The child's body is very weak. For a long time, the newborn is protected by passive immunity received from the mother. But this does not prevent the baby from becoming infected from a sick mother cat or becoming a target for a very virulent (poisonous) strain of a microorganism or virus. It takes much less time to save a baby than to treat an adult animal. All owners are advised to find out in advance what illnesses their kittens have, since awareness of the symptoms of the most common diseases will eliminate too late diagnosis.
Signs of illness in a kitten
The severity of symptoms depends not only on the stage of the disease, but also on the characteristics of the animal itself. Small pets are very difficult to tolerate any disease. It is not so difficult to guess about their ailment. It is enough to analyze their behavior and existing physiological disorders.
Behavioral changes
The owner should be alerted by sudden aggression or apathy, which is not characteristic of a good-natured and active pet. Depending on the cause of the illness, he may rush at family members or hide in secluded corners, avoiding sunlight.
Loss of appetite should not be ignored when even the patient’s favorite treats do not attract the attention of the sick person. If such behavior is associated with pain, do not be surprised by the appearance of plaintive meows and groans when trying to move from a warm bed.
External manifestations
Physiological symptoms are more obvious. Responsible owners never leave them unnoticed. External signs of illness include:
- increase or decrease in temperature;
- irregular pulse and difficulty breathing;
- problems with urination and intestinal upset (constipation, diarrhea);
- nausea and vomiting;
- redness, peeling, swelling and ulceration of the skin;
- hair loss and deterioration in its appearance (disheveled, dull, brittle);
- gait disturbance (strange movements, falling on the spot, lameness);
- increased lacrimation and runny nose;
- the appearance of discharge from the ears;
- bloating and loss of abdominal softness.
If at least one of these signs appears, it is recommended to contact a veterinarian as soon as possible. Some pathological conditions can be dangerous and contagious to other pets and even people. The patient should be isolated until diagnosis is made.
Respiratory diseases in cats and cats
Let's look at the most popular ones.
Asthma
Bronchial asthma is manifested by muscle spasms and narrowing of the lumens of the bronchi. Most often, asthma occurs due to an allergic reaction, which can be caused by both dust and food.
The cat begins to thrash and gasp, wheezing or whistling appears, the animal tries to stretch its body upward to make air access possible.
Pulmonary edema
Occurs as a result of improper or untimely treatment; fluid collects in the lungs, which prevents the pet from breathing normally.
Manifestation:
- dyspnea;
- anxiety;
- breathing occurs abdominally;
- mucous membranes become blue due to lack of oxygen;
- the cat takes the same poses for several days;
- coughing;
- wheezing.
Cough
Most often, coughing occurs when the pet is in normal condition, as he is trying to regurgitate a hairball, but if wheezing occurs and the cat begins to meow heavily, you need to consult a veterinarian.
Runny nose
It appears due to inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
Manifestations:
- sneezing;
- breathing occurs through the mouth;
- discharge;
- The cat rubs its nose with its paws.
Rhinitis can also manifest itself due to a foreign body, so in order to prevent the death of your pet, it is necessary to take it to a veterinary clinic as soon as possible.
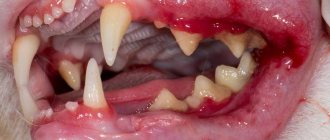
Calcevirus infection
Most often, kittens get sick; the infection is transmitted through saliva.
Manifests:
- high temperature;
- lethargy;
- the appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa;
- profuse salivation.
A runny nose and watery eyes may also appear.
Inhalation
Infectious diseases
The main causative agents of infections are bacteria and viruses. The pathologies they cause are highly contagious. In crowded conditions, it is recommended that not only the infected person be tested, but also the others. Most likely, they are already sick, so everyone will have to be treated together.
Panleukopenia (distemper)
Infection with distemper is accompanied by weakness, apathy, trembling of the limbs and matting of the fur. Sick animals do not respond to their mother and refuse not only feeding, but also water.
Over time, the symptoms are complemented by loose, foul-smelling stool streaked with blood and yellowish foamy vomit. Death from dehydration occurs within 3 days, so it is very important to consult a doctor at the first behavioral changes.
Peritonitis
Inflammation of the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity due to infection with feline coronavirus causes fever and loss of activity. Due to poor appetite and fever, the body quickly becomes exhausted. Yellowing of the mucous membranes and skin is observed.
If peritonitis is detected in a pregnant cat, it is necessary to separate her from her kittens at 4-6 weeks of their life. By this time, the antibodies produced in breast milk have broken down and can cause illness in the litter.
