Steroid medications
Glucocorticosteroids (GCS) are prescribed to relieve inflammation, reduce allergic manifestations, and relieve swelling. Depending on the condition of the animal, the veterinarian selects the drug and method of application. For severe acute forms of inflammation, GCS by injection is recommended: prednisolone, dexamethasone. These drugs have the following therapeutic effects:
- suppress the functions of leukocytes and tissue macrophages;
- reduce capillary permeability due to the release of histamine;
- increase blood glucose levels, stimulating insulin production;
- relieve inflammation;
- reduce swelling.
In order to relieve itching and restore the skin, a combined oral preparation, Stop-Itch, is prescribed, which is less toxic and safer than its analogues. The active ingredient is the steroid triamcinolone, and the auxiliary ingredients are pyridoxine, riboxin, succinic acid, and methionine. The drug prevents the production of inflammatory mediators, stabilizes the permeability of cell membranes, and improves the functional condition of the skin.
Treatment of the disease
If a cat has a swollen lower lip, the therapeutic effect depends entirely on the cause that caused this phenomenon. Below we consider methods of treating this problem depending on its pathogenesis:
- If this happened because the cat was switched to dry food, then simply change her diet and the problem will disappear in 5-6 days by itself.
- For injuries and burns, smear the affected area with such effective remedies as Levomekol, Sangel, Sanatol, Ranosan. They can be used both in the form of powders or gels, and in the form of ointments or sprays.
- If the owner suspects that the reason is an allergic reaction to something, then it is permissible to give him Suprastin.
- Oncological neoplasms are treated as follows: malignant - with chemotherapy and strong painkillers, benign - with surgical intervention.
- The fungus can be eliminated by such products as Fungivet-cream, Zoomikol, Imaverol.
- Inflammation with viral etiology is affected by Camedon, Anandin, Kanamycin.
- Lincomycin, Sinulox, and Levamisole have performed well in the fight against infections.
Each of the above drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor, based on the general condition of the cat, its age and weight. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances, this will only aggravate the problem and cause more suffering to your mustachioed friend.
Finally, I would like to say that neither a kitten nor an adult cat is immune from the occurrence of such a phenomenon. There are many reasons for this
Therefore, it is important to take your pet for examination to a doctor and, based on the recommendations received, carry out therapeutic therapy. Otherwise, the pet may die. The anomaly appears in the following situations:
The anomaly appears in the following situations:
- allergic reaction;
- change of feed;
- injury;
- tumor;
- acne.
Allergic reaction
With a hypersensitive response, in addition to swelling of the lip, other symptoms appear, for example, conjunctivitis or nasal discharge, skin rash. Interrupting contact with the allergen and using an antihistamine eliminates the problem.
Change of feed
Thin lips are observed when switching from wet to dry food. But most often the problem arises when an animal accustomed to natural nutrition is treated with dense granules. It is necessary to gradually transfer the pet to dry feeding or abandon it.
Injury
Damage occurs as a result of a bruise, a bite, or if the cat is stung by an insect. For minor injuries, they limit themselves to treating the affected area with an antimicrobial agent. What to do when the swelling does not go away for a long time? Contact the clinic. Otherwise, inflammation of the salivary gland will develop. It becomes clogged and a cyst forms. Treatment is surgical. The pathological cavity is pierced or removed.
The viral disease mainly affects unvaccinated young animals. In addition to a swollen lip, the disease manifests itself with other signs. Characteristic symptoms are tongue ulcers. Detected symptoms are the basis for contacting the clinic.
Tumor
In old animals, the appearance of a tumor on the lower lip raises suspicion of the formation of a neoplasm. The defect discovered in the early phase of the pathology is excised, and the animal recovers. If the cat owner ignores the tumor that has arisen, it will transform into malignant.
The lip is swollen due to a reaction to food, medicine and other allergens
A lip tumor in an animal (see photo) may be a consequence of its body’s reaction to an allergen, which can be prepared food, veterinary medicine, pollen from flowering plants, household chemicals, perfumes, etc. This phenomenon cannot be ignored. Allergies can lead to the death of a pet. If you suspect an allergic reaction, you should give your four-legged pet an antihistamine as quickly as possible: Suprastin, Tavegil, Zodak, Zyrtek, etc.
This is interesting: Treatment of Cats with Vodka
Using an antiallergic drug is not enough. Such medications are aimed only at eliminating allergy symptoms. They are unable to eradicate the problem. First of all, you need to prevent your pet from coming into contact with the allergen. If this is ready-made food, you need to stop feeding it to the cat. If a cat reacts sharply to the owner's perfume, you should stop using it. It is unlikely that you will be able to independently identify the cause of your pet’s allergies. It is better to entrust the solution to this problem to a veterinarian.
