In the apartment
An uncastrated cat living in an apartment causes a lot of inconvenience to its owner. If you are not going to castrate your pet, then be prepared to face problems such as:
- Tags. Most unneutered cats mark their territory in this way. This is the natural behavior of a sexually mature animal; it is useless to scold for it. Animals periodically mark the owner’s things, furniture and corners. The tags have a strong odor that is difficult to get rid of.
- Night screams. With a loud cry, the cat scares away rivals from the house and at the same time notifies the females of its presence.
- Aggression. With the onset of puberty, a previously affectionate, playful kitten can become an aggressive male. This is due to the action of testosterone, which encourages the cat to strive for leadership and conquer territory.
What happens if you don't castrate your cat?
If he is not sterilized, then there are two options: tolerate his behavior and take it for granted, or get rid of the animal and give it to friends. Radical option: just throw him out onto the street. In both situations, a good relationship with the cat will not work.
This is interesting! When asked whether a cat can be neutered, the answer is yes. However, this operation has another name - sterilization.
Spaying your cat will help prevent the birth of unwanted kittens.
Hormonal drugs
There are many special drugs designed to suppress sexual desire in cats. They are available in the form of drops, tablets or injections.
Hormonal drugs, including “Sex Barrier”, “Contrasex”, “Nonoestron”, “Stop-Intim” and others, are often used by owners of uncastrated cats, allowing them to temporarily reduce the troubles that their behavior causes.
A significant disadvantage of hormonal drugs is the enormous harm they cause to the health of the animal. Frequent use can lead to consequences such as diabetes, cancer and other diseases.
In case of emergency, veterinarians recommend using natural-based sedatives, such as “Cat Bayun” and “Stop-stress”. They are not as effective as hormonal ones, but they do not harm the health of the animal.
Cat castration and urolithiasis
Urolithiasis (urolithiasis) is the formation of soluble and insoluble stones (stones, sand) in the organs of the urinary system.
It is believed that this disease in cats is directly related to castration. However, it is not. Sand is formed due to an insufficiently balanced diet, low water consumption, and also due to a sedentary lifestyle in both castrated and non-castrated cats. But, due to the narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, in castrated men the risk of obstruction (blockage) with sand increases significantly. That is why we focus the issue on urolithiasis in cats after castration.
Symptoms of urethral obstruction in cats:
- the cat often sits in the tray for a long time,
- worries
- vocalizes pitifully (meows),
- after visiting the tray, the litter remains dry or slightly damp (the cat pees drop by drop),
- loss of appetite, refusal of water.
It is important to remember that the absence of urination for more than 12 hours is a reason to consult a veterinarian. Urine that does not find an exit from the bladder flows back into the kidneys, leading to irreversible damage
To treat urolithiasis, a series of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures are carried out aimed at evacuating urine, determining the type of stones, providing symptomatic treatment and adjusting the cat’s diet. In case of frequent relapses of urethral obstruction, an operation is performed - urethrostomy.
Feeding a castrated cat to prevent urolithiasis
Treatment of a cat with urolithiasis is expensive, and in the case of urethrostomy, the result is also unpredictable, so it is better for the owner to listen to the recommendations for proper feeding of a neutered cat to prevent the formation of sand in the urinary tract and prevent the development of the disease:
A castrated cat must be fed with special industrial food. The main task of such food is to ensure sufficient water intake, which helps maintain urine acidity at 6.0-7.0
This urinary pH range promotes the dissolution of tripelphosphates (the most common type of stones in cats) and prevents the formation of oxalates (insoluble stones). If for some reason the cat does not accept commercial dry and wet food, the owner should pay special attention to feeding homemade food. It is necessary to permanently exclude fish and seafood in any form from the diet, as well as anything that contains a lot of phosphorus, calcium and magnesium. Make sure your cat drinks enough water
According to scientific research, a cat weighing 4-5 kg should drink 150-200 ml of clean water per day. When feeding dry food, even more water is required. Remember that low water consumption is a direct path to urolithiasis!
If the cat walks alone
Owners of unneutered cats who let them outside feel like they are doing a good deed by letting their pet run around and socialize with other cats.
Such people forget about the many dangers that await a cat on the street:
- cars that can seriously injure or kill an unwary cat;
- flayers and simply cruel people who can kick a pet;
- scattered poisoned dog food that a cat might try;
- various infections, including those dangerous to people;
- hungry packs of dogs;
- fights with other cats, in which the animal may lose an ear or an eye.
In addition, most owners do not want to think about the fact that free-ranging pets reproduce uncontrollably.
Cat owners do not feel involved in the increase in stray animals, because all problems with kittens lie with cat owners, who either get rid of the kittens right away, or let them grow up and throw them away. This exacerbates the problem of homeless animals, and all animal owners who allow animals to roam are guilty of it.
Will a neutered cat's behavior change?
For owners who love their cat, this circumstance alone should become a powerful incentive to take the cat to the veterinarian without delay. Castration of a village cat greatly increases its chances of living to a respectable age.
In a sense, the animal's behavior does change after castration. He loses sexual desire, and the cat no longer goes on a spree for several days, risking being run over by a car or in the teeth of a vicious dog.
Often, owners do not castrate a cat, fearing that it will stop catching mice and will not be able to repel strange cats that accidentally wander into its territory. In fact, such “softness” of an animal after castration is very rare. Most animals after castration remain as active and vigorous as before.
Diseases
Unneutered cats are susceptible to the following diseases:
- Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland that occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the prostate tissue.