Calcivirosis
Like other pathological conditions, calcivirosis in recently born animals occurs in a rapid form. If a secondary infection occurs, the chances of salvation are almost zero.
Transmission of the pathogen occurs through direct contact with a sick person or through contaminated things. Calcivirosis can be recognized by excessive salivation, sneezing, fever, the appearance of serous fluid from the nose and eyes, as well as swelling and ulceration of the skin.
Conjunctivitis
Damage to the mucous membrane of the eye is accompanied by its redness, the formation of a cloudy film on the cornea, profuse tearing and eversion of the eyelids. The course of conjunctivitis is usually severe. Copious mucous discharge quickly becomes cloudy, mixing with pus.
In the purulent form, there is an increase in body temperature, loss of activity and appetite. Because of the pain, the animal practically does not blink, and its eyelids are glued together by the accumulating exudate.
Pathologies during pregnancy of a mother cat and during lactation
Some diseases of newborn kittens are associated with improper intrauterine development and flaws in feeding. To prevent them, it is necessary to strictly monitor the condition of the pregnant pet, preventing her from deteriorating.
Fading kitten syndrome
Pathology develops due to placental abruption. A kitten formed in such an afterbirth weighs 25% less than its brothers and sisters. He barely moves and drinks little. In especially severe cases, complete paralysis of the limbs is noted.
Due to dehydration and hypothermia, gradual decline and death are observed. There is no cure for this disease, so do not neglect to review your cat's diet during pregnancy.
Hypogalactia
Occurs when there is a deficiency of milk caused by poor feeding, too large an offspring or the first birth. Newborns are malnourished, so their body is quickly depleted.
To solve the problem, it is necessary to abandon breastfeeding in favor of artificial. Ready-made milk formulas sold in pet stores have similar nutritional value. After reaching 1 month, they can be replaced with complementary foods.
Toxic milk syndrome
Occurs during acute intoxication caused by damage to the mammary glands or uterus. Poisoning of newborns is accompanied by:
- bloating;
- dehydration;
- diarrhea;
- refusal to feed;
- plaintive meow;
- increased temperature (observed during blood poisoning).
With these symptoms, as with hypogalactia, you should switch to artificial nutrition and consult a veterinarian. He will select medications for symptomatic therapy, and in especially severe cases, prescribe antibiotics.
Oncology of cats and cats
If cancer is not detected in the early stages, the outcome can be fatal.
Mammary cancer
On initial palpation it may resemble a pea, but over time the tissue grows and a tumor forms, most often malignant. It is more often diagnosed in females who have not given birth. Short-haired breeds are often affected.
Symptoms
- Swelling of the nipples.
- Dense knots.
- Discharge.
- Ulcers on the skin.
- Temperature increase.
- Weight loss.
- Refusal of food.
- Lethargy.
At the first manifestations, you should show it to a qualified specialist.
Lymphoma
The most common disease that affects lymphocytes and lymphoid tissue.
Causes:
- ecology;
- heredity;
- leukemia
Symptoms
- Weight loss.
- Vomiting or diarrhea.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Dyspnea.
- Suffocation.
The main thing is to have time to show your pet at the initial stage of the disease in order to save his life.
Squamous cell carcinoma
It affects the epithelial layer of the skin and is most often formed in the mouth. It is removed surgically.
Symptoms
- Wounds that do not heal for a long time.
- Ulcers.
- Redness of some areas of the skin.
Cancers are most often found in the ears, nose, or mouth.
Sarcoma
The most aggressive type of cancer. It is necessary to monitor the cat, examine its skin, and also look in its mouth so as not to miss tumors. There are many types of sarcoma lesions, which most often cannot be cured, but only symptomatic treatment can make life easier for the pet.
Blood disorders
A low level of hemoglobin, a small number of red blood cells or their rapid destruction are very dangerous. These disorders are fraught with retarded growth and development, decreased immunity and hypoxic coma caused by lack of oxygen.
Anemia
Anemia is accompanied by pallor of the mucous membranes and delayed physical development. This pathology is often inherited or occurs as a complication of helminthiasis.
The condition of sick babies can be normalized with the help of iron. To do this, you need to select a special medicinal food or add iron-containing supplements to the diet.
Hemolysis
Occurs when the blood type of a mother cat and her cubs do not match. Antibodies that enter the body along with colostrum attack and destroy the red blood cells of newborns.
The destruction of red blood cells is accompanied by:
- yellowing of mucous membranes;
- darkening of urine to a brown tint;
- lethargy and refusal to feed;
- necrosis of tissue at the tip of the tail.
