Parasites are organisms that exist thanks to their hosts, feeding on their cells and blood. Human ectoparasites parasitize external organs or the surface of the skin. This group includes lice, bedbugs, fleas, and ticks. Feeding on human blood, they violate the integrity of the skin. The presence of ectoparasites is easily detected, because their presence causes such unpleasant symptoms as: pain during a bite, wounds, burning of the skin.
Classification
There are permanent and temporary ectoparasites. Species directly depend on the form of their life activity in the external environment.
Permanent parasites live and reproduce on the surface of the host’s body or inside it. Temporary - parasitize on the skin, hair, and fur of an animal. With the help of external organs, they receive food, which, as a rule, is skin scales or blood.
Most ectoparasites are arthropods. They are attached to the host’s body due to the existing special devices, which are special hooks and claws or spikes on the subcutaneous tissue. Many parasites represent the class of arachnids and insects, but there are also other types, for example, the leech.
Lice
Lice are permanent blood-sucking ectoparasites of humans. These small insects are not able to withstand starvation, so every day they feed on the blood of their host through their mouthparts, which are capable of piercing human skin.
Based on their ecological niche, lice are classified into:
- for body lice living in clothing;
- for head lice existing in the scalp. In particular, their habitat is hair with a round cross-section (beard, scalp hair, mustache);
- lice (pubic lice) - parasitize in the pubic area, on the genitals, in the anal area, they may appear in the armpits or on the hairy chest in men. They are not able to exist on the hair of the head due to their limbs, which are adapted to hold only on hair of a triangular section.
The lifespan of ectoparasitic insects of this suborder can last up to 45 days. Along with this, the female parasite can lay more than 10 eggs every day.
Lice have an oblong body shape, white in color, and can range from 1 to 3 millimeters in length. Females are one and a half times larger than males. The eggs of blood-sucking ectoparasites are nits that firmly adhere to hair and clothing.
Lice spread rapidly and cause a disease called pediculosis. Parasites pose a danger to humans because they carry infectious diseases, the most serious of which is typhoid.
Ectoparasites of dogs
There are four main species of the family of parasitic insects that feed on the blood of mammals. They cause concern with their bites, which cause itching and various allergic reactions, and are also carriers of certain types of worms and other diseases. There are four main types of ectoparasites:
- lice;
- lice eaters;
- fleas;
- ixodid ticks.
Lice
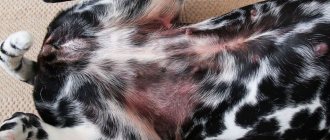
Small wingless parasites of yellow-gray color, reaching a size of 2 to 5 mm. They have a long head and a narrow body with three pairs of limbs with sharp claws that are firmly attached to the dog’s hair. They are carriers of pathogens of infectious diseases and contribute to the development of anemia and allergies in animals.
lice eaters
Very small translucent insects, body length no more than 2 mm. They feed on epidermal cells, blood and down of dogs. They are carriers of helminth eggs and fungi and can lead to complete baldness of the animal.
Fleas
Wingless insects are dark in color, ranging in size from 1 to 5 mm. Of the three pairs of limbs, the hind limb is the most developed, which allows it to jump long distances. They are carriers of encephalitis, plague, typhus, helminth eggs, salmonella, and lead to baldness and dermatitis.
Characteristic signs of the presence of lice, lice or fleas are itching, rash, dandruff, dullness and hair loss, aggressive and restless behavior.
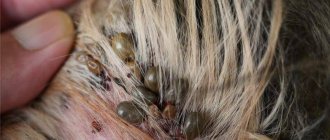
Ixodid ticks
The parasite is brown in color, ranging in size from 4-3 mm in a hungry state to 10-15 mm in a blood-fed state (the color changes to light gray). They live in dead wood, tall grass, and damp, shaded areas. They are carriers of pathogens that cause piroplasmosis in dogs.
Piroplasmosis is one of the most dangerous blood parasitic diseases in dogs. Toxic waste products of piroplasms lead to the destruction of red blood cells (anemia), liver degeneration (intoxication), cardiovascular failure and death.
If an attached tick is found on a dog, it must be removed by pulling it off with tweezers or hands protected with gloves to avoid transmission of possible infection. Treat the bite site with iodine or brilliant green, and place the tick itself in a container to be sent to the laboratory to analyze the existing infection.
The owner is required to carefully monitor the dog's well-being. Signs of piroplasmosis are lethargy, poor appetite, fever, dark urine (the color of beer). Any of the signs is a reason to contact a veterinary clinic for treatment.
Methods of disposal
The main source of infection is contact with sick people. This disease is not transmitted through pets. Ectoparasites perfectly adapt to their environment, gradually getting used to this or that poison. Lice must be removed in several stages:
- elimination of parasites;
- Thorough combing of hair to remove nits.
When resorting to traditional medicine, it should be taken into account that it will not be possible to eliminate ectoparasites on your own in one day.
The most effective folk remedies are hellebore water, table vinegar with a concentration of 9%, diluted with ordinary water in a ratio of 1:2, onion-garlic mask, tar soap.
Women can use hair dye containing hydrogen peroxide to combat lice. Boys can shave their heads bald to eliminate lice and nits.
Temporary ectoparasitic insects
Temporary are those insects that land on the human body to eat (the family of ixodid ticks, bedbugs, mosquitoes, horseflies). What danger does an attack by these insects pose to humans?
Ectoparasites carry serious infectious diseases: encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis, malaria, dengue fever and others.
Determining their presence is quite difficult, since the first signs are similar to the manifestations of acute respiratory infections. Insect bites can cause allergies, especially bees, wasps and midges. When scratching the affected area, saliva containing toxins can cause skin diseases (eczema, dermatitis).
