Description
Macrognathus comes from fresh and brackish water bodies of eastern and African countries. In nature, the maximum size of an eel is up to 40 cm, but in an aquarium the fish reaches 25 cm.
Appearance
The elongated body lacks pectoral fins, and the dorsal and anal fins are shifted towards the tail. There are spines on the back. The color is light brown or yellow, there are marble patterns on the sides, and on the back there are black dots bordered with yellow, reminiscent of eyes. A light stripe runs from head to tail. Some individuals have black vertical stripes on their bodies.
Behavior
The aquarium eel is a predator, but is tolerant of other large species. Able to stay on land for about 1 hour. Young macrognathus stay in groups. As they grow up, they become territorial, and then the eels are housed alone. After moving to a new aquarium, the fish are shy. During daylight hours they hide among shelters, and at dusk they swim out to hunt. An inexperienced aquarist can be bitten or injured by the spines.
Lifespan
In captivity, macrognathus live on average 5 years.
Macrognathus diseases and their treatment
The occurrence of pathologies is most often associated with poor living conditions and improper feeding. This type of fish is most susceptible to skin diseases. Excess mucus leads to the formation of ulcers. They are treated by increasing the water temperature (up to 32°C) and increasing salinity to 10%. Special anti-ulcer drugs are added to the water. Hexamitosis (affects the gallbladder and intestines) is also one of the common diseases. Her symptoms:
- Deterioration of appetite or loss of appetite.
- Mucous, thready excrement is white.
- Darkening of scales.
- Ulcers on the head.
- Swallowing and spitting out food, which is repeated regularly.
Other diseases:
| Name | Description |
| Poisoning | They may occur due to increased levels of chlorine and nitrogen compounds in the water or dirty soil. |
| Ichiophthiriasis | White pimples and inflammation appear on the skin. |
| Temperature shock | It occurs due to a sudden change in temperature, so it must be the same all the time. |
| Oodiniumosis | Excessive secretion of white-yellow mucus. The fish rubs against all surfaces in the aquarium. It is treated with special drugs. |
Diseases can only be cured at the initial stage, so fish need regular veterinary examinations. Therapy should be carried out by specialists. Having determined the cause of the pathology, they prescribe antibiotics. Hyperthermic water treatment can be used.
Macrognathus is a large and hardy fish that loves to swim. To create optimal living conditions for her, you need to work hard: change the water on time and do not neglect feeding; Make sure that the fish does not escape from the aquarium.
Breeding them is difficult, so only experienced aquarists should do this. If the fish is trained, it can eat directly from the owner's hands.
If the macrognathus does not like its living conditions, it can commit suicide by jumping out of the aquarium.
The fish is expensive and no less valuable.
Content
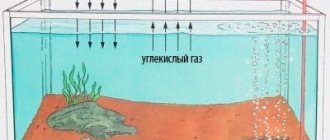
The range of hardness and acidity in which macrognathus lives is quite wide. Aquarium fish lead a sedentary lifestyle, so a large-volume tank is not required for macrognathus. It is more important to ensure good filtration, aeration and timely maintenance of the aquarium.
Aquarium
A 100-liter vessel is enough for one eel. A tight-fitting lid is required to prevent your pet from escaping. Remember that Macrognathus can fit through openings for wires and tubes.
Water parameters
| Temperature | 22–28 degrees |
| Rigidity | 5–16 dGh |
| Acidity | 6–8 |
| Brackish water | permissible concentration is 2–10 g per liter of water |
| Water movement | Weak |
Change no more than a third of the total volume of water and siphon the soil once a week. Add salt to the water.
Plants
Plant plants with a strong root system or in pots:
- ferns;
- cryptocorynes;
- Anubias;
- hygrophiles;
- Vallisneria.
Priming
Place smooth, fine soil at least 4 cm thick. Fine gravel or quartz sand will do. Eels burrow into the sand to get rid of excess mucus.
