Signs of pregnancy in a rabbit
Pregnancy in female rabbits is quite difficult to determine, but still some signs of pregnancy clearly demonstrate that mating was successful.
Physiological changes
It is possible to ascertain as accurately as possible that the female is pregnant only 14 days after mating. To do this, the animal is picked up (the female must be lifted by the withers, supporting the hind legs), turned with its head towards itself, and then laid out on a flat surface.
With your left hand you continue to hold the animal by the withers, and with your right hand you palpate the belly in the pelvic area. If the female shows aggression, then she should be lightly stroked on the belly.
The fact that mating was successful is indicated by the presence of oval seals resembling peas, which are located in a chain in the horns of the uterus.
If such a procedure is carried out by the breeder for the first time, for comparison you can palpate the belly of a female who is not carrying rabbits. If there is a concern that the procedure may be performed incorrectly or the embryos may be damaged, then it is better to seek help from a veterinarian.
About seven days after successful mating, the female’s belly begins to take on rounded shapes, however, it is quite difficult to immediately notice this due to the dense layer of fluff. But, closer to childbirth, it becomes difficult for the female to walk, so she spends most of her time lying down.
Changes in behavior
Changes in her behavior can also indicate that a female rabbit is pregnant: she becomes aggressive, does not allow the male to approach her, actively absorbs food, and begins to drink a lot of water.
Aggression is a behavior most often characteristic of large breeds. Little ones, on the contrary, can become very timid.
The animal's taste preferences may also change: it will refuse regular food, clearly demonstrating to its owner that it wants something different. But changes in diet, as a rule, are typical for the first week of pregnancy, and after seven days, everything returns to normal.
Often, a pregnant individual may suffer from toxicosis, which can be either pronounced or manifest in a weak form.
During toxicosis, the rabbit experiences difficulty breathing and frequent urination. Often the animal is in a depressed state. The individual may also experience malfunctions in the central nervous system. A sign of toxicosis is the appearance of the smell of acetone from the female’s mouth.
False pregnancy
But changes in behavior cannot 100% confirm the fact that the female is pregnant. This behavior can also be caused by a false pregnancy.
What are the causes of false pregnancy:
- Low vitality and sperm activity of the male.
- The presence of hormonal disorders in the female.
- Incorrect preparation for mating.
- The female rabbit gives birth without interruption.
- Diseases of the reproductive system in rabbits, including the presence of tumor formations.
The duration of false pregnancy can be up to 18 days. After this, the female’s hormonal levels stabilize and behavior returns to normal.
Toxicosis
Early pregnancy in a rabbit can sometimes be accompanied by toxicosis. Manifestations of the body’s negative reaction to pregnancy can be weak and have almost no effect on the normal rhythm of the animal’s life. However, in some rabbits the toxicosis is very pronounced, and then the help of a veterinarian is often required. Toxicosis that requires medical treatment manifests itself as follows:
- Frequent urination while maintaining the normal volume of urine output or its slight decrease;
- Breathing disorders associated with difficulty;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- Severe depression;
- A noticeable odor of acetone from the mouth.
If severe toxicosis occurs, which does not go away within 3 days, it is necessary to show the pregnant rabbit to a veterinarian.
How to confirm pregnancy in a rabbit
You can determine if a rabbit is pregnant in the early stages by her behavior. The behavior of the female changes dramatically:
- she begins to avoid males;
- shows aggression;
- It will be possible to be completely sure that the female rabbit has given birth by such a clear sign as the insulation of the queen cell (the place where the newborn rabbits will be located). This process is inherent in nature. It looks like this: the pregnant female begins to tear out the fur from her abdomen and use it to build a “nest”;
- The fourth obvious factor in pregnancy is weight gain. But in order to track this, it is necessary to carry out a control weighing of the animal before mating.
It will be useful for inexperienced livestock breeders and farmers to know that rabbits often experience a state of false pregnancy, when all the symptoms are present, but there are no fruits in the womb of the female. Doubts may arise up to 21 days after mating. The delusion will not last long if you check for the presence of fruits in the belly. The female's pregnancy status can be confirmed by palpating the abdomen. To do this, you need to turn the expectant mother on her back and stroke her belly to relax the animal.
If the “fluffy” shows temper, you should stroke the belly below, without turning the body over. You need to act carefully, without scaring the female or causing her pain. For comparison, you can perform a similar inspection with a female that has not had mating. Experienced rabbit breeders will quickly catch the difference and determine pregnancy, but beginners will need to learn.
Detection of embryos during palpation is a sure sign that a female rabbit is pregnant.
To the touch, future rabbits appear to be small balls
Experienced rabbit breeders grab the ears of the expectant mother, and insert the other hand between the hind legs so that the palm rests on the stomach and carefully probes the contents of the uterus
Even if previously the female was distinguished by a gentle disposition, then with the onset of pregnancy, she can begin to bite everyone who cares for her.
Before giving birth, female rabbits have round bellies, their breathing becomes frequent, and their movements around the cage are rare. Mostly they lie in a secluded place and move only to the feeder.
