucous membranes develop, and spontaneous bleeding is noted. In addition, quite often cats develop lymphosarcoma.
Diagnosis of FeLV is carried out using rapid tests or PCR. However, one must take into account the fact that cats with a latent form of the disease can give a false negative result.
There is no specific treatment for this disease. Sick cats are prescribed immunomodulators, antibiotics and anti-cancer drugs. Blood transfusions are indicated for anemia.
For specific prevention of feline leukemia, animals are vaccinated.
Also, when keeping cats in groups and in nurseries, it is necessary to comply with hygiene standards and sanitize the premises with disinfectants. Newly acquired animals must be kept in quarantine until they receive 2-fold negative results in diagnostic tests.
Lazareva N.V.
Veterinary laboratory assistant at the BIOVETLAB laboratory
RELATED PUBLICATIONS
Infectious diseases of dogs. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Infectious diseases: Parvovirus enteritis, Canine distemper, Adenovirosis and Leptospirosis.
Infectious diseases of cats. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Infectious diseases: Feline Herpesvirus (rhinotracheitis), Feline Panleukopenia, Calcivirus infection (Feline Calcivirosis) and Rabies.
THIS IS INTERESTING:
Rabies
The most dangerous viral zoonotic disease is rabies. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is myxovirus.
- Carriers are stray dogs, cats, wild carnivores.
- Infection - through saliva from the bite of a sick animal or defects in the skin and mucous membranes.
- Incubation period. After the bite, the animal is observed for 10 days. If no clinical manifestations occur, the animal is considered healthy.
- Symptoms are nervous phenomena.
- Forms of the disease:
- Violent. Excessive drooling, aggressive behavior, perversion of appetite, paralysis. Photophobia, hydrophobia. After 3-11 days the animal dies.
- Paralytic. Lasts up to 4 days. Paralysis occurs without an aggressive phase.
- Atypical. Symptoms erased. Ends in paralysis and death.
- Diagnostics:
- Lifetime - based on anamnesis, epizootic situation, clinical symptoms.
- Post-mortem - histological examination of the brain.
- Treatment. Injection of specific serum within 72 hours. If symptoms appear, treatment is ineffective.
- Prevention - annual vaccination.
Rabies in a cat
Treatment of viral infection in cats
The symptoms of viral diseases in cats are presented above; treatment in each specific case can only be prescribed by a veterinarian after examination and diagnostic measures. Sample treatment regimens are presented for informational purposes only. Remember that self-medication will not help the kitten, but can significantly harm its health.
Prevention of rabies
To date, a treatment regimen for rabies has not been developed; unfortunately, it is impossible to save your beloved pet. Sick patients should be euthanized at the slightest suspicion of the virus. After contacting a veterinary clinic, the owner should visit the hospital to undergo a course of vaccinations against possible infection. Annual compulsory vaccination will help protect your furry pet from infection.
Treatment of panleukopenia
The doctor prescribes Vitafel, as well as Gamavit or Maxidin. It is advisable to administer the drug over three to four days, the dosage is determined by the doctor. After normalization of external and internal clinical symptoms, the daily dose is reduced. To prevent complications, antibacterial medications (penicillins and cephalosporins) are used. To maintain water balance, Ringer's solution and Metoclopramide are used.
The rehabilitation period takes place on protein-vitamin and mineral complexes; Tsamax is involved in the rehabilitation.
Note! If you suspect panleukopenia, you should not give your cat analgin.
Treatment regimen for rhinotracheitis
The recovery regimen for rhinotracheitis includes Maxidin together with Gamavit, the latter can be replaced with Fosprenil or Vitafel. Veterinarians often prescribe specific serums to furry patients, as well as the antibacterial drugs Ampicillin and Tetracycline.
Timely and adequate treatment of rhinotracheitis ensures successful recovery in 100% of cases.
Complex therapy for calcivirosis
It is advisable to use Fosprenil and Maxidin; complex therapy also includes drugs aimed at eliminating clinical symptoms, as a rule, these are antibacterial agents and Gamavit. Vitafel (only in the early stages), Cerebrolysin, Aminovit have a high therapeutic effect.
Treatment for chlamydia
The veterinarian prescribes antibiotics to the patient such as Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin. Medicines are available in the form of injections and ointments, the latter must be placed under the lower eyelid. It is important not to interrupt therapy for two weeks.