Equipment
Devices you will need:
- Filter. Make sure that the filter does not create strong water pressure and is quite powerful. Mechanical, biological and chemical filters can be used. Filtration is more effective for mixed types. It is better if different devices are responsible for aeration and filtration.
- Compressor. Necessary for dissolving oxygen in water.
- Heater. Not required on an ongoing basis. Necessary in the absence of heating in the room, when the water temperature drops below 22 degrees.
Lighting
Blackheads don't like bright light, so make sure the lighting is moderate.
Do not allow the lamp to operate continuously; daylight hours should not exceed 12 hours. Monitor the water temperature. If the lamp heats the water too much, replace it with an LED or another one with low heat output and think about heat dissipation.
Maintenance and care
The aquarium must be covered , since macrognathus can crawl out into any crack. For an aquarium, a filter with moderate to strong water flow is recommended. Fish do not like bright sunlight, so you need to create shade by planting vegetation in the aquarium (or use moderate light that turns off at night). To create a familiar environment for fish, it is recommended to add 3-4 tablespoons of sea salt per 100 liters of water, but do not forget about other neighbors who may be harmed by salt. Macrognathus prefer clean, oxygenated water, so the aquarium must have a good aeration and filtration system.
Basic content rules:
- The aquarium must be covered with a lid, because fish can crawl out even into the smallest cracks.
- From time to time the water needs to be salted.
- The tank must have a good filtration and aeration system.
- Once a week it is necessary to change 25% of the water in the aquarium; The water needs to be completely changed every two weeks.
- The temperature level must be maintained all year round.
The physiology of macrognathus involves the frequent secretion of mucus, which needs to be gotten rid of. Excess mucus can lead to diseases, so to remove it, fish regularly bury themselves in the ground or rub against large stones. Sharp stones are inconvenient to burrow into and are dangerous: the gravel laid there must be checked for particles that could harm the fish. The soil layer should be at least 10-12 cm. Coarse washed sand is also good.
Decorations can include driftwood, decorations without sharp edges, and rounded stones. But it is recommended to lay them out in moderation so that the fish have room to swim. Plants must have developed root systems so that fish cannot tear them out by digging in the soil. If there are none, the plants need to be planted in the aquarium along with special pots to make them more stable. When planting plants, it is worth leaving empty spaces so that fish can burrow into them.
Feeding
Predators need live food:
- small fish;
- bloodworm;
- earthworms;
- small crustaceans;
- tubifex;
- terrestrial insects;
- shrimps.
Feed macrognathus in the evening. Treat live food with methylene blue or potassium permanganate. Avoid overfeeding. If there are more active inhabitants in the tank, the eel may be left without food due to its sluggishness. The main rule when feeding: monitor the process. Over time, you can diversify the diet with frozen and dry food with a high protein content. Sinking food in the form of granules is suitable.
View this post on Instagram
My eel has grown up (they named him Igor-eel Igor)))). You can see a little cold shrimp, guppies and catfish stuck #aquarium#aqua#eel#guppy#shrimps#akva#akvaryum#macrognatus#macrognatus_oculated#fish#cold#catfish#aquariumsome #catfish#Igor#KosarevsFamily_animals
A post shared by Yulia Kosareva (@yulakosa) on Jan 24, 2021 at 8:25am PST
Compatibility
Macrognathus are compatible with large non-aggressive fish:
- gourami;
- acanthophthalmus;
- botia;
- mastacembelas;
- mistusami;
- ancistrus;
- brocade catfish;
- plecostomus;
- astronotuses;
- parrot fish.
Neighbors for macrognathus should be similar in character and requirements for living conditions. Choose comfortable conditions for all your neighbors. Aggressive cichlids and small fish are a bad choice, because the former are dangerous to the eels, and the latter will be eaten. The potential mate should not fit into the eel's mouth, otherwise there will be no opportunity to eat it.
