Varieties
Nephritis in cats is classified primarily by the speed of its progression. In this regard, a distinction is made between acute and chronic forms of the disease. According to localization, this disease can be focal or diffuse. According to the degree of tissue damage, they are distinguished:
- glomerulonephritis, in which the kidney glomeruli begin to deteriorate and gradually die;
- pyelonephritis – stage of purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis;
- interstitial nephritis, in which the tubules become inflamed and urine infiltration occurs.
The latter type of pathology in cats is quite rare. Against the background of glomerulonephritis, an animal, among other things, may develop a lipoid form of the disease, accompanied by the replacement of kidney tissue with fatty structures and their degeneration. This pathological process is very severe and is considered incurable.
Signs of chronic glomerulonephritis and methods of combating it
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Chronic glomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory chronic kidney disease that initially affects the renal glomeruli and tubules, subsequently spreading to other kidney tissues. Slowly progressing, damaged kidney tissue is replaced by connective tissue, sclerosis occurs, leading to chronic renal failure.
Kidneys are paired organs that perform the function of urine formation through chemical self-regulation of the body, thereby removing foreign compounds and toxic substances from the body. They take part in carbohydrate and protein metabolism and in the formation of a number of biologically active substances.
The main load during blood filtration falls on the renal glomeruli with tubules and Bowman's capsule (nephrons). At the time of birth, nephrons have already formed, but continue to mature for about 10 years. Since new glomeruli are no longer formed after birth, their loss leads to kidney failure.
Upon completion of filtration, urine is excreted through the renal tubule into the renal pelvis, from where it drains into the bladder.
First of all, with glomerulonephritis, changes occur in the nephrons:
- Due to inflammation, microthrombi form in the glomeruli, which close the space in the vessels. Blood stops flowing into the nephrons. The entire procedure of blood filtration and the formation of primary urine in the affected glomerulus is disrupted.
- Since blood does not flow into the affected vessels, voids form in them, which are replaced by connective tissue. Nephron function declines.
- The more nephrons are involved in the process, the less blood is filtered by the kidneys, and kidney failure appears.
- Kidney failure leads to the accumulation of harmful substances in the body, and beneficial substances do not have time to return to the blood.
Stages
Chronic glomerulonephritis undergoes several stages:
- Compensation stage. This is an early stage in the development of the disease. At this stage, the kidneys are functioning without visible disturbances. There is a moderate increase in blood pressure and slight swelling. A slight increase in protein in the urine, a change in its density, the presence of modified red blood cells. The concentration of urine decreases.
- Stage of decompensation. At this stage, kidney function is impaired and renal failure occurs. Blood pressure numbers are high, the body is poisoned with nitrogenous compounds, and daily urine output increases. The level of protein in the urine increases, the presence of casts and red blood cells increases, and the density of urine decreases.
- Uremia. The most difficult stage. The kidneys cannot maintain the correct composition of the blood. Intoxication with residual nitrogen, creatinine, and urea appears.
Chronic glomerulonephritis can be infectious-immune and non-infectious-immune.
Types of glomerulonephritis:
- Latent glomerulonephritis. The most common type, it accounts for 45% of the total number of patients. Symptoms are mild. Slight increase in blood pressure, mild swelling. The disease can be identified by the results of a laboratory test: protein, red blood cells and white blood cells are increased in the urine. Lasts a long time, up to several decades. Systematic outpatient monitoring of the patient is required. Working capacity is not impaired.
- Hematuric glomerulonephritis is rare, accounting for about 5% of all cases of chronic glomerulonephritis. There is an increased content of altered red blood cells in the urine, which is why the urine is red or pink. Anemia is sometimes observed. Renal failure occurs infrequently, and the course of the disease is favorable.
- Nephrotic glomerulonephritis. It affects 25% of the total number of cases of glomerulonephritis. With this type, the pressure is increased, there is severe swelling, and little urine is produced per day. There is protein in the urine, the density of the urine is increased. In a biochemical blood test, cholesterol is increased and total protein is decreased. This type of glomerulonephritis progresses moderately, but rapid progression is also possible. Kidney failure develops.
- Mixed form of the disease. Occurs in 7% of cases. Repeats the symptoms of hypertensive and nephrotic types. It is characterized by a persistently progressive course and the formation of chronic renal failure.
Any form of the disease has two phases:
- Compensated. The kidneys are working normally.
- Decompensated. The kidneys work with impairment of their functions, chronic or renal failure progresses.