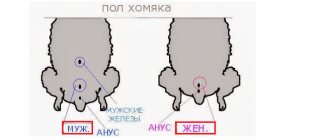
How to find out that a female rabbit is walking. How to detect heat in a female rabbit
How to determine heat in a female rabbit. The external genitalia of female rabbits are presented in the form of a loop - a slit located below the anus. The state of heat in female rabbits is determined the day before by changes in the genital organs and behavior. During hunting, which is repeated every 5-7 days, the loop turns red and swells, acquiring a bright pink color. The hunt lasts 26-40 hours.
How to determine heat in a female rabbit. In female rabbits that have become unmarried after a previous mating or are not covered in the first days after giving birth, as well as those that are being mated for the first time, the state of heat should first be identified in order to reduce the number of useless introductions of them to a male. The state of sexual heat in a female rabbit is determined by her restless behavior. She is aggressive - she can bite, scratch the cage with her paws, she can pluck out her fluff or carry hay or straw in her teeth for making a nest, she eats poorly, scatters food, approaches the walls of the cages (if she is in the vicinity of other cells) and rubs her muzzle against them, pushes it between the slats or into the hole in the metal mesh. A female that has given birth may scatter her offspring and not feed the babies. If the female rabbit is in a state of heat, then when you stroke her with your hand along her back, from head to tail, she raises her butt, taking a covering position, sometimes lies down on the floor of the cage and stretches out.
How to determine heat in a female rabbit. The onset of hunting in rabbits is influenced by their feeding conditions, light conditions, weather, and season of the year. The last factor is particularly influential. Factors that stimulate sexual estrus include separating young animals from female rabbits, feeding them celery, enhanced vitamin nutrition, prolonged lighting, and close placement with males. In order for female rabbits to better reach a state of heat, in spring, autumn and winter, approximately two weeks before mating and during mating, the duration of daylight hours should be increased with the help of additional artificial lighting to 6-18 hours. On cold winter days, female rabbits do not hunt well.
Refusal of rabbits
Abandonment of rabbits can occur for physiological reasons, for example due to a lack of milk from the female or stress due to the birth of several sick or dead rabbits. A poorly prepared nest can lead to the death of baby rabbits from hypothermia. Most experienced rabbit breeders prefer to breed two females at once, so that, if necessary, they can transfer the young rabbits from a rabbit that has lost milk to another whose milk supply is fine. A baby that is fed by its mother looks much better.
Another reason for a female rabbit’s refusal to give birth may be a state of intense heat. This happens in some rabbits immediately after giving birth or even the day before. In this state, the female rabbit does not build nests for the babies, gives birth to them outside the nest, tramples them, and does not allow them to suck milk. In this case, it is advisable to remove the female rabbit from the rabbits for 8-10 hours or immediately arrange a secondary mating if the rabbits are few. Most often this phenomenon is observed in young rabbits. After covering, the female rabbit calms down and, if she does not have mastitis, feeds her offspring normally. Naturally, you need to watch the nest very carefully in the first days.
How to identify a rabbit or a female rabbit. At what stage of a rabbit's development do you need to know its gender?
Do not rush to determine gender in the first days after birth. It is not possible to do this based on the external signs of the genitals. It's still in the early stages of development and looks the same. Even after a week, you are unlikely to know with great certainty who is who. For example, an experienced specialist - a breeder, who has been dealing with such issues all his adult life, determines the sex of rabbits no earlier than two weeks old, and then with a probability of about 90%. The older the rabbit, the more accurate the result will be. There is no point in such an early definition.
Preparing for the birth of offspring
After sexual intercourse, place the female in a spacious cage - throughout pregnancy and after lambing she should be kept separate from the rabbits. The male is able to fertilize the animal immediately after the previous birth, the female rabbit will become stressed and will not be able to feed the offspring that have already appeared. Some experienced farmers advise placing the female close to the male, but in different cages. To allow animals to communicate, place them nearby.
The pregnant rabbit is separated from the male, but not far away, so that the animals can communicate
If the room is hot, provide fresh air, but avoid drafts. If the pregnancy is delayed, it may be false or the offspring died in the rabbit’s body. Be sure to keep the veterinarian’s phone number nearby - if problems arise during pregnancy, lambing or after it, you can enlist the support of a specialist.
Rabbit cages
Preparing a nest for a pregnant rabbit
As soon as you have established that the female is pregnant, three to four days before the planned lambing, place a cardboard box or box in the cage - there she will build a nest for future babies
It is important to guess with time - if you put the box in too early, it will be used instead of the toilet
| Photo | Description |
| Step 1 | Pick up an unnecessary box or an old box in which the rabbit will build a nest. Choose a box that is larger in size than the female. |
| Step 2 | Make a hole in the box so that the expectant mother can easily get in and out of it. Carefully wash, clean and disinfect the future nest with hot water and a solution of potassium permanganate. |
| Step 3 | Place the box in the pen or cage where the pregnant female lives. Place a newspaper inside, add soft hay there, distribute some hay around the cage - the expectant mother herself will begin to further arrange the nest. |
Box, drawer as a nest for rabbits
The birth process: how do female rabbits give birth?
