Common hamster diseases and their treatment
Like all living creatures, hamsters are susceptible to disease. Their life is short, and the disease in hamsters always progresses very quickly. Therefore, it is important to notice in time that something is wrong with your pet and quickly provide help. Find out in advance where the veterinarian who treats ornamental rodents sees you. It would be a good idea to study the symptoms of diseases to which hamsters are susceptible. This will not only increase the chances of saving the baby, but will also help avoid infection yourself. After all, a person can become infected with many diseases from animals. People can get the same disease that hamsters get. This article tells you what diseases afflict Syrian, Djungarian, Campbell and other breeds of hamsters.
Skin and coat diseases
The fifth category of diseases is problematic conditions of the hamster's fur and skin . If you notice that your little rodent suddenly begins to lose hair and his skin is flaking and flaking, these are symptoms of eczema or dermatophytosis. Their cause may be either the stress of the Djungarian hamster or an allergic reaction. In order not to guess what it is, contact a veterinarian who will be able to determine the cause and accordingly prescribe the appropriate treatment in this case. If you notice that scratches have appeared on your hamster’s skin, then perhaps the reason lies in parasites such as mites and lice (in more detail why a hamster can itch is described here). They must be dealt with using special sprays and aerosols that are specifically designed for hamsters.
Poisoning ticks and lice on a hamster with a flea remedy for cats is strictly prohibited, this will simply kill the rodent!
Classification of diseases
According to the type, hamster diseases, like those in humans, are divided into contagious and non-contagious. The following diseases are contagious.
- Bacterial infections. Cause gastrointestinal, skin and other inflammatory processes.
- Viral infections. They affect the eyes and mucous membranes and cause tumors.
- Fungal. Mainly they cause skin diseases.
- Infection with parasites (fleas, ticks, worms).
Some of these diseases can be transmitted to people. You need to be extremely careful when contacting a sick animal and take it to a veterinarian as quickly as possible. Only a doctor, after performing tests, will make a final diagnosis and give a prognosis for the possibility of recovery. Unfortunately, many diseases are fatal to a hamster. But in any case, a loving owner will do everything in his power to ensure that the hamster recovers.
Non-communicable diseases include non-communicable diseases.
- Injuries and bruises caused by falling from a height or fighting with other cage occupants.
- Metabolic disease. For example, diabetes mellitus, which most often affects Djungarian hamsters.
- Diseases caused by stressful situations. These include heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Diseases in Syrian hamsters are most often associated with gastrointestinal infections.
Colds
Rodents, like us, are susceptible to colds. And a treatment similar to ours is to boost immunity with... fresh fruits and vegetables.
The second category of diseases is colds in hamsters . The symptoms in this case are quite typical - the hamster sneezes, sniffles, has decreased activity and is not as active as before, refuses to eat and play... Here, a viral infection is evident. It is quite clear that in this case you will not give antibiotics or injections to the dzhungarik (the baby is too small and it is very difficult to determine the required dosage of medications), but providing the rodent with fresh fruits that contain vitamins and strengthening the pet’s immunity in a natural way is to do this simply necessary. If the rodent’s body is strong enough and the infection is not too serious, your hamster, after a few days, will already forget about his illness...
When to sound the alarm
How to understand that a hamster is sick. If the animal is healthy, it is active, it has smooth shiny fur, clear, clean eyes and a good appetite. But if you notice that your pet is behaving unusually, take immediate action. Your hamster is sick if some of the following symptoms are noticeable:
- eats poorly or refuses food altogether;
- eyes become watery or festering;
- frequent loose stools;
- constipation, dry stool or no stool at all;
- blood dripping from the anus;
- difficulty or hoarse breathing, cough;
- nasal discharge or excessive drooling;
- wet or dull, matted fur;
- ulcers, wounds, peeling skin, bald spots on the skin;
- tumors, bloating;
- lethargy, low mobility;
- the hamster is trembling, although the room is warm.
An animal's underweight may also be a sign of illness. To find out if your pet is sick, weigh your pet periodically. The weight of an adult Syrian is about 90 g, the weight of a Djungarian is at least 30 g.
What symptoms might a sick pet have?