Immunity in leukemia
Scientists have not developed an individual and effective treatment regimen for leukemia; the main therapy comes down to mitigating the clinical picture of the infectious disease. A veterinarian can only prescribe medications that will provide significant support to the immune system to independently combat the disease. Their use will allow you to overcome leukemia and develop lifelong immunity; for a successful result, it is important to follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Injections for peritonitis
For peritonitis, Fosprenil injections are quite effective with a mandatory reduction in the symptomatic picture. To eliminate pathogenic manifestations, antibiotics, the drugs Gamavit and Sulfocamphocaine, are used. Veterinarians often prescribe antiviral agents and medications that stimulate the immune system.
Treatment for cat flu
Experts do not give a clear answer to the question of how to treat cat flu. The main recommendations are to use antibacterial medications, Gamavit, Fosprenil. When dealing with the flu, special attention is paid to improving overall well-being; the kitten must be provided with care and attention, protected from hypothermia and drafts.
Aueszky's disease
Cats are the first to get sick; productive animals become infected from them. A person becomes infected through meat. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is herpesvirus.
- Carriers are rodents, infected pigs.
- Infection occurs through eating virus-carrying mice, rats and contact with pigs.
- Incubation period. Up to eight days.
- Symptoms are nervous phenomena.
- Forms of the disease:
- Classic. Excitement gives way to depression. Constant meowing, drooling, vomiting, photophobia, itching, death.
- Atypical. Severe depression, the animal does not meow. Quick death.
- Encephalitic. Signs similar to the classical form. Additionally - aggressiveness, lack of coordination, paralysis.
- Gastroenteritis. Severe pain in the abdominal cavity, vomiting, sudden death.
- Diagnostics. It is necessary to distinguish between Aueszky's disease (pseudorabies) and rabies.
- Treatment. In the initial phase use:
- Immunoglobulin Vitafel.
- Immunostimulants - phosphoprenyl, immunofan, gamavit.
- Antibiotics - maxidin.
- Prevention has not been developed.
Panleukopenia
Feline distemper (panleukopenia) is the most dangerous disease with a high mortality rate. Survivors of a four-day illness become virus carriers. In the warmer months, young animals and old cats get sick. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is parvovirus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats, blood-sucking insects.
- Infection is through the air, flea bites, and cat feces. Intrauterine infection.
- The incubation period is 2...10 days.
- Symptoms:
- Vomit. Yellow-green mucous discharge with blood. Foul bloody diarrhea.
- Starvation.
- Cardiovascular failure.
- Body temperature >41°C.
- Conjunctivitis, rhinitis. Dry mucous membranes. Dehydration of the body.
- Coma. Sudden death.
- Diagnosis - clinic and epizootic situation. A blood test shows a drop in the number of leukocytes to 3*103/ml when the norm is 5.5...18.5*103. It is necessary to distinguish panleukopenia from non-contagious enteritis and toxoplasma invasion.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Administration of drugs is parenteral. The tablets cause a gag reflex. Apply:
- Subcutaneous injections of saline to relieve symptoms of dehydration.
- Hemostatic drugs.
- Vitamins of category B, to replenish spent reserves.
- Antibiotics to suppress secondary microflora.
- Diet food. The appearance of appetite is a favorable sign. Rehabilitation nutrition is as follows:
- Limiting carbohydrates at the expense of proteins.
- The first days - kefir and white bread soaked in low-fat meat broth.
- On the third day - specialized ready-made gentle food.
- A four-week ban on raw foods and vegetables is imposed.
Animals that have recovered from the disease acquire stable immunity to parvovirus. Antibodies protect offspring up to twelve weeks of age.
- Prevention - vaccination.
Prevention of viral infections
Prevention of diseases caused by viral infections is as follows:
- Maintaining a balanced diet.
- Ridding the animal of external and internal parasites.
- Regular vaccination with Quadricat, Nobivak, Purevax, Multifel, Felovax, Leukotsel. These vaccines protect your pet from rhinotracheitis, panleukopenia, leukemia, calcivirosis, chlamydia, and rabies.
Many viral infectious diseases are deadly, so it is necessary to promptly isolate sick animals and begin treatment as quickly as possible. Annual vaccination will protect your pet from many diseases.