Baby rabbits are born very easily. The female sits comfortably in her nest and begins preparing for lambing. The mother rabbit sits in such a way that after the babies are born she can immediately lick them. When the baby rabbits emerge from the birth canal, they are located between the hind legs of the female. Blind and hairless, they appear with their hind legs first. When all the rabbits are born, the female rabbit swallows the afterbirth and begins to lick the newborns. The farmer's help is not needed during lambing - the female will do everything on her own.
Newborn rabbits
Do not touch newborn rabbits unless necessary - you will leave your scent on them, and the mother will be able to eat her babies. If the baby rabbit falls out of the nest, return it back after wearing protective gloves. When babies' eyes open (around 10 days of age), check the animals for infections and unopened eyes. By the age of eight weeks, the rabbits are separated from the female, otherwise she may begin to get rid of them on her own.
| Period | Baby rabbit weight |
| At birth | 40-80 grams |
| A few days after birth | 50-100 grams |
| On the sixth day | 80-160 grams |
Monitor the number of stillborns. A few hours after giving birth, distract the female with a treat and check the litter. If there are dead ones, immediately take them from the nest and make sure that the rest are alive and moving. If a female has given birth to many rabbits, move several of them into the cage of another female rabbit who has recently given birth. Place the baby rabbit under the animal's fur and it will take on the responsibility of raising the offspring.
Offspring of rabbits
The birth of a new rabbit offspring is an exciting and joyful event in the life of every livestock breeder. Take good care of the females, feed the animal properly during pregnancy, help it arrange its nest, and it will thank you with strong and healthy rabbits.
What to do if the rabbit is pregnant
A pregnant rabbit requires special attention; the female is provided with good care and feeding.
Be sure to read:
When can you give birth to a female rabbit: the first time, after giving birth?
What conditions must be met:
- the animal is provided with a cage located away from drafts and bright light;
- cleaning is carried out regularly to keep the room dry and clean;
- It is not recommended to transplant and pick up the rabbit, so as not to provoke a miscarriage.
It is necessary to ensure that dogs and cats do not enter the rabbitry, and if possible, protect the female’s peace from loud sounds.
Feeding the animal
A pregnant rabbit should always have access to drinking water.
For the normal development of embryos, the rabbit must be provided with proper nutrition, the main principles being a balanced diet and moderation, especially in the second half of pregnancy.
Feeds must be saturated with proteins, vitamins and minerals; the missing components are introduced in the form of additives.
For the first 2 weeks, it is necessary to use mixed feed, oats in the diet; cakes and soybean meal are suitable as proteins.
Includes vitamin and mineral complexes:
- meat and bone meal and chalk;
- eggshell powder;
- salt and fish oil.
The second half of the period requires 45% concentrated feed, 53% high-quality haylage and 2% mineral supplements. It is allowed to provide additional hay and twig food.
Important! If the female is young, her diet is increased by 1/5 compared to mature animals, since a growing organism requires additional energy expenditure.
Possible problems during pregnancy
Mastitis in female rabbits
Pregnancy in female rabbits does not always go smoothly; in some cases complications arise:
- Mastitis . May occur due to unsanitary conditions and injury. The development of pathology is due to decreased immunity or hormonal changes. In order to stop the inflammatory process in the nipple in time, it is necessary to regularly examine the animal’s mammary glands. If redness and swelling appear, you should not delay calling the veterinarian.
- Cannibalism . Sometimes females eat newborn rabbits. The behavior is more often observed in primiparous rabbits, but occurs in experienced mothers.
The cause of cannibalism is the lack of water in the drinking bowl, as the female becomes thirsty after giving birth. A negative factor is a stressful state - bright lighting, lack of silence and privacy, as well as lack of nutrition: the animal tries to make up for the lack of valuable elements in the body.
Attention! When a female rabbit eats offspring during 2-3 births, she is discarded as a breeder and used for meat.
Preparing a nest for a pregnant rabbit
A box, a box as a nest for rabbits
A week before the expected birth, disinfected nest boxes are placed in the cage where the pregnant female is kept. They are filled 1/3 with hay and soft shavings; the rabbit will pluck the fluff herself.
If she doesn’t pluck it out so that the newborn naked rabbits don’t freeze, the owner will have to do it himself.
How is pregnancy going?
The pregnancy process is preceded by sexual heat, during which the female is covered by the male. You can determine that the mating was successful if you notice that the male fell backwards from the female rabbit, making a rumbling or squeaking noise. The fertilization process is completed very quickly, after which the male is removed from the female rabbit.
Signs of pregnancy
The pregnancy of a female rabbit can be determined by placing her in a cage with a male 5 days after mating. If the female is pregnant, she will not even let him near her, she will snarl and growl. To find out the exact due date, write down the date of mating. This will also help determine when to recoat the empty female.
About seven days after successful fertilization, the animal's sides become more rounded. A pregnant female, closer to her due date, generally looks like a big fluffy ball and almost doesn’t walk. You can check a rabbit's pregnancy by palpating, but this must be done very carefully. By the way, lumps in the stomach, which should be embryos, can also be a false pregnancy.
How long does pregnancy and the birth itself last?