View this post on Instagram
#aquarium #jar #aquarium science #aqua #water #fish #beauty #catfish #yinyan #ancitrus #angelfish #macrognathus
A post shared by Alevtina (@alchyona) on Sep 21, 2021 at 6:38am PDT
Care and maintenance of macrognathus in the aquarium
Unfortunately, many people think that macrognathus should only be kept in salt water. This is an absolute misconception, since this type of fish thrives in fresh water bodies.
It is advisable, of course, to add a little salt to the water in the aquarium so that semolina does not form. Asian species of eels of this type live in mineralized water. And African species usually live in fresh waters, such as Lake Victoria.
They all bury themselves in the sand, so before placing this type of eel in the aquarium, you should pour sandy soil into it. If you refuse this action, you may encounter various macrognathus diseases .
In the photo there is a fish Macrognathus ocellata
For example, fish will try to bury themselves in the sand, but as a result they will only scratch their skin, as a result of which microbes will penetrate there. It is difficult to get rid of microbes, so quite often such negligence of the owners leads to the death of the fish. Therefore, it should be noted that the care of macrognathus must be correct and you simply cannot do without sand. It is best to use quartz sand.
It can be purchased at any hardware store, where it is usually used for feeding. If the fish is still small, then 5 centimeters of sand will be enough. The sand in the aquarium is cleaned with the help of melanin. Cleaning must be done regularly, otherwise harmful microorganisms may form there.
For large eels, you should select a large aquarium, at least 100 liters. It is imperative to equip the aquarium with driftwood, caves and pebbles. It is also worth noting that this type of fish simply loves Java moss, but it is better not to add it to the aquarium; a few floating plants will be enough.
Reproduction
Eels are almost never bred in an aquarium. You will need hormonal injections and a spacious container.
Sex differences
Sexual maturity of macrognathus occurs at 2 years. Females are slightly larger than males. During the spawning period, greenish eggs are visible in the abdomen of the female.
Spawning
Before spawning, place the male and female together. Feed them high-quality protein food. For spawning, you can take a mixed-sex pair of fish or two males and one female. The minimum volume of an aquarium for spawning is 250 liters, at least a meter long. Comfortable temperature is 26–28 degrees, hardness is medium. Shelters, separator nets and plants are required. Inject a hormonal injection into the dorsal muscle of the fish.
Introduce the spawners into the spawning area and create low lighting. During spawning, the female can lay up to 1000 eggs; upon completion of the process, the parents are removed from the container. Egg incubation time is 3 days. The hatched larvae feed on the contents of the yolk sac for some time. Later taken from food:
- ciliates;
- microworm;
- Artemia nauplii;
- crushed food for adult fish.
The fry grow unevenly, so sort and remove the young as they grow.
Macrognathus
Family: Proboscis.
Comfortable water temperature: 22-26 C.
Ph: 6,5-7,0.
Behavior: non-aggressive.
Compatibility: With all peaceful fish, incompatible with cichlids (although if you make a lot of holes, then you can).
Macrognathus habitat: Burma, Thailand and India. Inhabits fresh and brackish waters in southeastern countries, East Asia: Mekong River, Southeast Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Chao Phraya River.
The shape of the fish is graceful - the “worm” differs from ordinary fish. The stigma of this fish is elongated, the body is like that of a conger eel and is very elongated in length. The dorsal and anal fins are located behind, resembling a caudal fin. The fish does not have pectoral fins. There are numerous spines on the back, which can cause injury when catching fish with your bare hands.
Macrognathus can be colored in brownish tones with an olive or beige tint. There is a blurred marble pattern on the sides, and yellow spots and transverse lines are scattered across the head and body. The body seems to be divided in half by a light stripe running on both sides. The fins are light brown or reddish, the dorsal fin is long with spherical dark spots bordered by a golden rim. The abdomen is much lighter than the body.
