Causes of pododermatitis in dogs
Pododermatitis (or pyoderma) is an inflammatory process on the paws of a pet. The pathology is considered difficult for medical diagnosis. In fact, it is not a separate disease, like a cold, but a sign of a number of diseases, like a high fever or a runny nose. In order to correctly prescribe treatment, the doctor must accurately determine which tissues are affected and by what exactly.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of pathology:
| Localization | Probable Cause |
| The wound is only in one place |
|
| Multiple lesions |
|
To understand how to avoid the disease or choose a treatment method if it appears, you need to get to know the causes in more detail. After all, the underlying disease needs to be eliminated, and only then its manifestations will disappear.
Did you know? If your dog's paws smell like chips, it doesn't mean he ate them. This is the smell of bacteria that settle on the skin of pets whose paws have not been washed for a long time.
Mechanical damage
Foreign bodies penetrate the skin of the paws when the pet runs around the area. The body tries to destroy such an object by attacking it. This is how the inflammatory process begins, followed by suppuration if the thorn is not removed immediately. The damaged finger swells, the pet tries to reduce the discomfort and begins to chew it.
It is quite possible that he will remove the object himself, but he may introduce an infection from the teeth into the wound. Don't wait for this to happen and just help him get rid of the problem. If the surface of the skin is burned, it is washed with water. And then they use anti-inflammatory antibacterial ointments - “Tetracycline” or “Ichthyol”.
Infections
Deep paw infections that are caused by bacteria or fungi are common in dogs. They get inside through the wound surface resulting from a cut with a sharp object.
This causes inflammation and is accompanied by:
- swelling;
- increased temperature;
- suppuration;
- lameness.
To avoid such a development of events, paws after a walk should be washed and inspected for damage. For washing, take a special paw washer. This is a glass with polymer bristles on the inner surface. Fill with water and detergent, put your paw in it and rotate the glass. The result is well-cleaned paws.
Did you know? The microflora of the human body is represented by 40 trillion different bacteria and microorganisms, while the body itself is formed by only 30 trillion cells.
If you notice a wound, it needs to be treated with an antiseptic. Choose Chlorhexidine, Mirastimin, Percutan or hydrogen peroxide - all of them are designed to disinfect the wound surface. Apply the product to a cotton pad and wipe the damaged area. Antibiotics are used to stop the inflammatory infectious process. Lubricate the paw with “Ichthyol ointment” or “Levomekol”. Do this at least 3 times a day until the signs of the problem disappear.
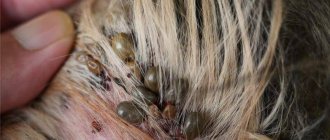
Parasites
The Demodex mite not only parasitizes the skin, but can also cause pododermatitis in dogs. It is believed that mites are constantly present on the skin in small quantities.
But when the immune system is weakened, they begin to actively multiply, which leads to:
- hair loss;
- swelling;
- constant itching;
- bleeding wounds.
Mites live in hair follicles. When one hair follicle is eaten, the parasite gnaws its way through the skin to the next, causing the dog a lot of unpleasant sensations. The tunnels made by mites become colonized with bacteria and inflammation develops. Treatment for Demodex Canis involves several medications and is prescribed by a veterinarian.
The list includes:
- anti-tick drug - “Ivermectin” 1% at a dosage of 0.1 ml per 5 kg of animal weight once, intramuscularly;
- antiseptic for treating the wound surface - “Ichthyol ointment” is applied to the skin every 8 hours;
- immunomodulator - “Immunofan”, “Hemobalance” or “Fosprenil”;
- to reduce the load on the kidneys - “Hepatovet”, “Karsil”.
An antibiotic may also be prescribed if there is a bacterial infection.
Important! Ivermectin is contraindicated in representatives of the Sheltie, Collie, and Bobtail breeds due to breed intolerance. It is also not prescribed to puppies under 6 months and pregnant or lactating bitches.