Viral rhinotracheitis
The disease affects the organs of vision and breathing. The mortality rate does not exceed 20% of the number of cases. Those who have recovered from the disease develop lifelong immunity. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms: The causative agent is the herpes virus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection - air, discharge from the genitals, eyes, nose. Infection is transmitted through food, contact between people and insects.
- The incubation period is 3...8 days.
- Symptoms:
- Acute form:
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva. Rhinitis.
- Cough.
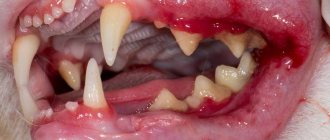
- Ulcers on the tongue.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membranes. Redness of the nose.
- Temperature >40°C.
The acute form ends with recovery after a decade.
- Chronic form:
- Constipation.
- Chronic rhinitis lasts for years.
- Bronchitis develops, developing into pneumonia
- Ulcers appear on the skin.
- The nervous system is affected.
- Abortions and stillbirths are recorded.
- Diagnosis: clinic, tests of nasal and eye secretions.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Apply:
- Universal antibiotics.
- Sulfonamides.
- Antihistamines.
- B vitamins. Ascorbic acid.
- Dietary nutrition consists of the use of liquid boiled feed.
- Prevention - vaccination.
Calicivirus
Types of infections in cats, their description
Rabies
A dangerous viral infection that affects the nervous system. It is transmitted to domestic animals from wild animals by a bite and always ends in the death of the animal. If signs of rabies are detected, a decision is made to euthanize the pet . The incubation period for an adult cat is 3 to 6 weeks; in kittens it appears much faster, within a week. Only a doctor can accurately determine the disease itself and its form.
© shutterstock
Plague
It is a highly contagious infectious disease and difficult to treat. Over 90% of cats infected with distemper die. Those who survive it acquire lasting immunity to the disease. A pet can get the virus through saliva; it is transmitted to kittens from a sick mother cat. The danger lies in the fact that all vital organs and functions of the body are affected. These include all organs and mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, and most dangerously, the spinal cord suffers.
Calicivirus
The disease affects the respiratory system. They get sick during the cold months. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is calicivirus.
- Carriers are sick cats, virus carriers.
- Infection is through the air and by contact.
- The incubation period is 1...3 days.
- Symptoms resemble those of rhinotracheitis. Calicivirus is complicated by stomatitis, diseases of vision and breathing. The disease lasts 7...21 days. Mortality - 30%.
- Diagnosis - clinic, epizootic situation, blood tests. Anemia and leukopenia are observed.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Apply:
- Universal antibiotics.
- Sulfonamides.
- Nitrofurans.
- Vitamins A, C, B12.
- Hyperimmune serum.
- Dietary nutrition, as for leukopenia.
- Prevention - vaccination.
Calicivirus
Coronavirus peritonitis
Presents a problem for fellinologists running a nursery. Among the many relatively harmless coronaviruses is a deadly one. The disease is difficult to diagnose. It resembles diseases of the brain, eyes, digestive organs and cardiovascular pathologies. Young animals up to two years old and old cats are affected. Mortality is high. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is the FIP coronavirus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection - through the air, discharge from the genitals, nose, eyes. Infection is transmitted through food, contact between people and insects.
- The incubation period is 21 days.
- Symptoms:
- Temperature >40°C.
- Symptoms of peritonitis.
- Vomit.
- Ascites.
- The stomach is swollen.
- Treatment is symptomatic. Universal antibiotics are used to destroy the accompanying microflora.
- Prevention. Not developed.
Coronavirus peritonitis
Leukemia virus
Destroys the immune system, causes the development of cancer. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is FeLV.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection is contact.
- Symptoms:
- Exhaustion.
- Heat.
- Starvation.
- Lethargy.
- Anemia.
- Dermatitis.
- Poor wound healing.
- Forms of the disease. There are three options for the development of events, with an equal degree of probability:
- The immune system produces antibodies, and the cat recovers.
- Asymptomatic virus carriers. A cat is dangerous to other animals. After a long time, the symptoms described above develop, and the animal dies painfully.
- The cancer progresses quickly.
- Diagnostics. Analysis for FeLV. If the result is positive, it is repeated after three months
- Treatment is symptomatic.