Ectoparasites are represented by mites from the class of arachnids. Unlike mosquitoes and midges, which can be easily eliminated from the skin, ticks must be removed following certain rules.
Tick removal
A dangerous arachnid creature must be eliminated using the following methods:
- If you apply paraffin or vegetable oil to a tick, the ectoparasite will pull out its proboscis due to lack of oxygen.
- A dangerous bloodsucker should be eliminated only in a medical institution.
The tick's head poses the greatest threat because it is where the virus is localized and enters the body through saliva. For this reason, any mechanical impact on the body of the ectoparasite can speed up the infection process. It is prohibited to squeeze or remove the tick in parts. Any part of the ectoparasites must be removed from the host's body (claws, suckers).
Fleas
There are a huge number of species of these blood-sucking arthropods. They are wingless insects whose bodies are flattened laterally. The head of fleas is equipped with a piercing mouthpart. It has three pairs of legs, of which one pair (the last) is the longest and is designed for jumping. Fleas are dangerous because they are transmitted from humans to animals and vice versa. Black crumbs, being the remnants of blood digested by fleas, indicate the presence of parasites.
Fleas are most aggressive in spring and summer; it is at this time of year that animals experience great discomfort from them: itching from insect bites, the formation of painful wounds, infection with endoparasites (internal parasites that live in internal organs), many infectious diseases, including plague, posing a danger to people. Fleas can survive up to 2 years. They live and lay eggs in rodent burrows, garbage, and animal fur. Worm-like larvae are white in color.
Fleas are able to migrate from natural to domestic environments. A flea bite can become a source of infection not only for plague, but also for endemic typhus. For this reason, it is necessary to treat both pet hair and disinfection of living areas using insecticides.
Wool-eaters (Vlas-eaters)
The most common ectoparasite of domestic animals is the lice beetle. The insect has a large head, a flattened body of a yellow-gray color. Its maximum length is two millimeters. Ectoparasites reproduce very quickly. The life activity of adult individuals outside of wool does not last long, because their food products are wool and skin scales. Due to their heat-loving nature, wool beetles do not live on human skin. Lice eaters carry a lot of infections that pose a threat to the life of the animal, including: infectious anemia and infection with tapeworms.
The whole truth about ectoparasites
Many different creatures live around us. We communicate closely with some of them every day, while we only guess about the existence of others. Let's talk about some creatures that often become uninvited “guests” - fleas, lice, lice eaters and various types of ticks...
Fleas
- annoying wingless blood-sucking insects that parasitize the body of an animal.
The body of fleas is dark brown, 2-3 mm long, flattened on the sides. Fleas are capable of jumping up to 200 times their body length. Only adults attack mammals. Female fleas, having fed on the blood of an animal, lay eggs, from which worm-like larvae emerge. Flea larvae live in floor crevices, feeding on organic matter and not parasitizing animals
.
Here the biological cycle of transformation of the larva into an imago (adult insect) occurs. Fleas live for about a year and are capable of prolonged fasting. Mammalian blood is needed by females to breed offspring. Fleas have a painful bite that causes severe itching, scratching and inflammation of the skin
.
Lice
- wingless blood-sucking insects with a flat body 2-3 mm long.
The females, having fed on the blood of the animal, lay nit eggs, which are attached to the hairs of the fur. The eggs hatch into larvae that feed on blood and after some time turn into adult insects
.
Lice live 1-2 months. Young animals are especially sensitive to lice
.
lice eaters
- small wingless insects with a flattened body 1-2 mm long, which feed on hair and epidermal scales.
Infection occurs through litter and care items
.
Favorite places for lice eaters to localize are the root of the tail, the inner surface of the legs and thighs
. With severe infection, parasites spread throughout the body.
Ticks
- one of the oldest groups of terrestrial invertebrates. Most ticks are characterized by small sizes (0.1-1.5 mm, rarely 15-25 mm), the body has a spherical or oblong-oval shape. The ends of the legs are often armed with claws and suckers, which help the tick to crawl and stabilize its body.
It should be borne in mind that there are products that act only on fleas or only on ticks. If you are looking for a product that is harmful to both fleas and ticks, harmless to pets, of high quality, and not expensive, pay attention to the preparations.
All drugs are developed on the basis of the Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Agricultural Sciences using both its many years of experience and the most advanced technologies of world science. API-SAN offers the following medications against fleas and ticks:
DANA drops on the withers - destroy all insects and ticks on the animal’s body. The drug is applied to one point, within 12-24 hours it “envelops the body”, creating a barrier to parasites for 6-8 weeks!
Auxiliary components reduce inflammatory processes in the skin and promote the penetration of the drug to the localization of parasites.
DANA spray is an insectoacaricidal spray. It has a long-lasting effect - against insects - 2-3 months, against ticks - 1 month. The spray has a contact effect, so ectoparasites die from just contact with the animal’s fur
.
The effect of the drug remains even if the animal is caught in the rain or takes a swim!
DANA spray is also
suitable for treating the surrounding area
(bedding, carpet, cracks and other places where animals like to rest).
DEMOS-LUX - insectoacaricidal shampoo - not only destroys parasites, but also provides excellent care for the hair and skin of the animal
. Its effect, unlike drops on the withers or spray, is immediate, but short-lived (about 2 weeks).
All of the above drugs are certified, have passed clinical trials and have proven themselves in practice.
Magazine "Zoo Tips", No. 08, 2005
Prevention
It is necessary to observe a set of sanitary and hygienic measures, that is:
- get vaccinated;
- carry out routine disinfection of living quarters;
- undergo systematic, monthly preventive treatment of animals with specialized sprays;
- adhere to hygienic standards for keeping pets and living conditions;
- inspect the animal after each walk.
Remember that all parasites (applies to endoparasites and ectoparasites), once in the body, pose a threat to human health.