The female rabbit is pregnant from 28 to 33 days. Most females bear offspring and go to lambing on 31-32 days. Movement in the abdomen begins to be felt on the 25th day, when the babies in the womb are almost fully developed. Quick breeding of rabbits takes a few minutes, but sometimes it lasts an hour or even more for a female rabbit. Accordingly, the birth of baby rabbits itself lasts a different amount of time - on average from 10 to 60 minutes.
Typically, a female rabbit gives birth at night or early in the morning and very rarely occurs during the day. Females give birth easily and usually do not require assistance. If you suddenly encounter a difficult birth, seek veterinary help.
How many rabbits can a female give birth to?
The number of cubs born is difficult to predict. There are known cases when the pregnancy of rabbits ended with the birth of 12 and even 15 rabbits. However, practice shows that litters usually contain from 5 to 8 babies. By the way, it is a well-known fact: the more cubs in the litter, the shorter the gestation period, and vice versa. Why this happens is unknown.
False pregnancy
Occurs when mating does not result in fertilization. Instead, a corpus luteum appears where the ovarian follicle ruptured. This condition is called false pregnancy. At the same time, for about 18 days the female behaves like a real mother: she carries straw for the nest and prepares down. You can determine that you are dealing with a false process by the sudden cessation of the activity of the beast.
After 18 days, the female is ready to let the rabbit in again. Why does this false process take place? Veterinarians say that the false situation occurs due to the low activity and viability of the male's sperm. Also, false “joy” happens if the rabbit is actively giving birth, almost without interruption. This happens on large farms, where rabbit pregnancy is an almost constant process.
Watch the video below about how a typical rabbit birth takes place. The female is very calm, she covers the babies with her body and paws, licking them as they are born.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=yNgtv4EOqYQ
Determining false pregnancy
If the male has reduced sperm activity or the female gives birth very often, a false pregnancy may occur. Such unsuccessful matings are quite common.
During a false pregnancy, the rabbit loses her appetite, and she shows very strong aggression towards everyone. This usually takes place within 2-3 weeks. After which she allows the male to approach and begins to behave as usual.
If this problem occurs frequently, you should contact your veterinarian.
When baby rabbits leave the nest
All rabbits begin to leave the nest at three weeks of age. Getting to know the “adult” world involves some nuances:
- From this moment, acquaintance begins not only with the external habitat, but also with “adult” food - the baby rabbits try food from their mother’s feeder, which should only contain products that are harmless to babies. Gradually, the eared animals will move from such complementary foods to the normal diet of adults.
- During this period, it is necessary to change the bedding in the cage so that the miniature rabbits do not get dust into their eyes. The best option is to temporarily lay down a clean, thick cloth or towel.
- Breeders conduct a control examination of the physiological development of the offspring. If it is discovered that the rabbits are not growing well, then the rabbit’s menu is immediately revised or the baby rabbit is transferred to a female with more high-calorie milk. If there is a weakened rabbit in the brood, it is better to remove it from the nest so that the female rabbit does not begin to notice the difference among the cubs and does not abandon the entire brood because of this.
- From the 28th day, rabbits begin to be vaccinated against diseases according to the approved vaccination schedule.
Video Inspection on the 3rd day after birth
Why do baby rabbits leave the nest early?
When a mother rabbit throws her cubs out of the nest or the baby rabbits begin to emerge before three weeks of age, there may be several reasons for this behavior:
Lack of milk in the female. A decrease in the amount of rabbit milk or a decrease in its nutritional properties indicates that the rabbit is not eating properly. To restore normal lactation, you should review the eared mother’s diet, make it more nutritious, and adjust the diet and volume of food. Taking good care of your rabbit is the key to getting healthy offspring from her. If lactation cannot be restored, then the offspring are placed with another lactating rabbit or artificially fed.
Increase in air temperature in the queen cell. In order for the baby rabbits to feel comfortable and cozy, the temperature in the nest should be controlled. When it becomes very hot and stuffy, the problem can be eliminated by moving the cage to a cooler room or to the open air under a canopy.
It is important to remember that the rabbits should not emerge from the queen cell before the due date. If this problem occurs, you should quickly find and eliminate the cause, otherwise you may lose the brood
When can weaning take place?
It is recommended that older rabbits be separated from their mother no earlier than 1.5 - 2 months of age, provided that they already eat full adult food, do without milk, and do not get sick. The weaning procedure is carried out gradually, removing 2 rabbits from the litter daily. In this way, the female will physiologically and painlessly stop lactation.
Typically, females are placed in cages of 3-4 individuals, and males are castrated or transferred to individual cages (provided they are kept for breeding).
After weaning, the most important aspect is the diet of the young animals. They should receive a high-calorie diet rich in proteins and carbohydrates. It is recommended to enrich the food composition with mineral and vitamin premixes. If 3-4-month-old young animals gain weight well and quickly, then the transition to adult food has taken place well, and the selected nutrition meets all the nutritional needs of actively growing organisms.