Allergy
Allergic pathologies very often lead to inflammation of the skin of the legs. The most common causes of allergic pododermatitis in dogs are food and environmental allergens - pollen, dust mites. But such allergies begin between the ages of 6 months and 3 years. Therefore, if your dog is older, then most likely the cause of pododermatitis on its paws is definitely not allergic.
What breeds are susceptible to the disease?
The shape of the paw can also cause pododermatitis. It is called conformational and occurs in dogs with a splayed foot shape. Due to this shape, the weight that presses on the hairy parts of the foot increases, causing inflammation of the hair follicles. Over time, it will lead to chronic inflammation of the paws.
In dogs with this pathology, wounds appear around the toes and in the area of flexion/extension of the pads. It is believed that the pathology occurs most often in German Shepherds and Labradors.
How do symptoms appear?
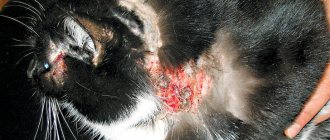
Pododermatitis is characterized by the following features of inflammation on the paws:
- wounds on the fingertips or between them;
- red or pink vesicles filled with blood;
- skin redness;
- swelling of the fingers or joint;
- the inflamed area may itch in some cases, but not in others.
The pet is limping and tries to protect its paw when walking. The disease can affect not only the skin, but also the claws, interdigital folds, the surface of the metacarpus and metatarsals. They swell, and in the later stages of the disease they fester.
Did you know? In the USA there is the only church in the world for dogs. It was built in the 19th century in Vermont by artist Stefan Hanek as a thank you to his pets who helped him recover from a serious illness.
Exactly how the paw swells is a secondary sign that influences the diagnosis. So, any paw can be injured by a foreign object. But an allergic reaction is more common in the front ones than in the back ones.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pododermatitis is a complex undertaking. The doctor needs to identify one from many possible causes and prescribe treatment in accordance with it.
Diagnostic algorithm:
- Examination of the dog's paws and interview of the owner. It is necessary to find out when and how the wounds appeared, as well as what the previous treatment was.
- Taking a scraping to identify mites.
- Microflora analysis to detect fungal infections.
- Diagnosis of allergies.
- Study of tissue characteristics for suspected hereditary diseases, epidermal necrosis and other hormonal or immune pathologies.
The disease should be diagnosed only after a thorough examination of all clinical signs. Some diagnoses are as simple as the presence of mites. And such as allergies can be identified only after excluding the possibility of a skin reaction to external or internal parasites. Hormonal pathologies are calculated based on the results of a blood test. Conformational pododermatitis in dogs is diagnosed based on the shape of the foot and only after other possible causes have been ruled out.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostics will help to find out the cause of the problem of interdigital dermatitis. To contact a veterinarian, you will need to spend 3 days without treating problem areas on the skin with anything.
To diagnose the disease, a blood test is prescribed.
The veterinarian will first order the following tests:
- smear from the damaged area;
- scraping to identify parasites;
- sowing for fungal flora.
Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- x-ray or computed tomography;
- blood tests;
- if the paws are positioned incorrectly, consult an orthopedist;
- if you suspect cancer, consult an oncologist.
Treatment of pododermatitis at home
Treatment for pododermatitis varies depending on the underlying cause:
- parasitic infestations are treated with antiparasitic shampoos, tablets, injections;
- infectious diseases require long-term use of antibiotics or antifungal drugs;
- foreign bodies are removed from the paws by minor surgical treatment;
- hormonal diseases will require a long, possibly lifelong course of hormonal medications;
- Allergic pathologies are treated by eliminating the allergen.
Conformational pododermatitis is the most difficult to cure, since the defect is caused by the shape of the patient's foot. In all cases, along with the main treatment course, you will need to maintain foot hygiene and avoid walking on rough terrain.
Important! Pododermatitis is characterized by periods of remission followed by exacerbation. Therefore, be sure to check with your veterinarian what and how to do at home in case of exacerbation of the disease.
Treatment for atopic form
Atopic is a disease of allergic origin that the patient will suffer from for life (chronic form).