- Diseases of the urinary system. Among them: urolithiasis;
- urocystitis (inflammation of the bladder);
- nephrosis;
- nephritis;
- pyelonephritis.
Castration will greatly reduce the risk of these diseases.
Thus, surgery is the safest and most humane way to solve all problems associated with cat behavior.
Complications in cats after castration: types, symptoms, treatment
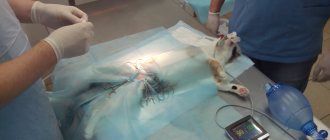
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, the animal does not feel anything. After castration, the cat needs special care. Compliance with all before and after operating procedures minimizes the likelihood of unpleasant consequences, but does not completely eliminate them.
Complications are divided into two groups: late and early.
The latter are observed more often and include:
- painful sensations;
- digestive disorders;
- bleeding;
- self-injury, for prevention, wear a protective collar for several days;
- inflammation, suppuration, abscess;
- prolapse of parts of the internal genital organs or intestinal loop;
- wound infection.
In the normal course of events, the pain goes away after 1-2 days. Your doctor may prescribe pain medications. Digestion is restored within a week, provided you follow the diet recommended by your veterinarian. For other manifestations, the animal is taken to a veterinary clinic.
Be sure to read:
A cat sleeps a lot and is lethargic after sterilization: normal or pathological, what consequences may occur after the operation
Late complications do not appear immediately:
- problems with urination as a result of injury to the ureter;
- formation of fistulas (when using the ligature method of sterilization);
- weakening of the urethral sphincter due to hormonal changes;
- urolithiasis disease.
To avoid late severe consequences, veterinary examinations are carried out regularly.
Pain reaction after surgery
Painful sensations are the most common type of complications. Removal of the gonads is a painful procedure performed under anesthesia. After leaving the anesthesia (2-24 hours), the predator marks the territory, urination is involuntary. Urine getting on the wound causes burning and pain.
An inflammatory process accompanied by unpleasant sensations is inevitable. Pets are trying to “lick” the wound. To avoid germs and additional trauma, a special collar is worn on the neck for 3-4 days.
With severe pain, behavior becomes aggressive. To alleviate the condition, the veterinarian prescribes pain medication. If the situation worsens, the pet is taken to the doctor.
Bleeding
Liquid discharge and ichor in small quantities are normal after surgery. A trickle of blood flowing from the wound should alert you. Bleeding can also be internal; the main symptom is a swollen abdomen.
Causes:
- insufficient compression of the skin during surgery;
- hypocoagulation;
- phlebeurysm;
- incorrect ligature application;
- the biological knot is loosely tied;
- seam divergence;
- vascular sclerosis;
- improper care after sterilization.
In case of bleeding from the vessels of the scrotum, artery of the vas deferens, or the stump of the spermatic cord, repeated intervention is necessary. After identifying the source of bleeding, the doctor torses or ligates the vessel.
The animal is tested for clotting. If the test reveals hypocoagulation, I prescribe therapy.
Scrotal swelling
Enlargement of the scrotum by more than 2 times, with inflammation spreading to the foreskin, peritoneum, and high temperature indicate infection in the body. Pathogenic organisms are introduced by violating the rules of antiseptics, poor pet hygiene, or lack of walks. The progression of the infectious process is facilitated by the accumulation of dead cells in the wound. The wound heals, creating favorable conditions for the formation of an abscess.
Treatment is carried out as early as possible. The doctor removes the adhesions and exudate that has accumulated in the scrotal cavity. The wound is treated with iodine solution. To avoid secondary adhesions, the affected area is treated with boron ointment. Treatment is carried out with titrated antibacterial drugs.
Be sure to read:
When can you bathe a cat after castration: what is it for, what products to use, how to wash
Tissue loss
In case of prolapse of the omentum, spermatic cord stump, vaginal membrane, severe infectious lesion. Tissues come into contact with microbes, and the immune response is weakened. Prolapse of the intestinal loop threatens the intestines to come out.
Treatment is surgical. The prolapsed part of the vaginal membrane or spermatic cord is amputated with an emasculator, and a ligature is first applied to the cord. The omentum is pulled out, tied with thread and cut off. The intestinal loop is set back, and the tissues that come out with it are cut off.
Inflammation of the common vaginal lining
When the testicles are removed, as a result of the reduction of the external levator testis, the tunica vaginalis is pulled upward. The shell leaves are soldered together, a cavity is formed, which is filled with exudate. Under normal conditions, the exudate resolves, but when pathogens enter, inflammation develops. The process causes an acute painful reaction.
Therapy is carried out by washing the vaginal lining with hydrogen peroxide. If necessary, remove pus and adhesions. To prevent the spread of the pathological process, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
Inflammation of the spermatic cord stump
Funiculitis begins with an increase in the cord of the inguinal canal; upon palpation, the organ is dense and motionless. The complication appears on days 4-5.
Causes:
- violation of antiseptic rules during intervention;
- incorrect ligature application;
- formation of a hematoma in the cord;
- stump loss;
- leaving large curls when unscrewing the spermatic cord.
- Treatment consists of treatment with antiseptic agents.
Retroperitoneal abscess
Treat secondary complications. Inflammation from the spermatic cord spreads through the lymph nodes to the abdominal cavity and the walls of the bladder. The process develops rapidly: the temperature rises, the cat refuses to eat, and suddenly loses weight.
After diagnosis, antibacterial or sulfonamide drugs are prescribed. If abscesses form, surgery is performed. Subsequently, the wound is washed with antiseptics.