An attentive owner can easily determine that his dwarf dog is sick. First of all, he will notice the following signs:
- decreased activity - the hamster constantly sleeps or lies in the corner;
- unkempt fur;
- loss of appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- the hamster's eyes cannot open;
- clear or purulent discharge from the eyes;
- wet face;
- hard breath;
- liquid excrement with an unpleasant odor;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- wet fur under the tail;
- bloody discharge from the anus;
- baldness;
- skin ulcers;
- shiver.
Contagious diseases in hamsters
An animal can become infected with a bacterial or viral infection in several ways.
- From other sick animals through direct contact or through its waste products.
- Through contaminated food or water.
- Insect bites.
- Through litter and uncollected excrement.
Respiratory infections are activated by hypothermia, stress and lack of vitamins in the body. You can tell that a hamster is sick by its behavior. He will become lethargic and apathetic. You may notice discharge from the nose. The young, strong hamster will recover in a few days. In weak individuals with reduced immunity, the disease can develop into pneumonia. The animal will cough and breathe heavily. In a few days he will die.
Tuberculosis develops in a weakened body when the tuberculosis bacillus enters the body. There are two forms of this disease, depending on the method of infection: pulmonary and intestinal. With the pulmonary form of tuberculosis, the hamster experiences a cough, shortness of breath, and decreased appetite. The intestinal form is characterized by severe diarrhea. This disease of hamsters, unfortunately, is incurable.
To prevent tuberculosis, the animal must receive adequate nutrition with the required amount of vitamins, the cage must be kept clean at all times, and the room must be periodically ventilated. It is necessary to avoid contact with sick animals and people. Not only can humans become infected with certain illnesses from a hamster, but rodents can also suffer from contact with a sick person.
Colibacillosis is an infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Escherichia coli. Characterized by very severe diarrhea. The stool is so thin that it looks more like urine, which is why the disease is also called “wet tail.” The hamster becomes lethargic, eats poorly, and quickly loses weight. If you notice such signs, you should urgently take the rodent to the veterinarian. The doctor will examine the symptoms and prescribe treatment. Antibiotics of the tetracycline group are usually prescribed and added to food or drinking water. In severe cases, chloramphenicol injections are prescribed.
Colibacillosis is a highly contagious disease. If the sick animal has been in contact with other pets, they will also have to be treated. The sooner you see a doctor, the more successful the treatment will be. Prevention of the disease - maintaining cleanliness in the cage. As well as keeping each animal in a separate cage.
Cystitis. A wet tail can be an indicator not only of colibacillosis, but also of cystitis - inflammation of the genitourinary tract. The animal experiences pain when urinating and is constantly thirsty. The disease occurs from hypothermia. Maintain the optimal temperature in the room where the baby lives, do not place the hamster’s cage in a draft. Cystitis can also be treated with antibiotics.
Diplococcosis is an infectious disease of the respiratory tract caused by diplococcal bacteria. Symptoms: weakness, lethargy, refusal to eat. The hamster is shaking and trembling, and his nose is running. Death occurs within 2–3 days if a special antibacterial serum is not administered in time.
Salmonellosis is an acute intestinal disease caused by Salmonella Escherichia coli. It also leads to death if treatment is not started in time.
Pneumonia is a common complication after respiratory infections if the patient does not receive proper treatment and proper nutrition. Or if the animal has a lack of vitamins in the body and lowered immunity. The disease can occur after severe hypothermia.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process of the eyes and eyelids. Eye diseases in Djungarians occur from hypothermia or are of a bacterial nature.
Intestinal parasites . You can determine that a pet is infected with worms by looking at its feces and by the fact that with a good appetite the animal loses weight. The condition of the fur is not the same as that of a healthy animal; it is faded or, on the contrary, greasy. In this case, you can buy a complex anti-worm drug (for example, Shustrik) at a veterinary pharmacy.
Bacterial and viral infections
The most dangerous diseases for the life of the dwarf are those caused by viruses and bacteria. They develop rapidly and can be fatal in a few hours or days.
Hamsters become infected with infectious diseases through airborne droplets, nutrition, or contact from other animals or people. Skin parasites are sometimes carriers of viruses or bacteria.
Colibacillosis
The disease is caused by E. coli. Normally, this bacterium is always present in the large intestine of Djungarians, but under certain conditions the number of pathogens increases sharply. The development of colibacillosis can be promoted by stress, eating low-quality food, and drinking dirty water.