Description of the most common causes
If a cat's lip is very swollen and there is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock, then the animal must be immediately hospitalized. This condition can occur after a bite from stinging insects in the muzzle area. It is also impossible to exclude diseases whose clinical picture may include this symptom. As for the frequency of occurrence, the following possible reasons should be kept in mind:
- Injury. A strong impact after falling from a height or colliding with hard objects can cause a cat's lip to swell if it hits its face. Minor damage does not require any action on the part of the owner, as it goes away on its own within a few days. If there is an open wound along with swelling, then it is recommended to carry out antiseptic treatment of the affected area. Most bruises and bruises go away within 2-5 days.
- Bacterial damage. It most often begins after the cat participates in a fight, in which he can receive an open wound after being bitten or clawed. With a bacterial infection, there is pus and redness. If the scratch occurs on the lip, it swells and hurts when touched. Most often, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is prescribed. The duration of the course and dosage are determined by the doctor, based on the severity of the clinical picture. If necessary, cytology of the fluid taken from the wound can be performed.
- Stinging insect bite. Even those cats that do not go outside at all have a high probability of being stung by a wasp or bee in the spring or summer. Very often such bites occur on the lips, which become very swollen as a result. In most cases, the swelling goes away within a few hours after the bite. If this does not happen or there is a possibility that the swelling spreads to the neck or nasopharynx, then immediate hospitalization is indicated for the animal to prevent possible suffocation. Moderate edema is most quickly relieved by injection of corticosteroids. Also, we must not forget about the sting that remains after the bite. After removing it, you can treat the wound with an antiseptic (iodine, brilliant green).
- Allergy. All swelling associated with the face is most often caused by insect bites or food allergies. Less commonly, a cat's lip may swell after taking medications or vaccinations. Decorative breeds suffer from food allergies more often than others. Therefore, owners of Maine Coons, Sphynxes, Persians, Abyssinians and exotics need to take a responsible approach to the choice of food. Along with swelling, other skin problems may appear in the form of peeling, redness and hair loss. The worst thing is when the process is complicated by itching, which can cause deep wounds. Allergies are difficult to treat, especially in cases of unknown etiology. In some breeds, switching to a hypoallergenic type of food is considered the only way out to somehow muffle the symptoms.
- Eosinophilic ulcer. Recently it has become very common in all breeds. Refers to autoimmune diseases. Characteristic symptoms include damage to the oral mucosa with pink ulcers, which are accompanied by pain while eating. Also often due to an eosinophilic ulcer, the lip and nasal area swell. Many experts associate this pathology with allergies, since changing food and bowls in many cases helps solve the problem.
- Abscess. The most common reason why a cat may have a swollen lip without visible damage. It can form due to infection in an open wound (scratch or small crack). A distinctive feature is that the appearance resembles a large pimple with a rod at the end. It is accompanied by severe pain, due to which the pet may even refuse to eat. Given their specific location, it is best to open such abscesses in a hospital setting to eliminate the possibility of infection getting into an open wound.
How to fix the problem
If the cause of the swelling is a callus due to a change in food, then it is enough to switch the pet to liquid food for a while. In this case, no additional treatment is required. If a cyst is present, it can be removed in a veterinary clinic.
If your pet has injured its lip, the affected area should be treated with antiseptics 3 times a day. A solution of Chlorhexidine is suitable for these purposes. It is not recommended to use drugs containing alcohol, as they can increase pain. The course of treatment depends on the nature of the injury.
Chlorhexidine has an antiseptic effect
If your cat's lip is swollen due to an insect bite, you should immediately apply a cool compress. Then carefully examine the affected area and, if necessary, remove the sting with tweezers. Just in case, it is recommended to give your pet any antihistamine: Suprastin, Zodak, etc. A quarter of a tablet is enough, which should first be crushed and mixed with water.
Suprastin eliminates the symptoms of an allergic reaction
If there is a burn, long-term rehabilitation therapy is required. For these purposes, it is recommended to use ointments such as Panthenol, Sulfargin and others. They need to be applied 2 times a day for a week or more. For allergies, antihistamines are used regularly
It is also important to identify the cause and eliminate it
Panthenol accelerates the healing of damaged tissues
Eosinophilic granuloma is treated with a complex of antibiotics (Doxycycline, Amoxicillin, etc.), as well as glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone and Hydrocortisone). The drugs have a strong effect on the body, so the course and dosage are determined only by the doctor.
Dexamethasone eliminates swelling
A viral infection is eliminated with the help of immunostimulants: Ribaflox, Fosprenil, Interferon, etc. If the cause of swelling is fungal flora, then Fungivet, YAM ointment, etc. are prescribed. These drugs are used in a course of at least 10–14 days.