Females of Macrognathus ocellata are larger than males. The fish can reach up to 40 cm in length. In aquarium conditions, it is usually smaller.
Macrognathus
Macrognathus is distinguished by its nocturnal activity and bottom lifestyle. During daylight hours, the fish hides in thickets of plants or buries itself in the ground, and at dusk it swims out in search of food. They may be less timid if they are kept together with other bottom-dwelling neighbors. In nature, fish can climb out of the water and stay out of it for about 1 hour.
Macrognathus is kept in a large aquarium. The aquarium is equipped with many shelters and planted plants. It is worth noting that these fish burrow into the ground, leaving only their nose outside, so sand or other fine and non-sharp soil is used as soil. An aquarium with fish must be closed; macrognathus can easily crawl out of the aquarium along the equipment wires or corners of the aquarium.
Macrognathus photo
Comfortable water parameters for keeping macrognathus: T 22-26C, acidity 6.5-7, dGH - 5-10. Aeration and filtration are necessary. As with any other fish, high concentrations of poisons are unacceptable: ammonia, nitrites and nitrates . Every conscientious aquarist should always have a set of drop tests on hand, at least for nitrate and phosphate.
Macrognathus photo
Fortunately, they have now become inexpensive, there are no problems with their assortment and acquisition. For example, we can with a clear conscience recommend you the cool UHE drop tests, , but they are sold only online. In stores in your city - offline, you can find inexpensive Vladox tests . Friends, watch out for nitrogen compounds, keep them in check and everything will be fine for you and your pets.
It would be useful to use clean water supply for deep water changes and use preparations that neutralize harmful substances. For example, Tetra AquaSafe - it removes chlorine compounds, heavy metals + contains B vitamins, iodine and other aquarium goodies.
Macrognathus photo
Fish become sexually mature at two years of age. Breeding macrognathus is difficult, because A hormonal injection is used to stimulate spawning. Within a few days, the producers need to be seated, fully and efficiently fed, and ensure optimal conditions. The spawning tank is taken from 250 liters and at least 1 meter in length. The water temperature is 26-28, the hardness is average, aeration and a filter are installed in the spawning tank.
Macrognathus photo
Shelters, substrate and netting are required. Suitable plants include Bolbitis and Microzorium. You can plant a couple of fish or two males per female. After the injection is made into the dorsal muscle, the fish are stocked and the spawning area is shaded. The female can lay up to 1000 eggs, which fall through the net to prevent the fish from eating her. After spawning, the fish are removed. After 3 days, the fry emerge and feed on plankton, small cyclops, and microworms.
Macrognathus
Feeding any aquarium fish should be correct: balanced, varied. This fundamental rule is the key to the successful keeping of any fish, be it guppies or astronotuses. With regard to macrognathus, feeding is more complicated. They prefer live food, they are gloomy fish and very suspicious. Look at our video (at the end, where the top is) there are shots of macrognathus feeding in a cichlid. The owner throws bloodworms into a bottle, places it near the macrognath hole, and they crawl out to feast.
Hence the conclusions, friends. It is advisable to feed Macrognathus in the evening; it would be good to use live or frozen food. You can use dry ones - branded ones, but the kind that reach the bottom and don’t dissolve quickly. For example, you can use sinking Tetra granules.
Video with macrognathus
Subscribe to our YouTube channel so you don't miss anything
See also:
Mastacembelus redstripe
Mastacembelus thailand Aquarium for beginners Predatory aquarium fish
Diseases
Skin diseases are characteristic of the species. The skin of macrognathus secretes mucus, which it gets rid of by burrowing into the ground. If the eel is not given this opportunity, damage to the skin begins. Macrognathus is susceptible to many typical fish diseases:
- Poisoning. If there is chlorine in the water and an excess of nitrogen compounds, the population of the reservoir is poisoned. Fish predominate in the upper water levels, and redness is noticeable on the skin. Check the water with tests, if there is chlorine, then replant the fish, dechlorinate or replace the water. In case of ammonia poisoning, clean up, replace 30–40% of the liquid with clean liquid and increase aeration. Be attentive to the cleanliness of the soil, because the eel needs to spend a lot of time at the bottom.
