Causes of plaque and provoking factors
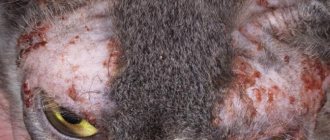
Brown, dry plaque that turns into a sticky, dark, foul-smelling mass that resembles coffee grounds can occur for several reasons. Regardless of the nature of the occurrence, the presence of an increasing volume of dirty brown substance in the ears is fraught with the occurrence of otitis media and the death of the cat.
The main reasons for the appearance of brown plaque in the ears of a pet:
- ear mite;
- water or foreign body entering the ear canal;
- severe hypothermia;
- old sulfur plug;
- head injury;
- bites, scratches;
- dermatitis of the auricle;
- infectious diseases.
Ear pathologies can occur in any cat, so it is recommended to periodically practice ear hygiene and monitor the health of the auricle.
Most often, provoking factors for the development of the disease are:
- insufficient care;
- keeping in damp, cold rooms or in a draft;
- poor quality feeding;
- chronic and acute infectious and non-communicable diseases;
- vaccination;
- weaning;
- stress;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- pregnancy;
- puberty;
- genetic predisposition;
- oncology;
- exhaustion;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- heredity.
Causes of ear disease in cats
In medicine, otitis media is most often diagnosed based on the symptoms described above. This is an infectious disease that, if not properly treated, can spread to all parts of the ear. Depending on the course, the disease can be chronic or acute. Therefore, if a cat has blood in the ear and scratched skin around it, this may be caused by the following reasons :
- allergy;
- the result of the activity of ear mites;
- penetration of bacteria or fungi;
- foreign bodies of plant or other origin;
- injuries.
If the inflammatory process has spread to the middle ear, it is most often caused by a mite. Without presenting a danger in itself, through its vital activity it provokes the development of special microflora, causing pathological reactions. If a cat has increased sensitivity to them, symptoms of inflammation appear much more often.
If pus begins to flow from your cat's ears along with blood, then this is most likely the result of infection with Staphylococcus aureus. A healthy animal is naturally protected from such intrusion, so if a cat scratches its ear until it bleeds due to germs, this may be caused by a weakened immune system or a change of residence.
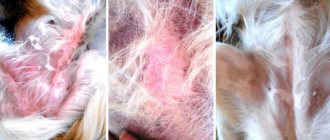
Also, a cat may scratch its ears until it bleeds due to hormonal imbalances. They are sometimes caused by taking certain medications. Some cat foods sometimes cause a similar effect. Additional signs of this may be other skin diseases associated with hair loss or flaking.
Diseases accompanied by the appearance of brown plaque in a cat’s ears
The most common diseases accompanied by the appearance of brown plaque in the ears of a pet are otodectosis and otitis media. Both pathologies are deadly, but with timely detection and referral to a specialist, they can be treated quite successfully.
Otodectosis
Otodectosis or ear scabies is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic sarcoptoid mites otodectos cynotis. It is impossible to see the parasite with the naked eye; the arthropod measures 0.2-0.5 mm. Carnivorous arachnids parasitize the external auditory canal, eardrum and auricle, feeding on epidermal scales, blood and lymph. To lay eggs, female mites make multiple punctures in the skin and penetrate into the subcutaneous layers.
Ear diseases in cats: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Hearing is of great importance for a cat, and in importance it ranks after sight and smell. The cat's ear is designed in such a way that it can pick up the most subtle sounds that will never be audible to a person, no matter how much effort he puts into it. There is an opinion that a cat’s hearing is much more developed than that of a dog.
Without the ear, an important organ of hearing, a cat would not be a good hunter, and it would be difficult for her to survive outside the comfort of her home in the difficult conditions of the outside world. Despite the fact that the cat has been living next to humans for several millennia, it has still not lost its excellent hearing qualities.
In home, or rather apartment, conditions, when a cat does not need to keep its ears sharp in order to be able to get food for itself or hear an approaching enemy, hearing has ceased to play a big role for it in the matter of survival. But this does not mean that the owner should neglect the health of his pet’s ears and not pay attention to diseases that may bother them.
Special cases
Sometimes brown plaque in the ears of a furry pet is not a symptom of otitis media or otodectosis. Particular cases of the appearance of brown matter in a cat’s ears include: plaque in only one ear, a strong nauseating odor from the ears and increased secretion of wax.
Plaque in only one ear
If dark plaque is found in only one ear, and the cat does not refuse food, itching, apathy and redness of the skin, this is simple contamination. The problem can be solved by simply removing the brown deposits using a cotton pad soaked in cleansing lotion. The next day, you need to check for dirt in the ear. If the brown mass reappears, you should contact a specialist.