YAM ointment is active against fungal flora
How to cure a kitten
To eliminate swelling of the lower lip in a kitten, treatment is the same as for adult pets. The only difference is that all drugs are used in reduced dosages. Therapeutic tactics directly depend on the provoking factor. For treatment, only local agents are often used: antifungal, antiseptic, antiviral and antibacterial.
To eliminate swelling of your pet’s lower lip, you need to contact a veterinarian in time.
This is especially important when treating kittens, since the baby’s body during the growth period is still very weak and susceptible to various infections. An integrated approach to therapy allows you to eliminate the cause of the problem and relieve your pet of unpleasant symptoms.
How to treat swelling at home
The lower lip often swells in cats of Persian and British breeds due to the peculiar structure of the muzzle. Sometimes the swelling goes away on its own, but if after a week the lower lip has not returned to its normal size, you need to see a veterinarian. It happens that there is no opportunity to show the animal to a doctor. Before treating your cat at home, listen to these recommendations:
- lubricate the swelling with Lugol's solution, Yoddicerin;
- give the animal antihistamines, preferably those suitable for infants (Desloratadine, Loratadine);
- carefully monitor your pet’s behavior;
- When bitten by insects, you must first remove the sting with tweezers, treat the affected area with vinegar essence 3% and soda, and apply ice.
It should be remembered that if you are the owner of a nursing cat, then treating your pet at home may be completely impossible. You need to go to a veterinary clinic for a professional examination, testing for bacteria and infections, and prescribing medications for your cat. If no parasites are found, antiparasitic therapy is still needed. If the disease is too advanced, and there is no way to quickly cure the cat, you will most likely have to treat the pet for the rest of its life and maintain its health with certain medications. Timely assistance, close care for your pet - and the animal’s health will always be in excellent condition.
Why does a cat's lower lip swell?
The tissues of the lips of cats have fairly soft skin, permeated with a dense plexus of blood vessels and a large number of nerve receptors. This part of the animal’s body is delicate and can be easily damaged. Any wound and swelling will be painful for your pet.
Normally, the lower lip of cats is thin and has a pale pink or brown color (depending on the color of the animal)
A warning sign that something is wrong with your cat's lips is that they become red and swollen. The main causes of edema are:
- Dental diseases. Most often, swelling of the lower lip occurs due to gingivitis - inflammation of the gums. The causes of this pathology are untreated caries, an unbalanced diet, weakened immunity, and complicated jaw injuries. Inflamed gums cause pain and discomfort to the cat, subsequently leading to loosening and tooth loss. If the process is chronic and constant tissue injury occurs when biting, an abscess may occur.
- Allergy. An allergic reaction in a cat can occur to food, insect bites, and household chemicals. In acute allergies, anaphylaxis or Quincke's edema may develop. These are deadly conditions, as the swelling spreads to the larynx and causes the airways to become blocked.
- Trauma and wound suppuration. Cats can get a wound on their lip or gum by eating too hard food or licking cans of canned food. A cat can damage its lip if it jumps poorly. Trauma often occurs after cats fight. Severe swelling of the injured lip is dangerous due to bacterial infection. Without help, a cavity with pus (abscess) develops. The danger is that purulent-septic contents can spread with blood throughout the body. This leads to pathologies such as osteomyelitis (inflammation of bone tissue), pyoderma (inflammation of the skin), liver damage, kidney damage, and general sepsis.
- Inflammatory diseases. Eosinophilic granuloma is common in cats. The clinical picture and pathogenesis resemble herpes that appears on the lips of humans. The main reason is genetic predisposition. A factor for the appearance may be a viral disease, weakened immunity, flea or tick infestation.
- Burns. A cat can get thermal, chemical and electrical burns to the lower lip. The reasons are carelessness of the owners (for example, those who forgot to hide household chemicals) and the curiosity of the animal. In everyday life, irons, heaters and other electrical appliances for various purposes can pose a danger to cats. Thermal burns can occur due to contact with boiling water or hot dishes.
- Benign neoplasms. Benign tumors are gingival fibroma, Jacobs ulcer or epulis. The tumor first grows on the gum, but in a complicated form it spreads to the lip area. The tumor may have the color of the gum itself or be paler, feels dense to the touch, and does not cause pain on palpation. It is formed due to a hereditary predisposition or as a complication of an untreated pathology (for example, fibroma often appears against the background of eosinophilic granuloma).
- Cancerous tumors. The most dangerous malignant tumor that can appear on a cat's lower lip is squamous cell carcinoma. First, redness and slight swelling of the tissue appear. After just a couple of months, the swelling increases 3-4 times. Then non-healing bleeding and festering ulcers appear. The tumor quickly spreads to neighboring tissues and lymph nodes. Unfortunately, it is not possible to completely cure a cat, but with the help of chemotherapy and surgery you can prolong your pet’s life.