The causes of allergies vary, but the symptoms are the same:
- itching;
- pale pink rashes on the skin;
- rash located in the bends of the joints;
- peeling, redness, cracks in the skin.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis in dogs:
- "Apoquel" - 0.4–0.6 mg/kg 2 times a day for 2 weeks. The drug is designed to quickly relieve itching and reduce skin inflammation.
- Oclacitinib is an immunomodulator. The dosage and duration of the course are prescribed by the veterinarian depending on the condition of the pet.
- “Prednisolone” - 1 mg/kg 1 time per day for a week, and then every other day for 2 weeks for accelerated healing.
- Constantly treat the paws with an antiseptic and lubricate them with “Ichthyol ointment.”
How to treat the bacterial form
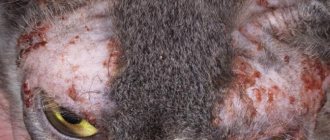
Fungal infections often cause pododermatitis in dogs.
This:
- yeast fungi of the genus Malassezia (Malassezia dermatitis);
- dermatophytes (dermatophytosis);
- various bacteria (interdigital pyoderma).
Yeast is always present on the skin. But if the immune system weakens, they begin to develop more actively. The disease manifests itself as itching, alopecia, peeling, swelling and the smell of rotten fish. Malassezia fungi affect not only the skin, but also the claws. They also change the color of the coat - in light breeds it becomes much darker in the affected area.
Medicine for Malassezia dermatitis is prescribed for life. Paws should be washed with shampoos containing azoles (Miconazole, Clotrimazole, Triclosan). Treatment - Ketonazole 5-10 mg/kg 1-2 times a day for 3 weeks.
Important! For weeping wounds, use Tsamax powder instead of ointment. Apply it to the surface treated with an antiseptic in a thin, even layer and cover the wound with a bandage.
Dermatophytosis appears not only on the paws, but also on the face. These are keratinized, thickened areas of skin on which hair has fallen out. The claws are not affected by this disease. Treatment will be prescribed comprehensively and will be accompanied by disinfection of the premises, bedding, and enclosure.
Interdigital pyoderma is accompanied by cysts in the interdigital spaces, swelling, ulcers, and deformation of the pads. Wounds look like suppuration when a foreign body enters. They get wet and are very painful. Treatment will consist of a long course of antibiotics. In some cases, surgery will be required to remove interdigital cysts.
Drugs used:
- "Amoxicillin" - 22 mg/kg 2 times a day;
- "Clindamycin" - 11 mg/kg 1 time per day;
- "Cefalexin" - 22 mg/kg 2 times a day.
Prevention and treatment of dermatitis
To prevent interdigital traumatic dermatitis, timely treatment of all wounds and monitoring of the healing process is provided. For local treatment, ointments (zinc ointment) are used. In addition, moisture should not come into contact with the damaged paw. Contact dermatitis is caused by chemicals coming into contact with your pet's sensitive paws. In such a situation, eliminating skin contact with the chemical irritant is indicated. After this, local ointment treatment is also carried out. Allergic dermatitis is quite difficult to treat. As a rule, allergies affect not only the paws, but also the ears, the skin around the eyes, and the mouth area. For food allergies, a hypoallergenic diet is indicated. For this purpose, the use of feed with hydrolyzed protein is recommended. In cases of severe inflammation, antiallergic drugs (diphenhydramine) are used. Chlorhexidine and tar shampoos are prescribed as local treatment. Bacterial dermatitis is caused by injury to the paw pads, a disorder of vitamin and mineral metabolism, or hormonal changes. To treat this form of interdigital dermatitis, systemic antibiotics (penicillin) are primarily used. The use of specific immunotherapy is also widespread. We are talking about polyvalent staphylococcal toxoid. Acaricidal agents (benzyl benzoate) are used to treat parasitic dermatitis. To combat psychogenic dermatitis, sedatives (phenobarbital) are indicated. To prevent the development of infectious diseases in dogs and maintain immune status, regular vaccinations are provided. To prevent parasitosis, animals are treated monthly with insecticidal preparations.
Chondroprotector for joints