Pungent, nauseating odor from the ears
Simultaneously with the formation of brown plaque, a sharp unpleasant odor from the ears most often indicates the development of otodectosis or otitis media. In particular cases, a combination of these symptoms is observed with suppuration in the ears, head trauma, neoplasm and food allergies. A veterinarian should be involved in identifying the cause of brown plaque and unpleasant odor.
Why does my pet's ear leak?
Subcutaneous mite activity
An unpleasant odor and discharge from the ear canal often occurs when infected with certain small parasites. Unpleasant symptoms are observed only when the tick has embedded itself under the skin. Owners can notice something is wrong by the restless behavior of the cat, which constantly scratches the problem area, shakes its head and has pathological exudate flowing from its ear. You can cope with the problem in the early stages, when the cat does not yet have discharge, with antiparasitic drugs. If the case is advanced, then you cannot do without veterinary help.
Veterinarians note that if discharge in cats occurs due to a mite, then it is distinguished by a brownish tint, while a copious amount of wax comes out of the ear canal, and soon pus.
Manifestation of the inflammatory reaction
If your pet is hypothermic, a bacterial infection may develop, resulting in ear inflammation.
If your cat's ears smell and bleed periodically, these may be symptoms of otitis media. Inflammation occurs as a result of exposure to such factors:
- hypothermia, which is accompanied by a bacterial infection;
- bite of a small insect, in particular a tick;
- mechanical damage to the ears;
- allergic reaction;
- bathing and insufficient drying of the pet's ears.
It is difficult not to notice the inflammatory reaction in the area of a cat’s ears, since the pathological process is accompanied by the following signs:
- purulent discharge from the ears;
- restless state;
- lethargy;
- redness of the ears.
Careless swimming
When using water treatments, special care must be taken to ensure that water does not get into the ears of your pet. Pets of the feline family do not tolerate bathing well and do not like bathing, as a result of which they can show aggression and anxiety. It is recommended that two people carry out the manipulation in order to hold the cat firmly, avoiding sudden movements that could cause water to get into the ears. When fluid gets deep into the ear canal, inflammation and pain occur. If after bathing the owners notice that the cat is constantly shaking its head and scratching its ear, then it is necessary to drip Vaseline or vegetable oil and contact a veterinary clinic.
Mechanical damage
In case of injury, it is important to check for foreign objects in the passage of the organ, since their remains can damage the eardrum.
This disorder is more common in cats, as they are prone to fights with other males. Due to injury, the animal begins to bleed from the ear canals. If the amount is small, the examination can be carried out at home to determine the size of the wound. It is also necessary to find out as soon as possible whether there is a foreign object left in the ear canal, which is likely to soon damage the eardrum. If there is a lot of blood flowing from the ear, then the cat needs to be taken to the veterinarian urgently, since the death of the animal is possible.
Cat treatment
A veterinarian should treat a cat with ear pathologies after conducting a comprehensive examination and identifying the cause of the formation of brown plaque. Self-medication is fraught with aggravation of the animal’s condition or the death of your beloved pet.
For otodectosis the following is prescribed:
- mechanical cleaning of the animal’s ears from plaque, pus and dried crusts using disinfectant solutions;
- acaricidal drugs;
- vitamin and immunostimulating agents;
- disinfection of premises and care items;
- treatment of other pets.
When otitis of the external, middle or inner ear is detected, therapy consists of the use of the following drugs:
- disinfectant solutions for cleaning the ear;
- antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drops and ointments;
- painkillers;
- novocaine blockades;
- injectable antibiotics;
- vitamins;
- immunomodulators;
- diet.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
To begin treating a sick animal, it is important to establish a diagnosis. To do this, use a visual examination of the ears for injuries, hematomas and other external damage. An otoscope is also used for diagnosis. Swabs are taken from the auricle, especially if there is blood or purulent discharge. To obtain a complete picture of the inflammatory process, a biochemical blood test may be prescribed.
To treat otitis in cats caused by mites or bacteria, drugs are prescribed that kill them. These include antibiotics and glucocorticoids. For hormonal disorders, medications are used that inhibit their further synthesis. In some cases, surgery is required to remove them.
The main thing in treating a pet is prevention. The owner should regularly clean the cat's ears with a cotton swab with hydrogen peroxide, then it becomes easier for the pet to maintain healthy ears.
Also, a cat may scratch its ears until it bleeds due to hormonal imbalances. They are sometimes caused by taking certain medications. Some cat foods sometimes cause a similar effect. Additional signs of this may be other skin diseases associated with hair loss or flaking.