The cat has a sore on her lip: Is there viral rhinotracheitis on her face?
Viral rhinotracheitis - herpes in cats, like other viral respiratory infections, is widespread. The disease affects everyone from the cat family; all breeds of cats are affected, regardless of age, with the exception of kittens up to two months of age, which receive antibodies from their mother with milk.
Risk factors for infection:
The peak of the disease in cats occurs during the cold and rainy seasons (winter, early spring, late autumn). When kept in crowded conditions, the infection takes on the character of a permanent enzootic.
Watch the video: Sore on a cat’s lip - on the face Calicivirus
The main route of infection is aerogenic, that is, through the air, which contributes to the rapid spread of the disease.
The most common routes of transmission are food, care items, people in contact with sick cats, and contaminated air. The disease is species-specific and is not dangerous for humans or other animal species.
If the cause of sores on a cat’s lips is viral rhinotracheitis, the clinical picture will be as follows:
- Copious nasal discharge.
- Decreased appetite.
- Lethargy.
- Fever.
- Cough.
- Ulcers on the lips that look like herpetic rashes in humans.
- Increased lacrimation, conjunctivitis.
The course of the disease can be acute, subacute and chronic; in advanced cases, severe pneumonia develops.
What kind of disease does a cat have on her lower lip?
More often the upper lip is affected on the right or left, less often on both sides at once. The ulcer has a clearly defined outline, its color is closer to brown, its size is 0.2-5 cm. There is no itching or pain, the pet clearly feels discomfort only at the time of eating or drinking. Therefore, the owner may notice that the pet has begun to avoid bowls. Additionally, the following can be found on the surface:
- plaques;
- miliary dermatitis;
- granulomas.
The same patient may experience different manifestations simultaneously. The localization of various manifestations of the disease can be: the abdomen or thigh, back or neck, lower lip or gums.
To exclude further manifestations of allergic dermatitis, it is recommended to conduct a special test. It will allow you to identify the problem to which the body develops a negative reaction. Often, tailed pets are allergic to dust, tobacco smoke, pollen, and mold.
Diseases affecting the oral cavity (mouth) and pharynx (pharynx) in cats are not uncommon. Such diseases are called oropharyngeal.
There are many signs that indicate that your cat has problems with the oral cavity or pharynx, including:
Loss of appetite. The cat stops being interested in food, or goes to the saucer, but refuses to eat;
Dysphagia
Swallowing disorder indicates difficulty eating or swallowing food—the cat eats with apparent caution, shows signs of discomfort, may drop food from its mouth, or has difficulty swallowing;
Ptyalism is excessive salivation or drooling from the mouth (sometimes with bleeding);
Halitosis is an unpleasant odor from a cat’s mouth; The cat scratches or rubs its mouth with its paws, sometimes shaking its head;
Weight loss - usually due to lack of appetite;
A few days ago I noticed a clear redness of the cat’s lower lip, since she previously had only white fur in this place. I decided to take a closer look and examined it: I discovered a small swelling on the lower lip, similar to herpes in humans, with several small blisters. I went to the veterinarian, they took blood tests to rule out one of the diseases. They didn’t test for herpes (since it’s not done here, but done in Moscow). They prescribed Chlorhexidine and Metrogyl Denta. What could it be?
After going to the doctor in the cold, the swelling subsided a little.
The analysis confirmed the presence of the syndrome. There were 11 units in the blood (I may be wrong about how the quantity is measured) and leukocytes were very slightly elevated, all other indicators were normal. They prescribed Dexofort 0.5 subcutaneously every 8 days, and after the symptoms disappeared, as relapses appeared.
Thank you very much for the consultation.
Mouth diseases in cats
Nature has provided a special system for maintaining oral health in cats. Even despite the lack of brushing, the diet and behavior of animals help keep them safe and sound. However, the home lifestyle has significantly affected the lifestyle of our pets, which is why oral diseases occur with enviable regularity.
Causes
One of the main reasons for the development of complications in a cat’s mouth is decreased immunity. Even competent prevention of oral diseases is not always able to prevent tooth decay and inflammatory diseases of the mouth and mucous membranes. A weakened animal is more often susceptible to more severe forms of disease and is not able to recover on its own.
Poor nutrition can also lead to problems with teeth and gums. The presence of only soft food in the diet does not allow teeth to be cleared of plaque, which leads first to the formation of stone, and then to other diseases.
The occurrence of wounds in the mouth often leads to the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane. Another cause of their disease may be a lack of vitamins and minerals, fungal and bacterial infections.
Symptoms
The very first “bell” about a violation of the normal condition of the teeth will usually be the appearance of difficult-to-clean plaque on the teeth. It can range in color from light yellow to dark brown. Over time, it only increases the area of distribution.