The cubs should be transferred to artificial feeding. It is also recommended to take blood tests for the entire family in advance to rule out breastfeeding without waiting for complications.
Pathologies caused by external factors
Many pathological disorders are caused by external factors. Their appearance is associated with improper care, neglect of asepsis rules and allergens - substances that cause acute intolerance in the body.
Inflammation of the navel
The reasons for the appearance of an inflammatory process in the navel include dental diseases of the mother, unsanitary conditions in the place where her babies are kept, or a violation of the length of the umbilical cord, when it is more or less than the required norm. The inflamed navel turns red, swells and oozes pus.
In the treatment of this pathology, anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptic ointments are used. They help relieve inflammation and prevent blood poisoning.
Hypothermia and its consequences
Often occurs in the absence of a mother cat who warms the cubs with her body heat. Another possible cause of hypothermia is unfavorable living conditions, when animals have to sleep on a cold floor or in a draft.
The body temperature of a frozen animal drops to 35.6°C, but does not affect mobility. It is preserved so as not to lose any remaining heat.
A “nest” with small pets should be equipped with a heating pad. To restore strength, use a glucose solution, pouring it into the mouths of all victims. Without timely help, mustachioed pets die due to disturbances in the functioning of the heart and brain.
Dehydration
Dehydration is not an independent disease, but is a symptom of other pathologies. With insufficient physical development, it is due to the fact that the animal is simply not able to independently reach the mother’s nipples.
Lack of moisture in the body is accompanied by a bright red coloration of the tongue and mouth, dry mucous membranes, weak muscle tone, low physical activity and loss of skin elasticity. A dehydrated baby should be constantly latched to the breast or bottle-fed. Additionally, rehydration medications may be required.
Allergy
Allergic reactions are provoked by flea bites, certain foods, pollen and other allergens. The little allergy sufferer constantly itches, sneezes, breaks out in small rashes, or suffers from hair loss. For recovery, it is necessary to eliminate all provoking factors and use antihistamines.
Stool disorder
This is another symptom that is not an independent pathology. Constipation and diarrhea occur with problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In babies, they are usually associated with overeating, familiarization of the body with new foods and stress when separated from the mother.
If, after reviewing the portions, returning to the regular menu and getting used to the new owner, the situation does not stabilize, you should be tested for infections and intestinal parasites.
Non-contagious diseases of cats
Most non-contagious diseases of cats arise due to violation by animal owners of the basic rules of care, feeding and maintenance. When kept in apartments, animals often become pampered and susceptible to disease. They are often fed very generously, haphazardly, with an excess of sweets.
Most often, animals suffer from diseases of the digestive and respiratory organs, metabolic disorders, and vitamin deficiency.
Cat diseases associated with internal dysfunction of the body are not transmitted to other animals and do not require quarantine or separate keeping of healthy and sick animals.
Compliance with the basic rules of keeping, feeding, and the owners’ knowledge of basic, simple techniques for helping animals helps maintain their health.
Publications 1 - 10 of 15 Home |
Prev. | 1
| Track. | End Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the lungs, which is quite widespread, but there is a fairly wide range of diseases characterized by the same symptoms - cough and shortness of breath.
-Go to publication-
Inflammation of the wall of the esophagus - esophagitis (from Esophagus - esophagus) usually develops due to foreign objects or acid reflux (stomach acid entering the esophagus).
-Go to publication-
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa or gastritis in cats is a signal that pathological processes are occurring in the pet’s body. At first glance, gastritis may seem like a minor problem, but without treatment, this disease can provoke the development of other, more dangerous diseases: oncology, ulcers, erosions, etc.
-Go to publication-
Hematoma is a type of bruising, a limited accumulation of blood in closed and open injuries to organs and tissues with rupture (injury) of blood vessels.
-Go to publication-
Hypertension is the name given to increased hydrostatic pressure in blood vessels, hollow organs, or body cavities.
-Go to publication-
Cryptorchidism (from the Greek kritos (hidden) and orchis (testicle)) is a condition where the testes are located outside the scrotum.
-Go to publication-
Feline lymphosarcoma (or otherwise lymphoma) is one of the types of cancerous neoplasia of white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes become malignant and begin to form tumors in areas containing lymphoid tissue. This disease is quite common in cats.
-Go to publication-
Urethral obstruction is a partial or complete disruption of the outflow of urine from the bladder due to the formation of a plug in the lumen of the urethra.
-Go to publication-
Nephritis - from the Latin nephos - kidney and itis - inflammation - a term that combines various inflammatory diseases of the kidneys. In cats there are:
-Go to publication-
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. To understand how dangerous pancreatitis can be, you need to know what function the pancreas performs.