Prevention of ear diseases and ear hygiene in cats
Prevention of ear diseases in cats consists of:
- ear hygiene;
- quality care and feeding;
- use of vitamin and mineral supplements;
- timely treatment of infectious and non-communicable diseases;
- avoiding contact with stray and infectious animals.
Ear hygiene in cats involves regularly cleaning the ears from dirt and wax plugs. To do this, you need to wrap your pet in a towel, secure it tightly and drop cleansing lotion into the ear.
For better penetration of the product into the external auditory canal, it is necessary to gently massage the base of the animal’s ear. After the massage, lotion with dirt and sulfur must be removed with a dry cotton swab. The final stage of the hygiene procedure is to reward the cat with her favorite treat.
Prevention
Your pet's ears should be inspected and cleaned regularly. Do not bathe the animal unless absolutely necessary. If water procedures are unavoidable, cotton swabs should be inserted into the canals. If dermatitis occurs on the inside of the shell, seek veterinary attention.
Ear cleaning
If discharge is detected from a cat’s ear, you need to clean the ear canal and apply medicinal drops. If there is no positive result, contact a veterinarian. Prevention consists of regular sanitation of the ears and the organization of a balanced diet for the pet.
We invite you to join our Zen channel and group on VKontakte or Odnoklassniki, where new articles for pet owners are published.
Similar articles:
- My cat has a nosebleed - what should I do?
- Inflammation of the lower lip in a cat
- Clear nasal discharge in cats
How to treat ear diseases in cats
Now we will dwell in more detail on the causes of the appearance of certain ear diseases, as well as on the issues of their treatment.
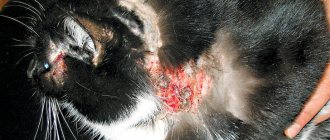
Hematoma is the result of mechanical impact on the auricle. Mechanical damage includes blows, ear tugging, insect bites, and scratching.
We recommend reading: Is Ringworm Treated in Cats?
Most often, a hematoma forms on the inner surface of the ear, somewhat less often on the outside. The ear increases in size, hangs down, there is limited, painful swelling that is hot to the touch. If left untreated for a long time, the pain only increases, and the hematoma can become infected with secondary microflora, leading to complications, for example, necrosis of the ear cartilage.
Externally, a hematoma manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the cat constantly shakes its head from side to side;
- scratches the ear with its paws, damaging it even more with its claws;
- anxiety and nervousness may occur;
- When you try to pat the cat on the head, it shows aggression.
The treatment is not complicated. If no more than 48 hours have passed since the formation of the hematoma, then the ears are fixed with a bandage on the back of the head and cold is applied. After a day, heat and irritating ointments are used for further treatment.
If these manipulations do not lead to visible improvements, it is best to take the cat to a veterinarian who:
- will open the hematoma;
- remove blood clots;
- wash the resulting cavity with novocaine along with antibiotics;
- will give further recommendations on what the owner should do for a favorable outcome of the disease.
Lymphextravasate
Lymphatic extravasation occurs for the same reasons as a hematoma, and the symptoms are largely similar to it. The only difference is in the treatment. With this disease, the use of cold or heat is strictly contraindicated, and treatment should be carried out by a qualified specialist.
With lymphatic extravasation, the liquid must be aspirated, that is, pumped out using a syringe. A simple layman, without certain skills and dexterity for this procedure, will only harm the furry pet.
Sometimes aspiration of excess fluid does not lead to visible results, then a minor surgical intervention has to be performed in the form of a skin incision and more thorough removal of the contents of the cavity, followed by suturing.
Necrosis of the auricle
Necrosis of the auricle appears as a result of:
- prolonged compression of the auricle;
- during the transition of purulent processes from surrounding tissues;
- infection with pathogenic microflora of lymphatic extravasates, hematomas and abscesses.
During the development of a purulent process in the area of the auricle, in the absence of proper or timely treatment, foci of inflammation are opened with the formation of areas of skin necrosis (necrosis), which lead to the appearance of large ulcers. The ear cartilage begins to be visible through the damaged areas, its blood circulation is disrupted, it becomes black in color, and an unpleasant putrid odor appears. The cartilage tissue rots, and the ear becomes completely deformed.
Treatment of necrosis is only surgical - either complete amputation of the auricle or its necrotic part is performed. The main thing is that the process should not be started so that the inflammation does not spread to the inner and middle ear.
Foreign bodies in the external auditory canal
In a cat's ear you may find:
- ear wax plug;
- accidentally fallen sand;
- plant parts;
- insect larvae, lice and other items.
Sometimes the presence of a foreign body in a cat's ear canal does not cause any concern and may go unnoticed, but more often it irritates the ear, leading to inflammation.