Redness and swelling of the gums indicate inflammation, and increased salivation and bleeding may be observed.
Advanced diseases of the oral cavity can be accompanied by the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane, tooth loss and destruction.
The cat's appetite decreases or it completely refuses to eat, this is due to increased pain when chewing. The drinking regime is maintained.
Treatment
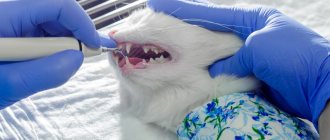
The easiest way to prevent serious oral diseases is to have your teeth cleaned in a timely manner by a veterinarian - he will not only help remove plaque, but also rid your cat’s teeth of tartar, and also apply a special solution to strengthen and prevent the re-formation of tartar.
For any pathology of the oral cavity, it is recommended to treat with special antiseptic solutions or astringent herbal decoctions.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Gas stove Hephaestus, how to turn on the oven
During treatment, it is recommended to switch the cat to soft food, returning to its usual diet after complete healing.
Sometimes a damaged tooth cannot be saved, in which case it is simply removed. In case of chronic oral diseases, it is even possible to completely remove all teeth.
Antibiotics are used when purulent complications occur; in most cases, wound-healing ointments are used.
If diseases of the oral cavity are associated with a complication of the underlying disease (for example, diabetes), then it is imperative to treat it.
Prevention measures
- Periodically buy special food to clean your teeth. Combine canned cat food and ready-made dry food, trying to give preference to the latter.
- Maintain a balanced diet and adequate intake of vitamins and minerals.
- Be sure to carry out supportive drug therapy for chronic diseases.
- Clean your teeth yourself at home - soft silicone brushes or a regular bandage are good for this.
Cats very rarely suffer from infectious diseases of the oral cavity; this can be explained by the slightly alkaline saliva and the content of antibacterial enzymes in it, which protect the animal from the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Bad breath should alert a cat owner and may indicate dental problems or an infection. Tartar that appears on your cat must be removed. An unkempt, sloppy appearance of a cat is an indicator that it has stopped licking itself; if they have diseases of the mouth, they are not able to do this.
This sign should alert cat owners, as should strong salivation, during which the hair on the chin, front paws, and chest becomes wet. Stomatitis or gingivitis in a cat may be indicated by an unpleasant odor from the mouth, which is noticeable even from a distance, but it can be confused with the odor from industrial food.
Symptoms of this disease occur as a result of periodontitis, when the periosteum of the tooth root is inflamed or in the case of an infectious disease in the cat’s oral cavity.
Injections or cuts from weeds while walking can cause irritation and the lips will begin to peel. Treatment for inflammation of the lips consists of washing the affected areas with an antiseptic solution and lubricating them with an ointment containing an antibiotic twice a day.
If a cat develops periodontitis, the cat's teeth need to be treated.
Lacerations
Lacerations of the mouth are most common in pets that often walk outside, in animals that like to sort things out with other cats. Owners of such pets often turn to the veterinarian at the clinic with a request to heal wounds after a fight.
Treatment of wounds consists primarily of stopping the bleeding, for which the cat is immobilized and, if necessary, sedatives are used. Small cuts are not sutured, but lacerations and deep wounds are stitched, especially if the bleeding does not stop. In cases where the wound is caused by an incorrect position of the tooth, it is removed.
During treatment, the cat’s mouth must be washed twice a day with a weak antiseptic solution and given specially prepared food, mostly soft.
Gum inflammation
When gum disease occurs, cats develop bad breath, which may indicate tartar or the accumulation of hair and food debris between the teeth; these are the primary causes of inflammation, which can lead to tooth decay and periodontitis.
When examining the mouth, the cat's gums will be inflamed, red, and in some cases bleeding. Then the edges of the gums may begin to recede, cracks and pockets form where food gets in and begins to rot, resulting in the formation of pus and caries.
The animal stops eating, becomes weaker, looks bad, and sometimes has increased salivation.
Glossitis is an infectious inflammation of the tongue, which often occurs with cat immunodeficiency, with leukemia, with viral immunodeficiency disease and with a whole complex of respiratory viral diseases.
In this case, foam appears at the mouth, severe salivation, the cat stops licking itself, looks unkempt, and refuses to eat due to severe pain in the mouth. Healing of the surface of a cat's tongue means the disappearance of thorns, it becomes smooth, varnished, and red.
Treatment is carried out by rinsing the mouth with a weak antiseptic solution, and antibiotic therapy is prescribed. In this case, the cat’s food should be soft and not cause irritation.
We suggest you read How to remove a stain from pants: useful tips
Stomatitis in cats
Stomatitis in cats occurs as a result of inflammation of the oral mucosa, and saliva is produced abundantly.