-Go to publication-
Publications 1 - 10 of 15 Home |
Prev. | 1 | Track. | End
Parasitosis and skin diseases
The main cause of dermatitis in a newborn is infection by parasites or fungi. In both cases, unbearable itching appears, and secondary infections quickly penetrate the scratches.
Helminthiasis
Helminths enter the body in utero, through mother's milk, from other animals or from the owner's street shoes. In addition to scabies near the anus, infected people experience vomiting, diarrhea, conjunctival lesions and bloating.
Some worms are dangerous to humans, so do not delay treatment. Anthelmintic drugs are used to kill parasites, but due to their toxicity, the dosage and method of use should be checked with a veterinarian.
Flea infestation
Flea infestation is very difficult for newborns. Due to blood loss, they become anemic. There is also a possibility of infection by tapeworm larvae and mycoplasmas carried by fleas.
If your baby is constantly itching, covered in ulcers and becomes irritable, book him in for an examination at the veterinary clinic. Anti-flea drugs are no less toxic than anthelmintic drugs, so you will need to consult a specialist.
Ringworm
Infection with fungi is accompanied by severe itching, hair loss, discoloration, peeling and inflammation of the skin. Ringworm is difficult to treat. Recovery takes at least 1 month.
The sick person is placed in strict quarantine, isolated from other family members. Fungal spores are very tenacious. To destroy them, it is necessary to disinfect the entire room and get rid of the infected person’s personal belongings, replacing them with new ones.
Ear mite
The presence of otodectosis can be easily determined by brownish-black discharge from the ears, periodic shaking of the head and redness of the affected skin. In severe cases of the disease, the animal may lose hearing, so do not delay treatment. All four-legged family members will have to be treated for scabies parasites, since the disease is quickly transmitted when keeping several pets at the same time.
Burns and electrical injuries in cats
Sometimes, after playing, cats can jump into a hot oven or spill a container of boiling water. Of course, this cannot be done without burns. In mild forms, skin redness and blistering occur. Cold applied to the damaged area helps a lot here. In more severe cases, hair loss may occur, the animal experiences severe pain, and the skin loses its natural color and becomes white.
It happens that a cat chews an electrical wire, which inevitably leads to electrical injuries. If this happens, under no circumstances should you pick up your pet or touch it at all until the power is turned off and the sockets are not de-energized. After turning off the electricity, you need to check whether the cat's heart is working. This can be determined by palpating the lower chest behind the left front paw. If the pet has lost consciousness, it must be taken to a veterinary hospital without delay.
Sometimes, having received a mild electric shock, the pet does not lose consciousness and remains in good health, but even in this case the cat needs to be examined by a specialist. Often, as a result of electrical trauma, burns appear on the oral mucosa.
How to protect your kitten from diseases
To protect your little pet, you need to take care of its health even before birth. This will be helped by competent care of the mother, who protects her offspring from infections until vaccinations are given.
Ensuring the normal course of pregnancy of the mother cat
Before mating, it is necessary to undergo all mandatory vaccinations in order to build immunity against the most dangerous viruses, and deworming. During pregnancy, a lot of attention will have to be paid to feeding and living conditions:
- Increase your daily food intake by 10%. In this case, there will be enough nutrients not only for the cat, but also for her offspring.
- Increase the frequency of feedings. Despite the increase in the norm, you cannot feed the daily portion in just 2 meals. Do not overload the stomach and feed your pet 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- Enrich your diet with vitamins and minerals. If your pet eats dry food, then choose a new product designed specifically for pregnant and lactating animals. When feeding natural food, it is better to discuss this issue with your veterinarian. Without preliminary testing, there is a risk of overdoing it or, conversely, not getting enough elements necessary during this period. Such a mistake is fraught with hypo- or vitamin deficiency.
- Create a safe and cozy "nest" to prevent childbirth under the sofa.
- Swap a large play set for a horizontal scratching post. An unsuccessful landing from a high surface can cause miscarriages.
By following these recommendations, your mustachioed pet's pregnancy will be easy and unnoticed. During childbirth, it is better to invite a veterinarian, since in an emergency he will be able to provide first aid.
Pre-vaccination period
This period is one of the most dangerous, but if the mother cat is vaccinated in a timely manner, there is no need to worry about the health of her offspring. For additional prevention, it is recommended to avoid walking outside, not to let small pets out into the hallway, and to put all outdoor shoes along with clothes in a tightly closed closet.