For treatment, the foreign body must first be removed from the ear, after which the ear canal is washed with a solution of soda or hydrogen peroxide (3%), and a few drops of camphor oil are instilled to reduce the pain reaction.
Neoplasms
The most common neoplasms in the external auditory canal are papilloma, sarcoma, and fibroma, which grow over time, leading to deafness.
The main features are:
- anxiety;
- ear scratching;
- manege, uncoordinated movements;
- lowering the head towards the affected ear.
Treatment of tumors inside the ear is only surgical.
Video version of the article:
Author of the article: Marina Chuprinina, veterinarian, specialization parasitologist-bacteriologist, especially for Kota Obormot.
Thank you for subscribing, check your inbox: you should receive an email asking you to confirm your subscription
Necrosis of the auricle appears as a result of:
Causes of suppuration
The fact that a cat's ear is festering should be a signal to action for the owner. Otitis is a fairly serious progressive syndrome that indicates the presence of the disease. Inflammation begins in the outer ear and, as it develops, moves to the middle and inner ears, which greatly complicates the situation. But there is no need to panic, just make an appointment with a veterinarian who will make the correct diagnosis. The reasons for ear infection in an animal can be:
- demodicosis (mite);
- the result of an allergic reaction;
- dermatitis;
- scabies;
- viral infections;
- bacterial infections;
- fungal infections;
- mechanical damage;
- pharyngitis;
- cold;
- rhinitis;
- absence or lack of cleansing procedures;
- foreign objects or water getting into the ear.
Street pets or free-ranging animals have a greater predisposition to this type of disease. An abundance of bacteria, infections, and parasites easily enter the cat’s body and provoke inflammation. Even drafts or low air temperatures can trigger otitis media. The third factor is street fights. In the process of defending territory, representatives of the cat family tend to show aggression to each other and damage the skin and other organs, including the ear.
Regular contact with other animals can also cause suppuration through infection. But even beloved pets that are kept exclusively on the premises run the risk of contracting otitis media. The fact is that human clothing and shoes can become a temporary shelter for harmful parasites. The only thing that an owner can guarantee for a beloved cat is cleansing procedures. Even a healthy animal needs to carefully clean its ears once every two weeks with an ear stick soaked in a special veterinary solution.
Types of otitis
The cat's ear consists of three main sections - the external (outer) ear, middle and inner ear. Based on these anatomical features, several forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Otitis externa - affects the outer part of the ear, the symptoms are usually mild, the most common form of the disease with a good outcome and simple treatment.
- Otitis media of the middle ear – general symptoms of inflammation appear, treatment is complicated, but in most cases the prognosis is favorable.
- Otitis of the inner ear is the most severe form, often occurs with complications, and the animal’s well-being suffers greatly. If you do not contact a veterinarian in time, your pet may even die from cerebral edema.
With improper or absent treatment, the acute form may transition to chronic. It is characterized by a long course with periodic exacerbations. Also, special attention should be paid to careful care and prevention of the cat in order to reduce the risk of exacerbations. A malignant development of the disease with the development of a purulent process is possible; in these cases, surgery may be required.
Bleeding from the ear - causes
Bleeding from the ear is a serious reason for which you simply need to contact an ENT specialist. Bleeding from the ear can be caused by various reasons; only a specialist can determine them. Almost all ear discharge, including blood, requires emergency medical attention.
damage to the auricle, ear canal. Damage (scratches or wounds) may be caused by a foreign object. This is exactly the reason why you can do without the help of a doctor, but only if the injury was not serious. In this case, the bleeding that appears can be stopped by yourself;
the appearance of polyps in the ear. After the mucous membrane begins to grow, it protrudes above the surface, resulting in pus with an odor. Hearing becomes weak;
damage to the eardrum due to a foreign body that remains inside the ear. Because of this, the bleeding will not be severe, but not only pain in the ear may appear, but also dizziness, headache, and vision problems;
Blood from the ear can also be caused by a glomus tumor, which is a benign tumor. It is formed in the bulb of the jugular vein. When it begins to increase, its growth is directed towards the tympanic cavity, closer to the ear canal. As a result, bleeding from the ear appears, and it can be profuse. Tinnitus also begins to appear, hearing begins to deteriorate;
We recommend reading: Rabies Vaccination Causes Stunted Growth
the appearance of a boil. (a boil is an inflammation of the hair follicle). Its appearance is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. At the very beginning, pain appears in the ear, which is accompanied by swelling. The skin around the ear becomes reddish and swollen. As a result, fever and headache appear. After the boil opens, from
Source