The cat may begin to shake its head, rub its face with its paw, refuse food, and will not allow itself to be examined.
To do this, it will be necessary to restrain the cat; when examining the mouth, redness is visible, the gums bleed, swelling and a bad odor appear. In this case, the cat will look sloppy, unkempt, and ruffled.
Her treatment for stomatitis must always be carried out in a hospital under anesthesia. The veterinarian will sanitize the mouth, remove tartar from the teeth, and remove diseased teeth. For treatment, antibiotic therapy and diet are prescribed, and the cat’s mouth is irrigated with an antiseptic every day.
The salivary gland of a cat can most often be damaged due to fights or contact with foreign objects.
In this case, the fluid begins to accumulate and rupture the duct, resulting in the formation of a mucous cyst directly in the gland - a mucocele.
Any of the cat's salivary glands can be affected in this way, but most often the cyst appears in the submandibular gland. In this case, a smooth, large and round cyst will be felt under the tongue on one side.
A mucosal cyst will prevent the cat from swallowing and breathing normally; when punctured, it will release mucus, a honey-colored substance. In some cases, puncture and washing may not be enough for the animal to fully recover; most often it is necessary to remove the gland completely.
The tumor most often occurs in an old animal, it is most often malignant, and looks like a dense, slowly growing lump.
It almost always forms on the neck or side of the muzzle. If such a tumor is not noticed in time or removed, then the stage of metastasis may begin; if everything is done on time, the animal will fully recover.
It is considered an autoimmune disease. The primary provoking factors are exposure to an allergen or infection by parasites. Research by foreign veterinarians puts forward a hypothesis about a genetic predisposition to this disease. It has been noticed that in 80% of cases, ulcers on the upper lip appear in purebred animals, but yard cats practically do not get this disease.
You can suspect that a cat has contracted Jacobs disease by the location of the spot: it usually appears on the upper lip and, in rare cases, on the oral mucosa or lower lip. Signs of inflammation progress quickly, the wound begins to deepen and become inflamed. The sore is difficult to heal. In advanced cases, the cat's teeth and gums are exposed.
Attention! It is quite easy to distinguish Jacobs disease from, for example, a trophic ulcer. With this disease, the cat does not experience any discomfort or pain.
In most cases, the owner does not immediately notice that the pet is sick and detects an ulcer only when there is clearly expressed eosinophilic granulation. Delayed treatment can lead to sarcoma or fibroma.
Tumor of the lower jaw in a cat: causes and treatment
Oral pathologies in cats are a rare occurrence. Most often, old or weakened animals encounter neoplasms, inflammatory processes and bacterial lesions of the mouth and jaw.
A tumor of the lower jaw in cats is difficult to treat at home and is difficult to diagnose, so you should consult a veterinarian.
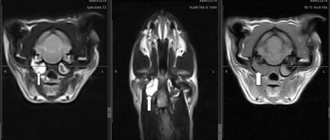
The results of the X-ray examination will allow us to draw conclusions about the nature of the tumor.
Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
If a cat's lower jaw is swollen, the likely cause is oral disease. In older cats we are talking about dental diseases. With age, teeth begin to loosen, lose hardness, and begin to crumble.
Any microcracks in the enamel lead to the development of a pathological process, which results in complete decay of the tooth.
In cats, the roots of the teeth are located deep in the gum tissue, so tooth decay can lead to the formation of a seal on the lower jaw. Associated symptoms:
- refusal to eat;
- jaw turned to one side;
- lethargy and weakness;
- no pain when pressed.
Typically, animals with dental problems refuse to eat.
At the same time, the cat experiences severe hunger and can in every possible way attract attention to its own bowl, but as soon as it is filled, the pet will turn away and leave. This is because chewing food causes pain.
The structure of the tumor will tell you about the possible causes. If a hard neoplasm is noticeable upon palpation, but the cat breaks out and does not allow itself to be touched, a cyst of the lower jaw is a possible cause. This neoplasm can be caused by dental diseases and is an overgrowth of bone tissue in the lower jaw.
If a soft and heterogeneous structure is noted upon palpation, the possible cause is an abscess, the development of which is due to the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. This happens when pathogenic agents penetrate deeply into the root of the tooth. The abscess must be opened surgically, but there are cases when it breaks out on its own.
Possibly what could cause a cat's eyes to fester?
Diseases of the oral cavity and teeth in cats are indicated by foul breath, red gums and impaired jaw movement during eating.
This pathology can only be treated surgically - it is necessary to remove rotten teeth, open an abscess or cyst. If the abscess has opened on its own, antiseptic treatment should be carried out several times a day to avoid secondary infection of the wound cavity.
During surgical removal, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection of healthy oral tissues.