Video NEWBORN BABIES
Feeding lactating rabbits
The rabbit's body experiences the greatest stress during lactation. Hence, lactating rabbits need to be fed abundantly and variedly throughout the suckling period. During the lactation period, a female rabbit produces up to 180 g of milk per day (sometimes more), which is necessary for the growth of the rabbits. Rabbit milk contains 34.2% dry matter, including 13% protein, 16.8 (sometimes up to 20%) fat, 2.4% minerals and 2% milk sugar. This high concentration of nutrients in rabbit milk explains the rapid growth of the baby rabbits themselves during the suckling period. To produce milk and maintain life, the female rabbit during the lactation period should receive approximately 2-4 times more nutrients in the diet than during the resting period. With 6-8 suckling rabbits, the female rabbit needs at least per day: from the 1st to the 10th day of lactation - 330 g of feed units, from the 11th to 20th - 440, from the 21st to 30th - 560 and from the 31st to the 45th day of lactation - 700 g of feed units. Digestible protein per 100g of feed units of the diet during this period should account for 16-18g. To produce 1 g of rabbit milk, approximately 0.9 g of feed units are consumed. The best food for baby rabbits during lactation is considered to be: in summer – clover, alfalfa, vetch-oat mixture, forbs; in winter - good forb or legume hay, potatoes, root crops, silage. From concentrates, rabbits are given oats, peas, cake, bran. The share of concentrates in the diet during this period is increased to 70-80% (in terms of total nutritional value). Rabbits per day can be fed from 100 to 300 g of hay, from 40 to 60 g of sunflower cake, 30 g of sunflower meal, about 5 g of feed yeast, 3-3.5 g of fish oil, up to 3-4 g of bone meal and up to 7 g of meat and bone meal, 2-3g chalk and 2.5g table salt. To increase the milk production of rabbits, milk-containing (green, juicy) feed and concentrates are introduced into their diets.
How to lead a female rabbit into the hunt. Stimulation of sexual estrus in female rabbits
Stimulation of sexual desire and ovulation. For female rabbits who have hypofunction of the ovaries, who refuse to accept a male after weaning the young, who do not produce offspring for a long time, or in the autumn-winter period, when female rabbits have reduced sexual activity, owners can stimulate estrus and heat using FFA injections, or gravohormone in a dose of 50-100 IU (10-15 IU/kg) intramuscularly, once. Owners of rabbits should keep in mind that after the administration of these hormonal drugs, the follicles do not ovulate. In order to induce the process of ovulation in a female rabbit, she needs an act of mating with a male, and when carrying out artificial insemination, the administration of hCG or Gn-RH.
When carrying out artificial insemination, rabbits with spontaneously manifested sexual heat immediately before insemination or 2-5 hours before insemination are injected with hCG in the ear vein at a dose of 25-40 IU. After the injection, ovulation in the rabbit occurs within 10-12 hours. For artificial insemination of females whose heat is absent or weakly expressed, 100 IU of FFA is injected 48-72 hours before the administration of hCG. Insemination of rabbits is carried out within an hour after the administration of hCG. Insemination of female rabbits twice with an interval of 6-8 hours can increase fertility by 10%.
One of the reasons preventing the use of artificial insemination in rabbit breeding is the possibility of the formation in the body of rabbits of specific antibodies to exogenous gonadotropins, as a result of which the effectiveness of the use of hormonal drugs may decrease after 3-4 inseminations.
Instead of hCG to induce ovulation in rabbits, it is proposed to use Gn-RH - dirigestran in a dose of 0.2-0.3 ml (10-15 mg), which, as experiments have shown, does not cause immune reactions with repeated use. In addition, GnRH can be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
Other methods of hormonal regulation and stimulation of sexual processes
To synchronize reproductive cycles in female rabbits, in addition to gonadotropic hormones or in combination with them, steroid hormones can be used. For example, feeding norethisterone acetate 10 mg and mestranol 0.3 mg for 10 days suppresses estrus and ovulation; after stopping the administration of drugs, all females simultaneously show heat with ovulation within 48 hours.
It is known that among the rabbits tested for pregnancy on the 10-14th day after mating with the male, there may be females with false pregnancies. With false gestation, the corpora lutea function for approximately 17-18 days; insemination of the female during this time is unsuccessful. In order to reduce the number of days of infertility in such females, experiments were conducted to induce regression of yellow days using various PGD2a drugs. Good results have been obtained with the use of the drug ilirene, the active principle of which is the synthetic prostaglandin tiaprost. Intramuscular administration of irilene in a dose of 1 ml (0.15 mg of active substance) did not have a toxic effect on the rabbit’s body. And for the resorption of corpora lutea, in case of false pregnancy, it is enough to administer 0.2 ml of the drug. In practice, it is recommended to administer the drug to unfertilized female rabbits on the 10-13th day after the previous mating, and to inseminate them on the 14th day.
In order to shorten the interval between litters in females that do not litter before the 32nd day of pregnancy, labor can be induced using oxytocin, prostaglandins or corticosteroids. If owners practice compacted births, then induction of labor with oxytocin one day before artificial insemination promotes higher fertility compared to insemination after spontaneous birth.
Preparing for childbirth
The animal behaves very calmly throughout the entire pregnancy period - this is one of the signs of pregnancy. Within a few days, the female begins to prepare the nest. Sometimes she may take a while to arrange the house and pull out the fluff just before the onset of labor. To make it easier for rabbits to prepare for childbirth, you can install a ready-made nest.