Symptoms of the disease:
- depression, lethargy;
- refusal to eat;
- wet fur in the tail area;
- watery diarrhea with a foul odor;
- sloppy look.
The prognosis for recovery is unfavorable. You can try to save the dwarf if manifestations of the disease are detected immediately. For enteritis, the hamster is given antibiotics, to which E. coli is sensitive. The dwarf is put on a diet for a day - he can only eat hay.
Important! If there are several hamsters living in a cage, then they should be seated at the first signs of illness. Otherwise, healthy individuals will also become infected with colibacillosis.
Diplococcosis
This disease is caused by diplococci, which affect the respiratory system. At the first signs of infection, it is necessary to take the dwarf to the veterinarian. If treatment is not started immediately, the hamster will die within 2 days.
Symptoms include loss of appetite, lethargy, and discharge from the nose and eyes. To fight the disease, a special serum with immunoglobulins is used.
Salmonellosis
The disease is caused by salmonella bacteria. Infection occurs through the nutritional route by eating food. The disease is acute, with signs of enteritis. The dzhungarik begins to have severe diarrhea. The stools are foamy and may contain blood. The hamster is very weakened, does not eat, lies in the corner.
Salmonellosis is difficult to treat in small rodents. Due to intoxication and dehydration, hamsters die within a couple of days. If treatment is necessary, it should be started as early as possible. Therapy with Chloramphenicol in the form of injections is recommended. The exact dosage is determined by the veterinarian.
Pneumonia
The disease affects the lungs. The inflammatory process is caused by viral agents. Sometimes pneumonia develops due to hypothermia. In Djungarians, even ordinary rhinitis can turn into pneumonia within a day. Signs of the disease:
- lethargy, apathy;
- noise on inhalation and exhalation;
- irregular breathing rhythm, shortness of breath;
- paleness of the mucous membranes is a sign of oxygen deficiency.
When a respiratory disease is detected in a Djungarian hamster, the first step is to move the cage to a warm place where there is no draft. More vegetables are introduced into the diet - they contain many vitamins to support immunity. To treat pneumonia in Djungarians, antibiotics are used - Tetracycline, Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol.
Aujeszky's disease
This viral disease affects the hamster's nervous system. Pseudorabies has vivid manifestations:
- severe anxiety;
- aggression, which is replaced by periods of apathy;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- the Djungarian hamster itches and wounds appear on the body;
- convulsions.
Aujeszky's disease is deadly and difficult to treat. You can save your pet only at an early stage with the help of immunoglobulins.
Non-communicable diseases
Non-contagious diseases of Djungarian and other breeds of hamsters primarily include injuries. They are injured mainly due to the fault of their owners. Rodents should not be allowed to walk on a table or other surface from which the homa could fall. When purchasing and installing a running wheel, it is necessary to exclude narrow (less than 0.5 cm) gaps so that the baby does not stick his paw in there and injure himself. If you have several dwarfs, place them in different cages. Otherwise, they will fight and may also injure each other.
Poor nutrition may be the cause
- dental diseases;
- inflammation of the cheek pouches;
- food poisoning;
- hemorrhoids (if blood drips from the anus, your pet may have a fissure there).
Non-communicable diseases also include complications of pregnancy and pathological childbirth in females. Sometimes blood under the female's tail appears as a result of a miscarriage.
Metabolic disorders
Metabolism is the proper functioning of all body systems. Food processing, energy production, removal of unnecessary and harmful products. The central nervous system is responsible for all this, but the glands that secrete hormones have a huge influence on metabolic processes. These include the thyroid and pancreas, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and gonads. Poor nutrition, poor environment, and hereditary factors affect the functioning of these organs. Violation of their normal functioning leads to a malfunction of the body as a whole. Diseases of Djungarian hamsters are often associated with metabolic disorders.
Diabetes mellitus can develop due to excessive consumption of carbohydrates. Hereditary predisposition to the disease also plays a role. You can find out that a hamster has contracted this disease by the characteristic smell of acetone, which comes from the rodent's saliva and urine. But only a doctor can make a final diagnosis by doing a blood test. Prevention of disease in Djungarian hamsters is a balanced diet, eliminating sugar from the diet, good care and an active lifestyle.