Malignant and benign neoplasms
Malignant tumors in the mouth of animals are rare. However, if the jaw of a cat over 13 years of age is swollen, cancer can only be ruled out after a comprehensive examination of the animal.
There are usually no specific symptoms for jaw cancer. The animal may become lethargic and refuse to eat, but these same signs accompany an abscess and dental problems.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the jaw and take a blood test to identify the inflammatory process. If the presence of a tumor is confirmed, an operation is performed to remove it, followed by tissue examination.
For malignant neoplasms, animals are prescribed a course of chemotherapy.
The danger of malignant neoplasms is that they are rarely accompanied by significant symptoms. A jaw tumor at the beginning of development manifests itself in the same way as dental problems, but can cost the cat his life.
With osteosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the jaw, pain is pronounced. The animal cannot chew, drink water, and does not allow the affected area to be touched. In some cases, syringe feeding may be necessary
It is important not to try to treat your pet on your own, but to visit a doctor in a timely manner
Other reasons
Swelling of the lower jaw and lips in cats can be caused by household injuries. An older cat may accidentally scratch his lip when chewing hard food. As a result, it will swell and upon external examination it will appear that it is a swollen jaw.
Burns to which animals that like to chew wires or taste food on the stove are also susceptible. Despite the apparent harmlessness, household injuries should be treated.
Any wounds and injuries are treated with an antiseptic; for burns, you should use a special product to speed up healing.
A cat has a sore on his lip: Treatment of viral rhinotracheitis
After confirming the diagnosis, the veterinarian will prescribe the following treatment:
- Complete feeding with soft, semi-liquid food, vegetables and cereals are excluded; in the first days of illness, the animal can be given low-fat meat broths, boiled chopped meat or fish, eggs and dairy products.
- Industrial feeds are given mainly in the form of pates, they should also be heated.
- If the animal completely refuses food, infusion therapy is carried out with Ringer-Locke and Glucose solutions.
- Systemic antiviral therapy (Famciclovir).
- Local treatment of sores with antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin) and antiviral ointment Acyclovir.
- Rinsing the nasal and oral cavities with antiseptic solutions.
- Symptomatic therapy: mucolytics for cough (Mukaltin), antipyretics for fever (injections of Analgin with Diphenhydramine).
- For severe conjunctivitis, Decta-2 drops
- Introduction of vitamins: Gamavit, Hemobalance.
- The use of a specific serum (Vitafel).
- If complications develop, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
- Immunomodulators (Fosprenil, Anandin).
This is interesting: Blepharospasm in cats treatment
The incidence of infectious rhinotracheitis in cats reaches 50%, mortality is 5-20%. After recovery from the disease, cats may become carriers of the virus.
The duration of the disease is 10-14 days, in some cases the disease drags on for several weeks and is accompanied by a rare cough and periodic runny nose. Cats with ulcerative stomatitis or pneumonia often die.
Predisposing factors
The main predisposing factor to the development of pathology is low immunity. A weakened animal gets sick more often, which causes an autoimmune reaction, expressed in the formation of eosinophilic granulomas. The following factors lead to a decrease in the cat’s body’s defenses:
Failure to comply with nutritional rules. The cat's diet should contain proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. Some owners prefer to save on their cat's nutrition by offering it food from their table. However, this menu does not provide the animal’s body with all the elements necessary for normal development.
Particular attention should be paid to the diet of cats with special needs (neutered, with chronic pathologies, aging). Improper care and poor living conditions. Different breeds of cats require different care
Some people should regularly treat their eyes to prevent inflammatory processes, while others are prone to ear pathologies, so you need to constantly monitor the condition of your ears.
- Feeding poor quality food. For purebred cats, you should choose premium and super-premium food. Economy options often contain a large number of preservatives, dyes and flavors that can accumulate in the body and provoke pathological processes.
- Using household chemicals to wash your pet's tray and dishes. Some chemicals can cause allergies. If it is not possible to eliminate dirt and unpleasant odors without special means, you should thoroughly rinse the objects that the animal comes into contact with.
- Past viral and bacterial diseases. After illness, the pet’s body becomes vulnerable to many pathologies.
The danger of the pathology is that at the initial stage, an inattentive owner may not notice that the pet is sick. Obvious symptoms of the disease appear when the disease takes on a life-threatening nature. Stages of development of a Jacobs ulcer on a cat’s lip:
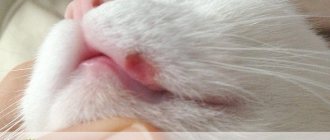
- The appearance of a small red spot on the upper lip (see photo). The animal does not experience any unpleasant sensations. It remains active and eats well. The inflamed area does not hurt or itch.