Another sign of imminent labor is increased appetite. Even the most fastidious female becomes gluttonous and eats everything in order to stock up on nutrients. Before and during labor, the female rabbit drinks a lot, so her drinking bowl should be filled to the top with clean, fresh water.
The box is installed four to five days before birth. Its width and length should be slightly larger than the female herself. Before giving birth, the female rabbit will line the box with hay and down. You need to change the bedding in the cage every day. In the first week after birth, it is not recommended to disturb both the mother and her offspring.
It should be noted. If a female gives birth for the first time, this process can bring her considerable stress.
You should prepare for the possibility that the birth may not be successful. At the moment the babies are freed from the birth membrane, the female can bite off the babies’ ears, paws and even heads. Sometimes it happens that a mother, experiencing stress, completely abandons her offspring.
To prevent the female rabbit from causing injury to her babies, she needs to trim her claws before mating. Since the female gives birth in most cases late at night, this process occurs independently. In this case, only the creation of conditions in which childbirth will take place depends on the person.
Young females need a little help in arranging the nest. To do this, the owner himself lightly plucks the fluff from the breast of the expectant mother.
Important! If female rabbits do not take care of their offspring at all, do not insulate the nests, give birth anywhere, or do not remove the films from the babies, as a result of which the babies die, then such rabbits are discarded and killed. After covering, the male should be placed in another cage, but so that he and the female can see and hear each other
Mated rabbits form a kind of family, and complete isolation will be very stressful for both of them. But it is still necessary to place the rabbits. And the point is not at all that the male can harm the babies
After covering, the male should be placed in another cage, but so that he and the female can see and hear each other. Mated rabbits form a kind of family, and complete isolation will be very stressful for both of them. But it is still necessary to place the rabbits. And the point is not at all that the male can harm the babies.
It is necessary to prepare for the birth in time. Very often proper preparation is not carried out, and this is a big mistake.
Pregnant and lactating females need large amounts of food and water. Make sure your rabbit always has fresh water and food in her cage.
Rabbits love silence, especially pregnant rabbits. Warn your family not to make noise near the cage or make sudden movements. Also, if possible, try not to transfer the rabbit into a new cage, especially if she is already in the late stages of pregnancy. A change in her usual environment can frighten her.
How to care for a rabbit during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the female rabbit breeder must apply a special diet for her, diversify the diet by adding vitamin and nutritional supplements, a lot of seasonal vegetables and herbs, and prepare a place for childbirth in the form of a special cage. In order for a female rabbit to safely bear and give birth to healthy, full-fledged rabbits, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for her. A nutritious, varied diet is one of the main conditions for a successful pregnancy. The diet of a pregnant woman must include the following nutrients:
- clean, fresh water should always be in the drinking bowl;
- nutritious feed, legumes, especially peas, beans, soybeans;
- sunflower seed cake, soybean meal (up to 50g/up to 30g, respectively);
- dry and fresh herbs, young grass if possible;
- bone meal, chalk, table salt;
- calcium, in the form of finely ground chicken egg shells, 1-2 g daily;
- fish oil in small quantities, daily intake no more than 2 g;
- boiled vegetables (potatoes, carrots);
- fresh vegetables (carrots, beets, white cabbage, zucchini);
- mixtures of cereals, forbs;
- additional nutritional supplements with added vitamins C, D, E.
A few days before giving birth, the daily food intake should be reduced by a quarter or a third, but fresh, clean water should be left in sufficient quantities. Just before the birth of the baby rabbits, the amount of food should be reduced by half; this will help to avoid the development of mastitis in the rabbit, significantly facilitate the birth process itself, and make the baby rabbits stronger and more viable.
During pregnancy, it is better to transfer the female rabbit to a separate cage, with the main focus on the cleanliness of the room and the general hygiene of the female. The cage should have:
- always fresh, clean, dry bedding made of hay, herbs, sawdust;
- muted atmosphere without bright sunlight or artificial light;
- comfortable temperature conditions;
- clean feeder;
- full ventilation, unhindered access to fresh air;
- box or box for the nest.
You can make a cage and feeder with your own hands; if this is not possible, a cage for a pregnant female can be purchased at a pet store or at a zoological market. The presence of a nest in the cage is mandatory, since small rabbits are born completely naked and blind, they lack body thermoregulation.
You can put clean sawdust, hay, finely chopped paper, and unnecessary rags into the nest. A cardboard box is perfect as a nest, but of course a wooden nest is better. A wooden queen cell will last much longer than a cardboard one; then it is made from a natural material - wood.
Rabbit breeding is an interesting, challenging, serious activity and very profitable, since the rabbit breeder receives valuable fur and tasty dietary meat in a fairly short time.
In the process of breeding this cute animal, many rabbit breeders have a lot of questions about breeding, care, nutrition and maintenance of rabbits. The main issues are related to the reproduction of rabbits, so every breeder of these cute fluffy animals must clearly know how long a rabbit’s pregnancy lasts, how to properly care for and feed a pregnant female during this difficult period of time for her, how to properly breed, what diet to choose, how to prepare a cage and nest for a full-fledged birth, how to avoid unpleasant diseases (toxicosis, mastitis) associated with conception, gestation, birth and feeding.