Stroke can also be classified as a disease that occurs due to metabolic disorders. With age and as a result of poor nutrition, cholesterol plaques are deposited on the walls of blood vessels, which prevent the normal passage of blood. At some point, the plaques completely block the vessel, it bursts, and hemorrhage occurs.
If your hamster is shaking or having convulsions, the end is probably near.
Sometimes attentive owners are concerned that the rodent has a yellow sore on its stomach. In fact, this is a scent gland, with the help of which the male marks his territory.
Prevention measures
The most important thing in preventing diseases in Djungarians is good care and proper nutrition. To keep your pet healthy, you need to feed it special grain mixtures with the addition of herbal granules. The diet includes rough food for grinding teeth - hay, branches of fruit bushes and trees, as well as succulent food - vegetables.
To prevent infection with infectious and parasitic diseases, it is important to limit the contact of the jungarik with other animals. The hamster is kept in a warm, ventilated area. The cage must be protected from drafts and direct sunlight. It is necessary to maintain cleanliness inside the hamster's home - change the bedding more often, wash the tray, feeder and pour fresh water into the drinking bowl.
The holiday house also needs regular cleaning - this is where the jungarik stores its supplies, which quickly deteriorate and become moldy. Eating such food can cause diseases of the digestive system.
It is important to take care of safety. You must not allow the dzhungarik to fall from a height. The cage should be equipped with comfortable ladders.
An attentive owner examines his pet daily and seeks veterinary help at the first signs of illness. Delay may cost the dwarf his life.
Diseases caused by stress
Stress factors for a small rodent can include loud screams, the operation of various electrical appliances, other pets and much more. Diseases that develop as a result of stress in Syrian and other breeds of hamsters:
- eczema (ulcers and peeling of the skin, hair loss);
- heart attack, cardiac arrest;
- complete or partial paralysis (can occur if the animal is very frightened).
To avoid such troubles, never yell at your baby or punish him for any pranks. Do not place the cage near a TV or speakers. Isolate the rodent from cats and dogs if they live in your home. If you just acquired a furry puppy, give him a few days to get used to his new place of residence, do not immediately start playing with him or raising him.
Common diseases of Djungarian hamsters
Djungarian hamsters are quite popular pets. These tiny rodents are perfect for families with children, as they have a playful disposition. They are quite easy to care for. Unlike other animals, such as dogs or cats, they do not require a lot of space and will not cause much trouble. These cute creatures are very clean and do not emit an unpleasant odor.
Owners of Djungarian hamsters need to familiarize themselves in advance with the ailments that can plague these small animals. It is very important to recognize the disease in time and help your little friend.
Description of diseases of Djungarian hamsters
There are various diseases in these small rodents. They can be either minor or very dangerous both for the rodent itself and for its owner.
The most common ailments of Djungarian hamsters include:
- Various types of injuries. These are mainly bruises, dislocations and fractures. Due to the fact that these pets are very fragile, the owner, unwittingly, can cause mechanical injury to his beloved animal.
- Viruses and various bacterial diseases. Their cause can be not only hypothermia, but also vitamin deficiency. You should also carefully ensure that the miniature animal is not in a draft.
- Eye diseases. There is a possibility of conjunctivitis occurring in hamsters. This disease can be caused by allergies, injuries, and respiratory infections.
- Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity in general. Djungarian hamsters may have various types of anomalies, as well as inflammation of the cheek pouch. Overgrowth of teeth can also become a serious health problem for animals.
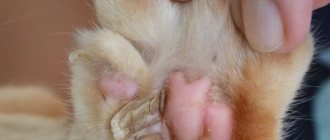
- Abscesses on paws.
- Gastrointestinal tract disorder.
- Obesity.
Djungarian hamsters can also develop infectious diseases. They are dangerous not only for the health of the pet, but also for the people who come into contact with it.
Such diseases of hamsters include:
- Salmonellosis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Plague.
- Tularemia.
- Rabies. This disease can occur from the bite of an infected predator. This happens quite rarely.
- Leptospirosis.
- Campylobacteriosis.
- Lymphocytic choriomeningitis. This disease is dangerous because in people it usually occurs without any symptoms.
- Dermatomycosis.
- Helminthiasis. Only one type of helminth can be dangerous for humans - the dwarf tapeworm.