The result of chronic glomerulonephritis is the formation of chronic renal failure. The very first symptom is a decrease in the relative density of urine (isosthenuria) and an increase in the amount of urine excreted per day (polyuria). Diuresis increases at night (nocturia). Signs of uremia appear. The body is poisoned with nitrogenous substances and uremia develops.
Tubulointerstitial nephritis is a disease that is known to a small number of people. According to medical statistics, this disease in most cases affects individuals over 60-65 years of age. Only in 2% of cases is it found in the younger population.
Basic concept
Tubulointerstitial nephritis is a nonspecific disease that affects the liver. A rapidly occurring inflammatory process negatively affects the hepatic soft tissues and its canal passages. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, atrophy is possible. The etiology of this disease varies.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Do-it-yourself chicken waterer from a bottle
In cats and dogs, symptoms of the disease appear in advanced cases, when 70% of the functional elements of the kidney have already died.
The first symptom is frequent urination. This symptom is not always paid attention to, considering that it is natural, but it is a very formidable symptom, since there is no secondary absorption of water from the kidneys into the bloodstream. To compensate for the loss of fluid in the body, animals begin to drink more.
Signs of uremia: apathy, depression, refusal to eat, exhaustion, dry hair, brownish coating on the surface of the tongue, the presence of ulcers on the tongue and gums, ammonia-like odor from the mouth when breathing. Vomiting, diarrhea and gastrointestinal bleeding appear. Anemia develops. As a result, the animal falls into a coma. In case of development of nerve-paralytic phenomena, the prognosis is 99% unfavorable.
Thus, only timely treatment can save an animal’s life even if the kidney tissue is severely damaged, but treatment must be systematic and supportive. As soon as you stop providing maintenance therapy, the symptoms of the disease will reappear.
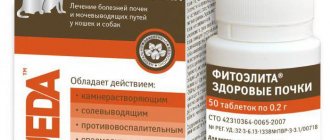
Treatment of chronic renal failure should be aimed at improving urination and detoxification. The drug “PHYTOELITA Healthy Kidneys” is absolutely indispensable. The mechanism of action of the drug is determined by the phytotherapeutic activity of biologically active substances from extracts, decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants that have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, salt-removing, stone-dissolving, restorative, reparative, analgesic and antispasmodic properties.
Medicine "PHYTOELITA Healthy Kidneys":
- has the ability to gradually loosen oxalate and phosphoric acid stones, urates formed in the kidneys and bladder,
- helps regulate the tone of the smooth muscles of the renal pelvis and ureter, which facilitates the process of excretion and removal of stones,
- reduces azotemia in renal failure,
- increases the excretion of sodium and, to a lesser extent, potassium,
- enhances the excretion of nitrogenous substances in the urine.
The drug is used for the prevention and treatment of kidney and urinary tract diseases - acute and chronic renal failure, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis and nephrolithiasis as an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, salt-removing, stone-dissolving, restorative, reparative, analgesic and antispasmodic herbal remedy.
In the treatment of acute forms of diseases, the drug PHYTOELITA Healthy Kidneys is administered orally, one dose every 2 hours for 1-2 days. Then 1 dose 3 times a day until the clinical signs of the disease disappear. The dose of the drug for dogs is one tablet per 10 kg of body weight, for cats and puppies - one tablet per head, for kittens 0.5 tablets per head.
When treating chronic forms of diseases, the drug is given 1 dose 3 times a day. The duration of administration of the drug should be equal to the duration of the disease.
Acute renal failure - its symptoms are similar to those of chronic renal failure - apathy, depression, refusal to eat, dry hair and peeling skin. A brownish coating appears on the surface of the tongue and an ammonia-like odor from the mouth when breathing. Vomiting, diarrhea and gastrointestinal bleeding appear, and anemia develops.
Acute failure occurs in the following cases:
- due to obstruction of the lower urinary tract, due to feline urological syndrome or congenital malformation of the bladder;
- after an abdominal injury, especially combined with a fracture of the pelvic bones, rupture of the bladder or urethra;
- during shock associated with acute blood loss or dehydration;
- after poisoning, especially with antifreeze.
As a rule, all symptoms develop very quickly, and the animal’s condition deteriorates sharply. The prognosis is often unfavorable.
When treating acute renal failure, the goal of treatment is to keep the animal alive until the kidneys are able to eliminate harmful substances from the body.
Treatment is mainly symptomatic:
- replenishing electrolyte deficiency and eliminating dehydration;
- correction of hyperkalemia;
- restoration of kidney function;
- removal of waste that accumulates due to urinary retention.