- Prevention. Vaccination. Isolation from other infected cats.
Leukemia virus
Infectious diseases of cats
Infectious diseases include viral and bacterial infections, diseases caused by microorganisms that are not viruses or bacteria (chlamydia, mycoplasma, rickettsia, etc.), as well as fungal infections (mycoses).
There are a number of diseases in cats that should be given special attention, as they can be transmitted to humans and are dangerous to their health. Diseases that pose a danger to human health include rabies, dermatomycosis, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, salmonellosis, panleukopenia, and hemobartonellosis.
Publications 1 - 10 of 11 Home |
Prev. | 1
| Track. | End The disease actinomycosis occurs in our pets. This is a rare infectious disease that occurs when radiant fungi - actinomycetes - enter the tissues of an animal.
-Go to publication-
Viral peritonitis is one of the most mysterious viral infections in cats, caused by coronavirus. Coronaviruses are common causative agents of serious diseases in animals.
-Go to publication-
Diseases that occur only in cats include hemobartonellosis or infectious anemia. This disease was first described in 1953 in the USA. The causative agent of the disease is feline hemobartonella, which parasitizes the red blood cells of cats. The development cycle of these parasites is 1-2 months. This pathogen can exist for a long time in the body of our cats and not manifest itself in any way. But under certain stressful influences, such as hypothermia, severe fright, infection, etc., the disease begins to develop rapidly. Often this disease becomes more active after childbirth. This disease is transmitted to cats through tick and flea bites, bites and scratches caused by sick cats.
-Go to publication-
Feline immunodeficiency is a viral infection characterized by damage to the immune system (abbreviated FIV - feline immunodeficiency virus or FIV-feline immunodeficiency virus).
-Go to publication-
Calicivirus in cats is a widespread and highly contagious viral disease of cats throughout the world, affecting mainly the respiratory system, with signs of damage specifically to the upper respiratory tract, but also with Calicivirus in cats, I would like to note ulcerations in the mouth, on the tongue, may be on the nose, in severe cases of pneumonia and even death.
-Go to publication-
Giardiasis is an infectious disease of cats caused by protozoa of the genus Giardia.
-Go to publication-
Among the many infectious diseases in our domestic cats, mycoplasmosis is often found.
-Go to publication-
Feline parvovirus (feline panleukopenia virus) is a highly contagious infection. It affects the gastrointestinal tract, bone marrow (lymphocytes and white blood stem cells), the cardiovascular system, and fetuses become infected in pregnant females.
-Go to publication-
Feline parvovirus is a virus that causes severe illness in adult animals and particularly in kittens. Possible death. The same disease is known under the names “feline infectious enteritis”, “feline panleukopenia” or, colloquially, “feline distemper”.
-Go to publication-
Rhinotracheitis is a widespread respiratory disease of cats caused by feline herpes virus type 1. The disease is species-specific and does not pose a threat to other animal species and humans. It occurs in acute and chronic forms.
-Go to publication-
Publications 1 - 10 of 11 Home |
Prev. | 1 | Track. | End
Feline immunodeficiency
This is the feline version of human HIV. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is the FIV virus.
- Carriers are sick and recovered cats.
- Infection is contact.
- The incubation period is long.
- Symptoms:
- Exhaustion.
- Heat.
- Refusal of food.
- Lethargy.
- Anemia.
- Diarrhea.
- Encephalopathy.
- Leukopenia.
- Stomatitis, glossitis, gingivitis.
- Udder tumor.
- Rhinitis, conjunctivitis.
- Pyoderma.
- Dermatitis.
- Wounds do not heal well.
- Diagnostics. Serological tests for FIV.
- Prevention. Isolation from sick cats.
Feline immunodeficiency
Herpes
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The causative agent is the herpes virus.
- Transmitted intraplacentally.
- The incubation period is 3 days.
- Symptoms:
- Depression.
- Purulent conjunctivitis.
- Keratitis.
- Yellow-green diarrhea.
- Ulcerative stomatitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Stillbirth.
- Treatment is symptomatic.
- Prevention - vaccination.
We invite you to join our Zen channel and group on VKontakte or Odnoklassniki, where new articles for pet owners are published.
Similar articles:
- If your cat has food allergies
- Ringworm Caution: What Pet Owners Need to Know
- Why are cats overweight?