How long does pregnancy last
Before talking about how long a rabbit walks while pregnant, let's look at how to determine pregnancy. The check is carried out somewhere on the fifteenth day after mating. Babies in the womb can be palpated. To do this, you need to take the female by the ears and scruff of the neck with your right hand, and with your left hand, take it between the hind legs. Place your thumb on the right side and the other fingers on the left. If the rabbit is pregnant, you will be able to feel a chain of balls in the stomach.
Also during this period the behavior and appearance of the animal will change. A female in position reacts aggressively to the male's advances. It happens that the expectant mother even bites her owner and constantly hides in the house. Within a week, the female rabbit begins to plump up, and closer to giving birth, it becomes more difficult to bear a litter, and she can move very little.
Nesting is another sign that your rabbit is pregnant. The expectant mother will carry hay in her teeth, build a nest, insulating it with fluff torn from her own belly.
Let's note a few more signs before we find out how long rabbits stay pregnant. While waiting for babies, the taste preferences of the expectant mother may change. The female begins to drink more liquid and may throw food out of the feeder, making it clear that she wants something else.
Sometimes a change in behavior can become a sign of a false pregnancy. In this case, the duration of aggression is no more than 18 days, after which the animal calms down and can allow the male to approach again.
So, it's time to find out how long the gestation period lasts in domestic rabbits. Basically, the female bears babies for 28–35 days. It is noteworthy that large rabbits (Giant breed) stay pregnant longer than small ones. The number of embryos can also increase or decrease the gestation period in rabbits. Young mothers usually give birth to no more than 5 cubs.
Gestational age
The farmer needs to know how long the pregnancy of his long-eared ward lasts so that he can prepare in time for the important day of giving birth. Pregnancy lasts on average 30–31 days, minimum 28 days, maximum 35. It is difficult to accurately determine this period in each individual case, since this can be influenced by several circumstances.
The duration of pregnancy depends on:
- breeds (large ones walk longer, small ones - less);
- first or second pregnancy (firstborns stay pregnant the longest);
- health status and stress;
- the number of fetuses developing in the abdomen.
Dependence of gestational age on the number of cubs in the litter and the functioning of the mother’s body. If there are a lot of rabbits, it is more difficult to carry them, so the mother’s womb is freed from them earlier.
How long after birth can a female rabbit be born?
The physiology of the female rabbit is such that she is ready for mating already on the 2nd or 3rd day after the birth of the offspring. In the wild, rabbits mate as soon as the female goes into heat. In the warm season, rabbits are more active, hunting occurs every 7-9 days, and in winter productivity decreases.
Signs of sexual heat:
- Changes in behavior. Female rabbits become restless and even aggressive.
- The genital loop swells and acquires a bright pink color.
Early weaning of rabbits from their mother affects their immune system
There are different technologies for mating rabbits, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- industrial technology;
- compacted litter method;
- standard technology.
Although a female rabbit is capable of bearing offspring almost 10 times a year, large farms practice rabbit breeding technology that allows them to produce only 7 offspring per year. In each litter, at least 5-6 rabbits are born.
This method of breeding rabbits allows you to get a larger number of litters per year. According to it, the female rabbit is allowed into mating 2-3 days after giving birth. In this case, the rabbits are taken away from their mother on the 28th day after birth. Disadvantages of this technology:
- the rabbit’s body wears out quickly;
- the cubs grow up weak, with low immunity;
- a female rabbit can destroy the offspring due to a lack of nutrients in the body.
Rabbit breeding techniques
- they give the breeding rabbit a rest, since she does not have to feed her cubs;
- They raise a full-fledged replacement offspring, it receives milk for at least 1.5 months.
This method of breeding rabbits is practiced mainly on small private farms. It lies in the fact that rabbits are weaned 45-50 days after birth. At the same time, you can mate a female rabbit a month and a half after giving birth. This method has a number of advantages, although it allows you to get only about 35 rabbits per year:
- farmers regularly receive numerous and viable offspring;
- the rabbit’s body is not depleted, as it has time to recover after giving birth and feeding the babies;
- after weaning from their mother, the cubs are already able to eat adult food;
- The maternal qualities of the rabbit are preserved, she does not eat the offspring, and does not refuse to feed them.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=subscribe_widget
Each farmer decides for himself when to cover the female rabbit after giving birth. He must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each animal breeding technology and make a decision. By practicing the method of compacted births, he risks the health of the rabbit and her offspring. By choosing other methods, he does not receive such a large litter per year, but gives the female the opportunity to restore strength after the next litter. This has a beneficial effect on her maternal qualities and ability to feed her cubs.
Features of rabbit breeding
Rabbits develop very quickly and become sexually mature. Large breeds mature in 6–7 months, and small decorative rabbits are ready to mate from 3 months. Young females give birth to 4–5 babies per litter, and experienced mothers give birth to up to 9 babies. These furry animals have the ability to reproduce very intensively.
One female rabbit can give birth 8 times in a year. But experienced and caring rabbit breeders breed a female no more than 5 times a year, so that this does not affect her health and the offspring are not harmed. So, from one eared mother you can get 35–40 cubs, which makes rabbit breeding a very profitable business.