How often is it diagnosed and what are the causes?
Nephritis can develop in cats:
- after a bacterial or viral infection;
- due to poisoning, including medications;
- due to poisoning by waste products of worms;
- after hypothermia;
- with leptospirosis;
- for allergies and urolithiasis;
- after injury, etc.
The disease is diagnosed in cats, unfortunately, quite often. This pathology accounts for about 0.8% of all non-communicable internal diseases. In older animals, this figure can reach up to 2.5%.
Causes
Inflammatory processes in the kidneys occur under the influence of the following harmful factors:
- unbalanced diet;
- consumption of human food;
- eating poisoned mice;
- intoxication with waste products of helminths;
- allergic conditions;
- infectious diseases;
- side effects of medications;
- intoxication with anthelmintics, as well as insecticides if used incorrectly;
- cystitis, urolithiasis.
During the aging process, the subtle effects of unfavorable factors accumulate, which leads to the development of inflammation.
Signs of disease development
Of course, all lovers of these pets should know what symptoms appear most often in cats with nephritis. Signs of this disease in acute form, in addition to problems with urination, are:
- decreased appetite and depressed state;
- pain when pressing in the kidney area;
- swelling of the eyelids, paws, base of the ears;
- jaundice.
In case of acute nephritis, a sick cat begins to go to the litter box very often. At the same time, the amount of urine she produces decreases.
Chronic nephritis in cats can be preliminarily diagnosed by the presence of symptoms such as:
- frequent “trips” to the tray with large amounts of urine;
- unpleasant ammonia odor from the animal’s mouth;
- apathy;
- vomiting and persistent diarrhea.
The body temperature of a cat with a chronic form of the disease remains normal. The urine of cats with kidney nephritis is usually cloudy and brown or reddish in color. While visiting the tray, sick animals may take unusual poses or make strange sounds.
With nephrosis in cats, among other things, immunity sharply decreases. And this, in turn, can lead to infection of the pet with fungi, viruses or bacteria. Quite often, with nephrosis, anemia is also diagnosed in a cat.
Symptoms
Experts identify several types of disease; glomerulonephritis, interstitial, pyelonephritis and genetic predisposition. Please note that the symptoms of nephritis in a cat and a cat are identical. Depending on the severity of the disease, there are many pronounced symptoms. Let's look at which ones :
- General depression, sick appearance and decreased appetite in the cat.
- When you press in the kidney area with nephritis, pain appears.
- During the disease, the mucous membranes are affected, and swelling of the eyes and ears appears at their base.
- The urine becomes very dark and cloudy, and may contain pus and blood.
- A characteristic specific smell appears, the urge to urinate with nephritis increases, but the amount of urine decreases. In some cases, a cat may make plaintive sounds while urinating.
- Due to possible damage to the body by intoxication during nephritis, vomiting appears and thirst increases.
- Body temperature and blood pressure increase.
- The appearance of dry mouth, as a result of which cats often lick their lips.
- Perhaps the appearance of an ammonia odor from the animal's mouth.
- Some cats and kittens experience decreased skin elasticity and foul-smelling diarrhea.
- In rare cases, shortness of breath may occur with nephritis.
Self-medication in most cases aggravates the course of the disease, especially with infectious nephritis in a cat, and can lead to irreversible consequences. As the disease worsens, kidney failure and inflammation of the bladder may occur. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using laboratory tests of the animal’s urine, ultrasound of the kidneys and a general examination of the animal by a veterinarian. In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be ordered.
© shutterstock
What to do first
If such a disease is detected, the pet, of course, may be prescribed medication. Both nephritis in cats, the symptoms of which were discussed above, and other diseases of the genitourinary system, with the correct selection of drugs and when used according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor, go away quite quickly.
A cat with such a pathology, of course, should first be shown to a veterinarian. In any case, after detecting symptoms, your pet should immediately be put on a starvation diet. Also, the animal must be kept warm.
A sick pet should be fed frequently. At the same time, the cat’s diet should definitely include foods that contain large amounts of potassium, calcium and carbohydrates and are low in table salt and protein. It would be a good idea to give a sick cat, for example:
- low-fat fermented milk products (kefir 1%);
- cereal and vegetable porridges;
- low-concentrated meat broths.
In case of acute nephritis in cats, fried, salted, smoked and baked foods should never be given to pets. Also, owners of such animals will have to refuse to purchase industrial feed. In case of an acute form of the cat, you can try to help by replacing the water in its drinking bowl with a decoction prepared from diuretic medicinal herbs.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent a disease than to eliminate its consequences. We suggest you familiarize yourself with the basic preventive measures that will help keep your pet healthy.