Parasitic diseases
Skin diseases caused by parasites pose a great danger to dzungarians. They greatly deplete and poison the pet’s body with toxins. If left untreated, the hamster may die.
Fleas and lice eaters
Djungarian hamsters very rarely have fleas. The likelihood of infection exists through contact with other animals - cats or dogs. Signs of the disease:
- anxiety due to itching;
- the hamster is going bald;
- scratches, wounds, and scabs appear on the body.
To destroy skin parasites, a special powder or spray for rodents is used. When applying the product, it is important not to get it into the mouth, nose and eyes of the dwarf. It is recommended to carry out 2-3 treatments at intervals of 7-10 days to completely destroy the parasites.
Demodicosis
This disease is caused by scabies mites. They penetrate the skin and cause severe itching. When infected with scabies, the skin on the muzzle, ears, paws and near the anus becomes crusted. The hamster itches and tears its skin, which exposes itself to even greater danger. A secondary infection can enter the damaged epidermis, which will lead to inflammation.
Attention! With demodicosis, the waste products of ticks poison the body and weaken the immune system of the dwarf. If therapy is not started, he will die within 1-2 months.
Curing demodicosis is quite simple. Dzhungarika is bathed in a bath with a 0.5% bromocyclen solution 2-3 times with an interval of 10 days. If a disease is detected, the cage and equipment are treated with the same composition.
Worms
Helminths in domestic dwarfs are very rare. Most often they are affected by tapeworms and nematodes. Infection occurs by eating contaminated food or grass from the street; sometimes fleas act as carriers of the infection.
Signs of helminthiasis:
- loss of appetite;
- exhaustion;
- bowel disorders.
Niclosamide, Praziquantel, and Piperazine are used to remove worms from dzhungarik. The dosage will be prescribed by your veterinarian. Medicines are given in liquid form from an insulin syringe without a needle.
Diseases of Djungarian hamsters and their treatment
Djungarian hamsters are domestic miniature, decorative rodents. Djungaric hamsters live from 1 to 4 years. Four years of age is considered a rarity among hamsters; such rodents are considered long-lived
.
Djungarians do not like being in sunlight for a long time
; they are negatively affected by loud sound and bright fast clips on television.
Diseases of Djungarian hamsters depend on the conditions of detention. Hamsters require a spacious cage
, since the animals themselves are active animals, and they also do not tolerate the accumulation of garbage and excrement in their habitat.
proper nutrition has a great influence on hamsters . In this way, you can achieve a healthy life expectancy for the animal. Long-term research has revealed that their diet must include vegetables and fruits, namely carrots and zucchini. It is these two food products that contain the very elements that have a positive effect on the digestive system of Djungarian hamsters.
Habitats and how to arrange a cage. Diseases of Djungarian hamsters
Since some people keep Djungarian hamsters as a pet, their habitat is a cage or a specially equipped terrarium with oxygen supply. Thus, a person can easily track the life cycle of animals. There should be no high structures in cages and terrariums
.
These animals are so agile that they are sometimes clumsy, and this can cause further injury, for example, if they fall from a height. If a hamster falls, it can get bruises or scratches
, which in turn can worsen, leading to more serious consequences. Close observation with due attention to the hamsters will give you the opportunity to promptly notice any deviations from the usual norm.
Let's together highlight some important aspects when arranging the future home of the Djungarian hamster
. The cage should contain a sippy cup, feeders, a house and wheels for games, since these animals, as mentioned earlier, are very mobile. The presence of stairs, tunnels and other household items at your request. Some people arrange the presence of two furious elevations in the cage.
These animals are not very endowed with the instinct of self-preservation by nature; only the close attention of their owners, as well as care for such a cute creature, will help prolong the life of the animal. If you once came up with the idea of getting a Djungarian hamster and you think that you will have no problems coping with such a small creature, then you are mistaken. Before getting an animal, it is worth talking with knowledgeable people who have experience in handling such animals. If you decide to give a gift to a child, then you should give a gentle lecture on handling and care. Any animal in the house is a great responsibility for their owners. The lecture will help you prevent your child from further disappointment.