- Ichthyophthyriasis (“semolina”). White specks appear on the eel's skin and it becomes restless. Treat semolina with drugs intended for scaleless fish. The use of preparations containing copper is prohibited.
- Temperature shock. Due to a sudden change in temperature or keeping eels in too warm or cold water, pets can die. When changing water, check the water temperature in different tanks, do not exceed the recommended amount of water to be changed. If the temperature deviates from what is comfortable for acne, adjust the heater. During the summer, place frozen water bottles in the reservoir.
- Oodiniumosu (“velvet rust”). A sick individual itches against aquarium objects, a large amount of mucus is released, and a yellowish coating appears on the body. The disease is treated with bicillin-5. Apply the product overnight or shade the vessel. Remember that the product disrupts the biological balance. You can use malachite green in small doses or other special-purpose products. Before applying the medicine, read the instructions; the medicine may be harmful to macrognathus.
How do individuals reproduce?
By the beginning of spawning, the females hide, and the males begin to pursue them. Macrognathus does not reproduce well in captivity, so it is impossible to do without special hormonal injections that are given into the spinal muscle. Sometimes spontaneous spawnings occur without injections. After 11-14 hours the fish are ready to spawn. The pair selected for breeding is transplanted into a tank, where it is fed generously with a special high-protein diet. A female and two males can also be planted.
The spawning tank must be at least 20 liters and no shorter than a meter in length. You need to install a good filter and aeration system in your aquarium. The water hardness should be less than in the main aquarium - this will bring macrognathus closer to the natural habitat in which spawning occurs during the rainy season.
The water temperature in the spawning tank should be 26°C, a plastic mesh should be installed at the bottom, moss and small plants should be laid. Spawning lasts several hours. During this period, it is better not to disturb the fish.
The lethargy of the fish and their desire to burrow into the ground indicates the end of spawning, after which the individuals need to be transplanted into a regular aquarium. During spawning, about 1000 eggs are released, which sink to the bottom of the aquarium or attach to plants and the walls of the tank. The fry appear after 3-4 days. They feed on the yolk sac for several days and then begin feeding on their own. The basis of their diet should be brine shrimp and worms, as well as crushed dry food for adult fish. To maintain their health, the water temperature should not exceed 26-28°C.
It is necessary to regularly change the water and use drugs to destroy the fungus (to avoid disease in young fish). It is necessary to observe the growth of young fish and remove them, sorting them by size.
Reviews
The aquarium eel has captivated many. The varied behavior of pets is noteworthy. For some aquarists, the eel is mobile and accepts most types of food; for others, macrognathus hides in the ground and eats exclusively live food.
Photo
Adviсe
- Don't turn on the lights suddenly. First, turn on the dim light in the room, and after a few minutes, turn on the aquarium lamp.
- If the eel is outside the aquarium, place it in a container of water separately from other inhabitants. Do not disturb your pet for a while and monitor its condition.
- Frozen food should not be re-frozen.
- Place the aquarium away from sunlight to prevent excessive algae growth.
In addition to the ocellated fish, the Siamese macrognathus fish (Macrognathus siamensis) is popular. According to the description, macrognathus resemble mastacembelas, so they are often confused. Popular among the mastacembels are Moore's mastacembelus moorii, mastacembelus erythrotaenia, and mastacembelus armatus.
Previous
FishSmall peaceful cuneiform rasbora
Next
FishMicrorasbora galaxy - a beautiful and unusual fish
Asian species: difficulty of classification
Two different species are imported from Southeast Asia: Macrognathus and Mastacembelus. The differences between them are often minimal and some are extremely difficult to distinguish.