- Proper nutrition. It is necessary to provide cats and kittens only with high-quality food, preferably home-cooked. If you can’t cook yourself, you can feed him dry food of at least premium class. It should also be excluded from the diet; salted, smoked, fatty, fried.
- Physical exercise. A sedentary lifestyle in cats leads to the formation of excess fat cells and metabolic disorders. This can cause kidney disease, including nephritis. Therefore, the pet must be provided with a sufficient amount of physical activity. For example, playing with a ball or using special game “fishing rods”.
- Avoid hypothermia. To prevent kidney disease, you need to keep your cat warm and avoid drafts.
- Weight control. If your pet is overweight, then it is necessary to use a health-improving diet.
- Taking vitamins. Premium and superpremium cat food contains a sufficient amount of vitamin complexes and no additional vitamin intake is required. If the diet consists only of natural products, without the use of dry food, then it is necessary to add vitamins to the food.
- Drinking water. For proper kidney function, it is necessary to provide the animal with constant access to clean, drinking water. Cleanliness of the cat's litter box. It must be regularly treated with special disinfectants.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Anandin for cats composition and release form instructions for use
The prognosis for the acute course of the disease is in most cases unfavorable. Therefore, the sooner a cat gets to the doctor, the greater the chance of a quick cure for nephritis without complications. If, when symptoms are detected, it is not possible to hospitalize the animal yourself, keep the pet warm and limit access to food until the doctor arrives.
>Chronic nephritis in a cat treatment
How to make an accurate diagnosis
Unfortunately, the symptoms of nephritis in cats are very similar to the signs of many other diseases of the genitourinary system - cystitis, bladder damage, kidney stones, etc. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis in this case can only be made by a veterinarian.
At the clinic, a cat with suspected nephritis will first undergo laboratory tests of urine and blood. The veterinarian will also most likely prescribe an abdominal ultrasound for the animal. In addition, when diagnosing this disease, procedures such as electrophoresis and x-ray examination of organs can be performed.
If nephritis is suspected, the urine of cats is checked primarily for changes in pH and specific gravity. Also, in this case, doctors can conduct research on the subject of an increased number of leukocytes and red blood cells, as well as a high concentration of salts. If kidney inflammation is suspected, veterinarians usually conduct a blood test, both general and biochemical.
Treatment regimen for nephritis in cats
A sick pet should be kept warm during therapy. In any case, it is impossible to let the animal go outside, especially in the winter season. In the acute form of the disease, veterinarians first prescribe a 12-hour fast for cats.
With nephritis, the animal usually experiences quite severe pain. Therefore, in most cases, such pets are prescribed analgesics and antispasmodics. Actually, the treatment of nephritis itself is carried out using broad-spectrum antibiotics, hormones and sulfonamides. The cat may also be prescribed iron and calcium supplements and diuretics. In some cases, nephritis may even require surgery.
Folk remedies also help cats with kidney inflammation very well. For example, you can offer your animal a warm infusion of bearberry or lingonberry leaf.
Duration of treatment
If help is provided to your pet on time and in accordance with all the rules, its nephritis will most likely go away within 7-10 days. Otherwise, the disease will enter an advanced stage and curing the cat will be much more difficult or simply impossible.
Chronic nephritis can last for months in a pet. In addition, this disease is classified as recurrent. This form of pathology in cats, unfortunately, is practically untreatable. That is why, if symptoms of acute nephritis are detected, the animal should be treated immediately. In this case, the disease in cats goes away with virtually no consequences.
Types of jade
Inflammation of the kidneys is distinguished by the severity of the process. It can be manifest or chronic. Depending on the tissue damage, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Glomerulonephritis. The kidney glomeruli are destroyed and gradually die.
- Pyelonephritis is a purulent inflammation of the renal pelvis.
- Interstitial. In this case, the kidney tubules become inflamed and urine filtration is impaired. It is rare in cats.
Disease prevention
Preventing the development of nephritis in cats is quite easy. To do this you need:
- do not allow the animal to become hypothermic;
- carry out deworming on time;
- use medications correctly for various diseases;
- feed the animal only with high-quality purchased mixtures.
Of course, cat owners need to put household chemicals away as well. Also, measures to prevent nephritis include physical activity for the animal (within reasonable limits). The cat should be given more attention, for example, by playing with it.