How to tell if a female rabbit is pregnant
Determining the gestation, or pregnancy, of a female is not so easy. Of course, there are certain signs that occur most often. But each rabbit has an individual character and may react to her “interesting” situation differently than others. In addition, a false pregnancy at first can manifest itself in the same way as a real one.
Palpation procedure
Starting from the 15th day after mating, it is already possible to feel embryos that have grown to the size of a cherry. And on the 25th day, the rabbits are fully formed and moving in their mother’s belly. During this period, with the help of palpation, i.e., feeling with your fingers, you can verify that the female is pregnant.
Important! Experienced rabbit breeders recommend not palpating yourself, but contacting a veterinarian for this.
One careless pressure with a finger can provoke a miscarriage. Performing these simple steps is not easy, because not all animals allow themselves to be touched calmly
In addition, it is not always possible to accurately determine the presence of embryos, especially for beginners
It is not easy to perform these simple actions, because not all animals allow themselves to be touched calmly. In addition, it is not always possible to accurately determine the presence of embryos, especially for beginners.
By external signs
Some signs of pregnancy are noticeable if you are observant. A week after mating, the fertilized rabbit begins to gain weight. Her belly is rounded, which can be overlooked due to her fluffy fur.
Also, her behavior can change dramatically:
- activity is replaced by calmness, cautious movements, or, conversely, the previously calm female becomes hyperactive;
- fearfulness and shyness: seeks shelter and hides in it;
- irritability and aggression towards relatives and towards humans;
- eats more than usual;
- if you lightly press on the nipple, droplets of milk protrude from it (at a later date);
- there is a lot of fluff in the cage.
For some expectant mothers, their behavior does not change at all, which makes it difficult to determine pregnancy.
Find out at what age rabbits are ready to mate.
Aggression towards the male
A pregnant female's attitude towards individuals of the opposite sex changes radically. Being in a common cage, she behaves aggressively with them, does not allow them to approach, growls at them. The pregnancy of a female in a separate cage can be checked 5 days after mating.
They place the male next to her again and watch how she behaves. If she allows the mating to happen again, she has not been fertilized. A pregnant rabbit does not allow her gentleman to approach her, runs away from him, growls and, on the contrary, chases him around the cage, hits him with her paws and bites.
Nesting
A few days before giving birth, you can notice that the expectant mother is running around the cage, carrying bundles of hay in her teeth. She collects it and puts it in a pile in one place. The female lays fluff on top of the hay, which she pulls out from her chest and belly with her teeth. In this way, the animal prepares for the birth of its babies. She builds a nest of hay, insulating it with her down. This house should be soft and warm so that the cubs feel comfortable in it.
Did you know? The female rabbit has a special structure of the uterus: it is bifurcated. Thanks to this, a female can become pregnant from two males at the same time.
Rabbits usually engage in this type of construction 3–4 days before giving birth. Some do this the day before the birth. But there are also those whose builder instinct awakens after the appearance of the rabbits. Young rabbits with their first pregnancy may not do this at all. Then you will need human help.
How to find out if a rabbit is pregnant
In the early stages, it is difficult to understand that conception has occurred, but there are methods for detecting pregnancy.
A 100% reliable method is ultrasound , which allows you to control fertilization within 6 days after coating.
Ultrasound is the best method for determining pregnancy, which gives 100% accurate results already on the sixth day after mating
But the method is not always available; carrying out the procedure in a veterinary clinic is complicated by transportation, a large number of females, especially in large farms.
Therefore, rabbit breeders focus on the following methods:
- analysis of external changes and behavior;
- palpation;
- replanting with a male.
As pregnancy progresses, the female’s weight also changes due to the growth of embryos and an increase in the mass of the fertilized uterus. For diagnosis, it is necessary to weigh the animal before mating.
Approximately the weight should increase:
- after 7 days – by 29 g;
- after 14 days - at 59
The diagnostic method cannot be considered reliable, since the female also gains weight due to eating more food.
Palpation procedure
Checking for pregnancy by palpating the rabbit's abdomen gives an accurate idea of the presence of embryos in the uterus. Caution is important here.
Palpation procedure for a female rabbit
It is recommended that experienced rabbit breeders perform these manipulations so as not to frighten the animal and cause miscarriage. If you don’t have enough experience, it’s better not to take risks and call a veterinarian.
The examination is carried out on the 14-16th day after mating.
How the procedure is carried out:
- The female is placed on a horizontal surface: a table or a wide bench.
- Hold the scruff of the neck with your hand to ensure its immobility.
- The other hand is placed under the stomach in the pelvic area and carefully palpated.
The fingers feel the compacted area of the pregnant uterus; small oval seals the size of a hazelnut are found in its horns. These are developing embryos.
Attention! When palpating, it is important not to confuse the embryos with lumps of feces: the latter feel harder and smaller to the touch.
By external signs
In the early stages, the appearance of a pregnant rabbit does not change, young animals are playful , eat well and jump, sometimes this behavior persists until childbirth.
After a week, depending on their temperament and character, the females become calmer, more careful, or, conversely, active and irritable. Some are so aggressive that they bite the owner when trying to pet the animal.
The female's belly is noticeable from the 3rd week of pregnancy , she moves more slowly, may show dissatisfaction or hide in the nest when approaching the cage.