- Increased formation and appearance of a weeping wound with an unpleasant odor. The danger of this stage is that various infections can join the main pathology. The ulcer does not heal after using antiseptics, and the bacterial infection threatens the pet’s life as it quickly spreads throughout the body.
- Deepening of eczema. Gradually, the ulcer grows and affects the soft tissues. In the last stage, the wound becomes so deep and large that the gums and teeth are visible through it. The cat experiences severe pain, becomes lethargic, and refuses to eat or drink. It is very difficult to cure an animal at this stage, since the body is so weakened that it does not respond well to therapy. Most often, the pet dies from concomitant pathologies.
Untimely treatment of the disease causes activation of oncological processes. The cat may develop fibroma or sarcoma.
Swelling of the lower jaw in cats - what does this sign indicate?
Even the most attentive care is often not enough to protect your pet from illness.
Often, owners pay attention to signs of illness in cats too late - the disease progresses and requires long-term treatment under the supervision of a veterinarian
In order not to be late with the help of a specialist, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the main signs of dangerous diseases in advance. One of the signals from the body that indicates illness is that the cat’s lower jaw is swollen.
What problems does such a symptom indicate, and how to properly respond to an alarming manifestation?
Causes of swelling
If a cat has a swollen lower jaw, you should not delay contacting a veterinarian and treatment - there are many factors dangerous to the health of the animal that provoke such a manifestation. Among the causes of tumors, the most common are:
- Diet changes. If solid food is introduced into your pet's daily menu, calluses and swelling often appear - hard particles rub the lip.
- Insect bites. A pet's prolonged stay on the street often ends in an attack and bite by a wasp, bee, or even mosquito.
- Injuries. Outdoor games, falls, attempts to chew on a hard object can result in injury.
- Allergy. A negative reaction to external or internal stimuli provokes swelling and swelling.
- Reaction to helminths. As with allergies, the cat’s body is able to respond to the work of parasites with a tumor.
- Pathologies of the salivary glands, injuries of the lower lip.
- Cancer diseases. Malignant tumors can affect any part of an animal’s body, often even in the oral cavity.
Just like people, animals can develop rashes or occasional pimples. Often the rash occupies the lips of a pet, which results in an enlargement of the lower jaw.
Additional signs that should alert owners
With the development of severe diseases, an increase in the lower jaw is often accompanied by additional symptoms
Knowing what to look for, you will be able to react correctly - contact a veterinarian and undergo a course of therapy. If a cat's lower jaw is swollen, the following signs should alert you:
- an unpleasant smell of rotting or pus appears from the oral cavity;
- the swelling has a dense, hard structure; when pressed, the cat shows that it is in pain and does not allow the formation to be touched;
- the animal refuses to take food, it is thirsty because the cat does not drink;
- small transparent blisters with purulent contents appear on the oral mucosa;
- body temperature rises, the pet becomes lethargic and looks sick;
- cloudy mucus flows from the nose and eyes.
It is difficult to determine what causes such manifestations on your own, so it is not recommended to use any drugs or home remedies without preliminary diagnosis. Only if it is known for sure that the tumor was caused by an insect bite, the introduction of solid food into the diet, or an allergy, can you do without the help of a veterinarian.
Photos of cats with swollen chins
Once it has been possible to determine why the cat’s lower jaw is swollen, treatment can begin. In some cases, the manifestation can be dealt with quite easily:
- in case of injuries, it is enough to treat the wound with an antiseptic; if the damage is too serious, it is better to consult a specialist - you may need stitches;
- when using solid food, it is enough to simply adjust the pet’s menu - give softer food;
- for insect bites, treat the painful area with an antiseptic, remove the sting if necessary, apply a cold compress;
- if the lower jaw is damaged after contact with other animals, consult a doctor - there is a risk of contracting dangerous diseases;
- in case of an allergic reaction, it is recommended to use antihistamines, but only with the permission of a veterinarian, after an accurate diagnosis and identification of the allergen;
- For viral infections, use antibacterial medications.
Oncological diseases that provoke the development of a tumor in the lower jaw can only be treated by a veterinarian. To get rid of the problem, it will be possible to undergo a surgical operation to remove the tissue affected by the disease.
Pet owners need to remember that jaw swelling often indicates complex pathologies occurring in the cat’s body. It is not recommended to hesitate - timely help from a veterinarian will save not only the health, but even the life of your pet.
Associated symptoms
If a cat's lower lip is swollen, then this in itself is a symptom of various kinds of pathological processes in the body. However, in most cases, if the lip is swollen, it happens for completely harmless reasons. You should be wary only if there are accompanying negative signs.
Alarming symptoms:
- hard swelling structure;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- discharge of pus;
- blisters on the mucous membrane;
- the lip turned red;
- significant swelling;
- bad breath;
- spread of the tumor to surrounding tissues;
- discharge from the eyes and nose.