There is often confusion in the sources, leading to confusion when purchasing and maintaining them.
Representatives of the family can be from 15 to 100 cm in length, and in character from shy to aggressive and predatory, so you need to decide what kind of fish you need before purchasing it.
mastacembelus erythrotaenia
One of the representatives of the family that is difficult to confuse is the red-striped mastacembelus (Mastacembelus erythrotaenia). The gray-black background of the body is covered with red and yellow stripes and lines.
Some of them pass through the entire body, others are short, and others have turned into spots. The dorsal and anal fins are edged with red. The red-striped mastacembel is the largest of all, growing up to 100 cm in nature.
In the aquarium they are much smaller, but still, to keep a red stripe you need at least 300 liters of volume.
- Latin name: Mastacembelus erythrotaenia
- Name: Red-striped Mastacembel
- Homeland: Southeast Asia
- Size: 100 cm
- Water parameters: pH 6.0 - 7.5, soft
- Feeding: small fish and insects
- Compatibility: Very territorial, does not get along with others. The neighbors must be big
- Breeding: not bred in an aquarium
Mastacembelus armatus or armored one (lat. Mastacembelus armatus) is often found on sale, but there is a very similar one called Mastacembelus favus.
They are probably imported and sold as one species. Both are light brown with dark brown spots. But in armatus they are concentrated in the upper part of the body, and in favus they descend to the stomach. Mastacembel favus is significantly smaller than armatus, reaching 70 cm versus 90 cm.
- Latin name: Mastacembelus armatus
- Name: Mastacembel armatus or armored
- Homeland: Southeast Asia
- Size:90 cm
- Water parameters: pH 6.0 - 7.5, soft
- Feeding: small fish and insects
- Compatibility: Very territorial, does not get along with others. The neighbors must be big
- Breeding: not bred in an aquarium
Mastacembelus armatus
Among macrognathus, there are three species that are found in the aquarium. Coffee mastacembelus (Mastacembelus circumcinctus) is light brown or coffee in color with cream spots and vertical stripes along the lateral line.
- Latin name: Macrognathus circumcinctus
- Name: Mastacembel coffee
- Homeland: Southeast Asia
- Size: 15 cm
- Water parameters: pH 6.0 - 7.5, soft
- Feeding: larvae and insects
- Compatibility: peaceful, will not offend anyone larger than a guppy
- Breeding: not bred in an aquarium
Mastacembelus circumcinctus
Macrognathus aral is olive or light brown in color, with a horizontal stripe running along the lateral and dorsal lines. Its color differs from individual to individual, usually they are darker at the edges and lighter in the center. The dorsal fin has several spots (usually four), dark brown inside and light brown outside.
- Latin name: Macrognathus aral
- Name: Macrognathus aral
- Homeland: Southeast Asia
- Size: up to 60 cm, usually much smaller
- Water parameters: tolerates brackish water
- Feeding: small fish and insects
- Compatibility: peaceful, can be kept in groups
- Breeding: bred haphazardly
Macrognathus siamese (Macrognathus siamensis) is one of the most common in the aquarium. In some sources it is also called Macrognathus aculeatus, but this is a rare species that is unlikely to ever appear in hobbyist aquariums.
However, the Siamese is sold here as ocellated. Siamese Macrognathus is light brown in color with thin lines running across the body. The dorsal fin is covered with spots, usually about 6 of them.
Despite the fact that the Siamese is significantly inferior in beauty to other types of eels, it will win in terms of unpretentiousness and size, rarely reaching 30 cm in length.
- Latin name: Macrognathus siamensis
- Name: Macrognathus siamese, Macrognathus ocellata
- Homeland: Southeast Asia
- Size: up to 30 cm
- Water parameters: pH 6.0 - 7.5, soft
- Feeding: small fish and insects
- Compatibility: peaceful, can be kept in groups
- Breeding: bred
Macrognathus siamensis