Diseases of Djungarian hamsters and symptoms
Despite the fact that these rodents are miniature, they face a number of dangers. Some of them can be dealt with on your own, but for more serious diseases, be prepared to contact the YA-VET veterinary care center. In principle, distinguishing a healthy hamster from a sick one is not so difficult. A healthy hamster has dry, smooth-to-the-touch fur with a slight shiny sheen, even, measured breathing, and a dry rim of the eyes and nose. The behavior of a healthy dwarf is playful and active, and the appetite should also be saturated.
In a sick hamster, symptoms usually appear immediately, since their metabolism is very fast, the presence of a wet tail, accompanied by diarrhea, blood discharge is also possible, which can subsequently bring such an unpleasant symptom to the animal as dehydration, which causes the body temperature to rise, and behavior changes to the point of complete lethargy. Next comes death. All diseases with complications can worsen and move into other phases of the disease, building a whole chain of unpleasant painful events.
What diseases lie in wait for Djungarian hamsters?
Diseases of Djungarian hamsters are varied, let's look at some of them.
1 Mechanical injuries or bruises, fractures, scratches and even fainting occur as a result of a fall from a height or during the manifestation of your boundless love for a rodent. Such falls are fraught with bruises to internal organs. Symptoms are a painful appearance of your animal, namely problematic movement and curvature of the limbs.
2 Colds - here, in general, the disease and accompanying symptoms are characteristic, as with any living creature. The activity of the animal is reduced, pain is accompanied by sneezing, snoring, and lack of appetite. It is easy to notice the presence of the disease by the low activity of the hamster.
3 Eye diseases are conjunctivitis, purulent discharge, sticking of the eyelids. A visual examination of the animal will give a complete picture of the presence of the disease. But there is also an incurable disease called cataracts in the eyes of a hamster. In this case, the animal requires much more care and attention.
4 Another common problem is the problem with the teeth of a rodent; excessive growth in the length of the teeth interferes with the life of hamsters; also, due to mechanical injuries, any parts of the teeth can be damaged. To identify this disease, it is enough to conduct a visual examination.
5 Skin and coat diseases - dermatophytosis and eczema are accompanied by skin exfoliation and hair loss. This disease is very easy to identify by performing a visual examination.
6 Intestinal diseases - an upset stomach of the baby is accompanied by loose stools and an unpleasant odor.
7 And finally, the most common problem is the formation of lumps; many owners have the opinion that a newly formed lump is a cancerous disease. Do not worry, it is important to contact a qualified specialist who will accurately determine your pet’s disease. Perhaps it was an unfortunate injury from a fall.
8 Constipation – improper feeding, lack of moisture and dry food contribute to poor digestion. The disease can be identified by highlighting the symptoms - small droppings in the cage, other forms of bending during bowel movements, the animal makes a squeak. Also loss of appetite.
9 Allergies – such a small creature is also susceptible to allergic reactions. The symptoms are similar to those of humans - sneezing, itchy nose, liquid discharge from the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose.
10 Shedding - in general, this cannot be called a disease if we assume that shedding is inherent in nature, but there are also pathological complications when the fur comes off due to a lack of vitamins in the animal’s body.
11 Obesity is not so much a disease as it is an oversight of the owners. By pampering his animal with goodies, the owner of the hamster, without knowing it, dooms him to gain excess weight, which in turn causes shortness of breath and great stress on the heart. Fat hamsters don't live long.
Diseases of Djungarian hamsters transmitted to humans
At home, the diseases that will now be described are quite rare.
, but it’s still better to be prepared for any ailment of the domestic dwarf. And so let's look at:
- Rabies - the hamster begins to behave aggressively, squeaking and biting for no reason.
- Tuberculosis - makes hoarse moans, breathes heavily. Weight loss and decreased activity.
- Parasites Ticks - itching, wounds, hair loss, rodent squeaking, abscess.
- Listeriosis – fainting, loss of coordination.
- Tizzer's disease - severe diarrhea, apathy, the hamster is shaking.
Dental problems
Very often rodents have... dental problems...
The fourth category of hamster diseases is dental problems . If your rodent suddenly loses its appetite, the reason for this may be an injury related to its teeth. To do this, you need to examine the hamster's mouth and check that all the incisors are intact. Also, as an option, it’s possible that your dwarf’s teeth are being bothered by too long teeth - in this case, you will need to seek help from a veterinarian to shorten their length, or try this procedure yourself. However, if you still doubt your abilities and have never done this before, contact a specialist!